Abstract
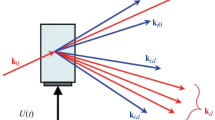
Planar i.e. waveguide Bragg-deflectors are becoming increasingly important for applications of low laser power, eg. in signal processing devices. There are several advantages of planar devices compared to bulk devices. Figure 1 compares the two versions of a light deflector or modulator. In the bulk version the laser beam is focused into the interaction volume. For a given modulating field strength, which is limited by dielectric break down, nonlinear or thermal effects, a certain interaction length L is required to achieve a given diffraction efficiency or modulation depth. Due to diffraction of the freely propagating beam in a bulk device (Figure la) the beam spreads to a diameter D = (λL/π)1/2 yielding a minimum interaction volume V = D2L≈λL2/π. If we confine instead the light beam in a slab waveguide of depth d≈λ *, we only have diffraction spreading in the lateral dimension of0 the beam and the necessary interaction volume is reduced by a factor d/D≈λ0/D. For the same interaction medium the required drive power is consequently reduced by a factor of (λπ/L)1/2, ie. typically several orders of magnitude.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Preview
Unable to display preview. Download preview PDF.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
F. Auracher, R. Keil and K.H. Zeitler, New Electrooptic Bragg Deflectors with Low-Insertion Loss and Multiple-Beam Capability, Siemens Forsch. - u.Entw. - Ber. 10: 44–47 (1981).
J.M. Hammer and W. Phillips, Low-loss single-mode optical waveguides and efficient high-speed modulators of LiNbxTa1-x03 on LiTa03, Appl.Phys.Lett. 24: 545–547 (1974).
J. Noda, N. Uchida and S. Saku, Electro-optic diffraction modulator using out-diffused waveguide layer in LiNb03, Appl.Phys.Lett. 25: 131–133 (1974).
G.L. Tangonan et al., Electrooptic diffraction modulation in Ti-diffused LiTa03, Appl.Opt. 17: 3259–3263 (1978).
Chen S. Tsai, Guided-Wave Acoustooptic Bragg Modulators for Wide-Band Integrated Optic Communications and Signal Processing, IEEE Transact, on Circuits and Systems, CAS-26: 1072–1098 (1979).
M.K. Barnoski et al., Integrated-Optic Spectrum Analyzer, IEEE Transactions on Circuits and Systems, CAS-26: 1113–1124 (1979).
M.W. Casseday et al., Wide-Band Signal Processing Using the Two-Beam Surface Acoustic Wave Acoustooptic Time Integrating Correlator, IEEE Transact, on Sonics and Ultrasonics, SU-28: 205–212 (1981).
J.M. White, P.F. Heidrich and E.G. Lean, Thin-Film Acoustooptic Interaction in LiNb03, Electr.Lett. 10: 510–511 (1974).
W.R. Smith Jr., Design of Bragg Cells for SAW/lntegrated Optic Signal Processing Devices, Proc. of the 1979 IEEE Ultrasonics Symposium, 98–101.
E.A. Kolosovskii, D.V. Petrov and A.V. Tsarev, Influence of the parameters of a diffused waveguide on the frequency dependence of the acoustooptic interaction efficiency, Sov.J. Quant.Electr. 10: 998–1000 (1980).
C.S. Tsai, M.A. Alhaider, Le T. Nguyen and B. Kim, Wideband guided-wave acoustooptic Bragg diffraction and devices using multiple tilted surface acoustic waves, Proc.IEEE. 64: 318–328 (1976).
T.R. Joseph and Bor-Uei Chen, Broadband Chirp Transducers for Integrated Optics Spectrum Analyzers, Proc. of the 1979 IEEE Ultrasonics Symposium, 28–33.
Chin C. Lee, Kuan-Yang Liao, Chin L. Chang and Chen S. Tsai, Wide-Band Guided Wave Acoustooptic Bragg-Deflector Using a Tilted-Finger Chirp Transducer, IEEE J.Quant.Electr., QE-15: 1166–1170 (1979).
Kuan Y. Liao, Chin L. Chang, Chin C. Lee and Chen S. Tsai, Progress on Guided-Wave Acoustooptic Bragg-Deflector Using a Tilted-Finger Chirp Transducer, Proc. of the 1979 IEEE Ultrasonics Symposium, 24–27.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 1983 Plenum Press, New York
About this chapter
Cite this chapter
Auracher, F. (1983). Planar Electrooptic and Acoustooptic Bragg-Deflectors. In: Martellucci, S., Chester, A.N. (eds) Integrated Optics. NATO Advanced Studies Institutes Series, vol 91. Springer, Boston, MA. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-1-4613-3661-7_12
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-1-4613-3661-7_12
Publisher Name: Springer, Boston, MA
Print ISBN: 978-1-4613-3663-1
Online ISBN: 978-1-4613-3661-7
eBook Packages: Springer Book Archive