Abstract
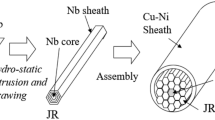
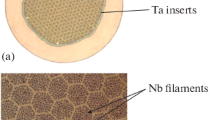
In the conventional bronze technique of manufacturing multifilamentary Nb3Sn superconducting wires (Fig. 1), a composite billet having niobium cores in a bronze sleeve is hot-extruded and drawn down to a rod. The number of filaments is increased by assembling these rods into a starting billet, which is again hot-extruded and drawn. After the cycles of assembly and reduction are completed, the rod is drawn down to a fine multifilamentary wire. Intermediate anneals must be given frequently to soften the bronze matrix. Finally, a diffusion anneal produces Nb3Sn at the niobium-bronze interface.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Preview
Unable to display preview. Download preview PDF.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
J. Breme and C. H. Massat, The effect of hydrostatic extrusion on the superconducting characteristics of tin-bronze/niobium polymer conductors, Metallwiss. Tech. 33 (1979).
“Experimental Evaluation of Hydrostatic Extrusion for the Fabrication of Multifilamentary Superconducting Wire,” Report submitted by Battelle to the Division of Magnetic Fusion Energy, Energy Research and Development Administration (1976).
V. Thadani, B. Avitzur, Y. T. Chou, and T. Luhman, A comparison of hydrostatic extrusion versus wire drawing as a method of producing Nb3Sn superconducting wire, in: “9th NAMRC Proceedings,” SME, Dearborn (1981).
T. Luhman, M. Suenaga, D. O. Welch, and K. Kacho, Degradation mechanism of Nb3Sn composite wires under tensile strain at 4.2 K, IEEE Trans. Magn. MAG-15 (1979).
T. Luhman, Metallurgy of A15 conductors, in: “Treatise on Materials Science and Technology,” Vol. 14, T. Luhman and D. Hughes, eds., Academic Press, New York (1979).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 1982 Plenum Press, New York
About this chapter
Cite this chapter
Thadani, V., Luhman, T.S., Avitzur, B., Chou, Y.T. (1982). Superconducting and Mechanical Properties of Cold Hydrostatically Extruded Monofilamentary Nb3Sn Wires. In: Reed, R.P., Clark, A.F. (eds) Advances in Cryogenic Engineering Materials . Advances in Cryogenic Engineering Materials , vol 28. Springer, Boston, MA. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-1-4613-3542-9_68
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-1-4613-3542-9_68
Publisher Name: Springer, Boston, MA
Print ISBN: 978-1-4613-3544-3
Online ISBN: 978-1-4613-3542-9
eBook Packages: Springer Book Archive