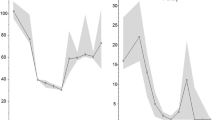
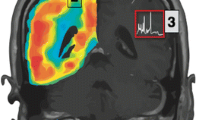
Abstract
Stroke is most often due to the occlusion of a single intracranial artery, resulting in incomplete focal ischemia. This has an immediate deleterious effect upon cerebral energy metabolism and dependent processes (Lowry and Passonneau, 1964). There is a rapid decrease of high-energy phosphate intermediates, a shift toward reduction of mitochondrial respiratory chain metabolites, increased lactic acid, and acidosis in the ischemic focus (Goldberg et al., 1966; Michenfelder and Theye, 1970). Most investigators have considered that acidosis causes or contributes in a major way to cellular damage in ischemic brain (for a review, see Welch and Barkley [1986]). In recent clinical studies of acute focal ischemic stroke, using the capability of 31p nuclear magnetic resonance spectroscopy (NMRS) to dynamically measure the brain intracellular pH, we observed a transition from acidosis to alkalosis in ischemic brain as early as 18 hr after the onset of stroke (Levine et al., 1987). Positron emission tomography (PET) has corroborated the finding of alkalosis in clinical studies of subacute and late focal ischemic stroke (Syrota et al., 1985; Hakim et al., 1987). A rapid transition from acidosis to alkalosis has also been observed in experimental stroke models of either focal or global complete or incomplete ischemia, with or without reperfusion (Kogure et al., 1980; Mabe et al., 1983; Paschen et al., 1985; Yoshida et al., 1985). In this chapter we explore in clinical patients with cerebral ischemia (1) the significance of brain acidosis and (2) the currently unknown mechanisms and meaning of what we have termed the acid-to-base pH “flip-flop.”
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Preview
Unable to display preview. Download preview PDF.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ackerman, J. J. H., Grove T. H., Wong G. G., Gadian D. G., and Radda, G. K., 1980, Map** of metabolites in whole animals by 31P NMR using surface coils, Nature 283:167–170.
Adams, H. P., Olinger, C., Marler J. R., Biller, J., Brott T. G., Barsan W. G., and Banwalt, K., 1988, Comparison of admission serum glucose concentration with neurologic outcome in cerebral infarction, Stroke 19:455–458.
Asplund, K., Hagg, E., and Helmers, C., 1980, The natural history of stroke in diabetic patients, Acta Med. Scand. 207:417–424.
Atkinson, D. E., 1968, The energy change of the adenylate pool as a regulatory parameter, Biochemistry 7:4030–4034.
Behar K. L., den Hollander J. A., Stromski M. E., Ogino, T., Shulman R. G., Petroff, O. A. C., and Prichard, J. W., 1983, High-resolution lH nuclear magnetic resonance study of cerebral hypoxia in vivo, Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 80:4945–4948.
Berger, L., and Hakim, A. M., 1986, The association of hyperglycemia with cerebral edema in stroke, Stroke 17:865–871.
Bottomley, P A., Drayer, B. P., and Smith, L. S., 1986, Chronic adult cerebral infarction studied by phosphorous NMR spectroscopy, Radiology 160:763–766.
Choi M. U., and Abramson, M. B., 1978, Effects of pH changes and charge characteristics in the uptake of norepinephrine by synaptosomes of rat brain, Biochim. Biophys. Acta 540:337–345.
Chopp, M., Frinak, S., Walton D. R., Smith M. B., and Welch, K. M. A., 1987, Intracellular acidosis during and after cerebral ischemia: In vivo nuclear magnetic resonance study of hyperglycemia in cats, Stroke 18:919–923.
Chopp, M., Welch, K. M. A., Tidwell, C., and Helpern, J. A., 1988, Global cerebral ischemia and intracellular pH during hyperglycemia and hypoglycemia in the cat, Stroke 19:1383–1387.
Cox N. H., and Lorains, J. W., 1986, The prognostic value of blood glucose and glycosylated hemoglobin in patients with stroke, Postgrad. Med. J. 62:7–10.
Degani, H., Laughlin, M., Campbell, S., and Shulman, R. G., 1984, Kinetics of creatine kinase in heart: A 31-P NMR saturation and inversion-transfer study, Biochemistry 24:5510–5516.
Fishman, R. A., 1973, Brain edema, N. Engl. J. Med. 293:706–711.
Gadian, D. B., 1982, “Nuclear Magnetic Resonance and its Application to Living Systems,” Oxford University Press, Oxford, England.
Gadian D. G., Radda G. K., Richard R. E., and Seeley, R J., 1979, 31-P NMR in living tissue: The road from a promising to an important tool in biology, in “Biological Applications of Magnetic Resonance” (R. G. Shulman, ed.), pp. 463–535, Academic Press, New York.
Goldberg N. D., Passonneau, J. V., and Lowry, O. H., 1986, Effects of changes in brain metabolism on the levels of critic acid cycle intermediates, J. Biol. Chem. 241:3997–4402.
Gordon R. E., Hanley P. E., Shaw, D., Gadian D. G., Radda G. K., Stout, P., Bore, R J., and Chan, L., 1980, Localization of metabolites in animals using 31-P topical magnetic resonance, Nature 287:736–738.
Gordon R. E., Hanley, P.E., and Shaw, D., 1982, Topical magnetic resonance, Prog. NMR Spectrosc. 15:1–47.
Hakim A. M., Pokrupa R. P., Villanueva, J., Diksic, M., Evans, A. C., Thompson, C. J., Meyer, E., Yamamoto, Y.L., and Feindel, W. H., 1987, The effect of spontaneous reperfusion on metabolic function in early human cerebral infarcts, Ann. Neurol. 21:279–289.
Hope P. L., Costello A. M., Cady E. B., Delpy, D. T., Tofts, R.S., Chu A., Hamilton, R A., Reynolds, E. O. R., and Wilkie, D. R., 1984, Cerebral energy metabolism studied with phosphorous NMR spectroscopy in normal and birth-asphyxiated infants, Lancet ii:366–370.
Horikawa, Y., Naruse, S., Tanaka, C., Kimiyoshi, H., and Nishikawa, H., 1986, Proton NMR relaxation times in ischemic brain edema, Stroke 17:1149–1151.
Jacobson, K., and Cohen, J. S., 1981, Improved technique for investigation of cell metabolism by 31-P NMR spectroscopy, Biosci. Rep. 1:141–150.
Kempski, O., Staub, F., Jansen, M., Schodel, F., and Baethmann, A., 1988, Glial swelling during extracellular acidosis in vitro, Stroke 19:386–392.
Kogure, K., Busto, R., Schwartzman R. J., and Scheinberg, P., 1980, The dissociation of cerebral blood flow, metabolism, and function in the early stages of develo** cerebral infarction, Ann. Neurol. 8:278–290.
Kraig, R. P., 1989, Interrelation of glial pH to ischemic brain edema, in “Proceedings from the 16th Princeton-Williamsburg Conference,” Stroke.
Kraig R. P., Pulsinelli W. A., and Plum, F., 1985, Behavior of brain bicarbonate ions during complete ischemia, J. Cereb. Blood Flow Metab. 5:S227–S228.
Kraig, R. P., Pulsinelli W. A., and Plum, F., 1986, Heterogeneous distribution of hydrogen and bicarbonate ions during complete brain ischemia, Prog. Brain Res. 63:155–156.
Kuschinsky, W., and Wahl, M., 1978, Local chemical and neurogenic regulation of cerebral vascular resistance, Physiol. Rev. 58:656–689.
Kwee I. L., and Nakada, T., 1988, Phospholipid profile of the human brain: 31-P NMR spectroscopic study, Magn. Res. Med. 6:296–299.
Levine S. R., Welch, K. M. A., Bruce, R., and Smith, M. B., 1987, Brain intracellular pH “flip-flop” in human ischemic stroke identified by 31P NMR, Ann. Neurol. 22:137.
Levine S. R., Welch, K. M. A., Dietrich, K., and Helpern, J. A., 1988a, Regional heterogeneity of brain pH and phosphate metabolism in early humans stroke, Ann. Neurol. 24:128.
Levine S. R., Welch, K. M. A., Helpern J. A., Chopp, M., Bruce, R., Selwa, J., and Smith, M. B., 1988a, Prolonged deterioration of ischemic brain energy metabolism and acidosis association with hyperglycemia. Human cerebral infarction studied by serial 31-P NMR spectroscopy, Ann. Neurol. 23:416–418.
Lowry O. H., and Passonneau, J. V., 1964, The relationship between substrates and enzymes of glycolysis in brain, J. Biol. Chem. 239:31–42.
Lund-Anderson, H., 1979, Transport of glucose from blood to brain, Physiol. Rev. 59:305–352.
Mabe, H., Blomqvist, P., and Siesjö, B. K., 1983, Intracellular pH in the brain following transient ischemia, J. Cereb. Blood Flow Metab. 3:109–114.
Mayevsky, A., Nioka, S., Subramanian V. H., and Chance, B., 1988, Brain oxidative metabolism of the newborn dog—correlation between 31-P NMR spectroscopy and pyridine nucleotide redox state, J. Cereb. Blood Flow Metab. 8:201–207.
McMillan, V., and Siesjö, B. K., 1983, The effect of phenobarbital anesthesia upon some organic phosphates, glycolytic metabolites and citric acid cycle-associated intermediates of the rat brain, J. Neurochem. 20:1669–1681.
Melamed, E., 1976. Reactive hyperglycemia in patients with acute stroke, J. Neurol. Sci. 29:267–275.
Michenfelder J. D., and Theye, R. A., 1979, The effects of anesthesia and hypothermia on canine cerebral ATP and lactate during anoxia produced by decapitation, Anesthesiology 33:430.
Mitchell, P., 1961, Coupling of phosphorylation to electron and hydrogen transfer by a chemi-osmotic type of mechanism, Nature 191:144–148.
Mohr, J. P., Rubenstein, L. V., Tatemichi T. K., Nichols, E T., Caplan L. R., Hier D. B., Kase C. S., Price T. R., and Wolf, P. A., 1985, Blood sugar and acute stroke: the NINCDS pilot stroke data bank, Stroke 16:143.
Moon R. G., and Richards, J. H., 1973, Determination of intracellular pH by 31-P magnetic resonance, J. Biol. Chem. 248:7276–7278.
Myers R. E., and Yamaguchi, M., 1976, Tissue lactate accumulation as cause of cerebral edema, Neurosci. Abstr. 2:1042.
Nedergaard, M., and Diemer, N. H., 1989, Hypoglycemia reduces infarct size in experimental focal cerebral ischemia, in “Proceedings from the 16th Princeton-Williamsburg Conference,” Stroke.
Nencini, P., Kushner, M., Reivich, M., Chawluk J. B., Zimmerman, M., Rango, M., Jamieson D. G., and Alavi, A., 1988, Hyperglycemia and metabolism in cerebral infarction, Neurology 38:368.
Nunnally R. L., and Hollis, D. P., 1970, Adenosine triphosphate compartmentation in living hearts: A phosphorous NMR saturation transfer study, Biochemistry 18:3642–3646.
Paschen, W., Sato, W., Pawlik, G., Umbach, C., and Heiss, W.-D., 1985, Neurologic deficit, blood flow and biochemical sequelae of reversible focal cerebral ischemia in cats, J. Neurol. Sci. 68: 119–134.
Pelligrino, D., and Siesjö, B. K., 1981, Regulation of extra-and intracellular pH in the brain in severe hypoglycemia, J. Cereb. Blood Flow Metab. 1:85–96.
Petito, C. K., 1987, Post ischemic transformation of perineuronal glial cells, in “Cerebrovascular Diseases” (M. E. Raichle and W. J. Powers, eds.), pp. 103–106, Raven Press, New York.
Petroff, O. A. C., Prichard J. W., Behar K. L., Alger J. R., den Hollender J. A., and Shullman, R. G., 1985, Cerebral intracellular pH by 31-P NMR spectroscopy, Neurology 35:781–788.
Pettegrew, J. W., Kopp S. J., Dadok, J., Minshew N. J., Feliksik J. M., Glonek, T., and Cohen, M. M., 1986, Chemical characterization of a prominent phosphomonoester resonance from mammalian brain. 31-P and 1-H NMR analysis at 4.7 and 14.1 Tesla, J. Magn. Reson. 67:443–450.
Pettegrew J. W., Kopp S. J., Minshew N. J., Glonek, T., Feliksik, B. C., Tow, J. P., and Cohen, M. M., 1987, 31P nuclear magnetic resonance studies of phosphoglyceride metabolism in develo** and degenerating brain: Preliminary observations, J. Neuropathol. Exp. Neurol. 46:419–430.
Plum, F., Cooper, A. J. L., Kraig, R. P., Petito C. K., and Pulsinelli, W A., 1985, Glial cells: The silent partners of the working brain, J. Cereb. Blood Flow Metab. 5:S1–S4.
Prichard J. W., Alger J. R., Behar K. L., Petroff, O. A. C., and Shulman, R. G., 1983, Cerebral metabolic studies in vivo by 31-P NMR, Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 80:2748–2751.
Pulsinelli, W., Sigsbee, B., Waldman, S., Rawlinson, D., Scherer, P., and Plum, G., 1980, Experimental hyperglycemia and diabetes mellitus worsen stroke outcome, Ann. Neurol. 8:91.
Radda, G. K., 1986, The use of NMR spectroscopy for the understanding of disease, Science 233: 640–645.
Roberts, J. K. M., Wade-Jardetzky, N., and Jardetzky, O., 1981, Intracellular pH measurements by 31-P NMR. Influence of factors other than pH on 31-P chemical shifts, Biochemistry 20:5389–5394.
Shoubridge E. A., Briggs R. W., and Radda, G. K., 1982, 31-P NMR saturation transfer measurements of the steady state rates of creatine kinase and ATP synthetase in the rat brain, FEBS Lett. 140:288–292.
Siesjö, B. K., 1978, “Brain Energy and Metabolism,” pp. 327–329, John Wiley & Sons, New York.
Siesjö, B. K., 1981, Cell damage in the brain: A speculative synthesis, J. Cereb. Blood Flow Metab. 1: 155–185.
Siesjö, B. K., 1985a, Acidosis and brain damage: Possible molecular mechanisms, J. Cereb. Blood Flow Metab. 5:S225–S226.
Siesjö, B. K., 1985b, Acid-base homeostasis in the brain: Physiology, chemistry, and neurochemical pathology, Prog. Brain Res. 63:121–154.
Siesjö, B. K., Smith M. L., and Warner, D. S., 1987, Acidosis and ischemic brain damage, in “Cerebrovascular Disease” (M. E. Raichle and W. J. Powers, eds.), pp. 83–95, Raven Press, New York.
Syrota, A., Samson, Y., Boullais, C., Wajnberg, P., Loc’h, C., Crouzel, C., Maziere, B., Soussaline, F., and Baron, J. C., 1985, Tomographic map** of brain intracellular pH and extracellular water space in stroke patients, J. Cereb. Blood Flow Metab. 5:358–368.
Wanke, E., Carbone, E., and Testa, R L., 1979, K+ conductance modified by a titratable group accessible to protons from the intracellular side of the squid axon membrane, Biophys. J. 26: 319–324.
Welch, K. M. A., and Barkley, G. L., 1986, Biochemistry and pharmacology of cerebral ischemia, in “Stroke, Pathophysiology, Diagnosis and Management” (J. M. Barnett, J. R. Mohr, B. M. Stein, and E. M. Yatsu, eds), pp. 75–90, Churchill-Livingstone, New York.
Welch, K. M. A., Helpern J. A., Robertson, W M., and Ewing, J. R., 1985, 31P topical magnetic resonance measurement of high energy phosphates in normal and infarcted brain, Stroke 16:151.
Welsh, E A., Ginsberg M. D., and Rieder, W., 1980, Deleterious effect of glucose pretreatment on recovery from diffuse cerebral ischemia in the cat, Stroke 11:355–363.
Yoshida, S., Busto, R., Martinez, E., and Ginsberg, M. D., 1985, Regional energy metabolism after complete versus incomplete cerebral ischemia in the absence of severe lactic acidosis, J. Cereb. Blood Flow Metab. 5:490–501.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 1992 Springer Science+Business Media New York
About this chapter
Cite this chapter
Welch, K.M.A., Levine, S.R., Martin, G.B., Helpern, J.A. (1992). Cellular and Metabolic Significance of Cellular Acid-Base Shifts in Human Stroke. In: Bazan, N.G., Braquet, P., Ginsberg, M.D. (eds) Neurochemical Correlates of Cerebral Ischemia. Advances in Neurochemistry, vol 7. Springer, Boston, MA. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-1-4615-3312-2_17
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-1-4615-3312-2_17
Publisher Name: Springer, Boston, MA
Print ISBN: 978-1-4613-6458-0
Online ISBN: 978-1-4615-3312-2
eBook Packages: Springer Book Archive