Abstract
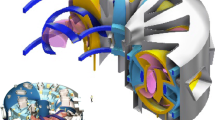
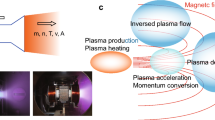
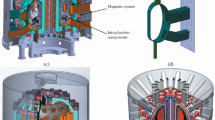
Diagnostics for helical systems are reviewed. A helical system is expected to be a disruption-free steady-state reactor since no plasma current is required. Different types of medium-sized helical systems such as CHS1, W7-AS2, Heliotron E3 and J4, H-1NF Heliac5 and HSX have been developed and constructed. Recently, a large helical device (LHD) has been constructed in Japan and another large one (W7-X8) is under construction in Germany. These two devices are fully equipped with superconducting magnets, modern diagnostics and high power heating systems. The plasma parameters are expected to be comparable to large tokamaks. While most plasma diagnostics are similar to those for tokamaks, there are also specific features: (1) measurement of vacuum magnetic flux surfaces; (2) intrinsic 3-D structure including divertor; (3) intensive diagnostics for the electric field; (4) diagnostics to verify device design elements; (5) high density diagnostics; (6) steady state operation. W7-X optimization principles call for sensitive current diagnostics (Pfirsch-Schlüter and bootstrap currents) and tomographic means to verify the reduced Shafranov shift as well as fast particle confinement diagnostics11. Steady state or long pulse operation fulfills the demands of correlation diagnostics as Te fluctuation measurements, it allows for coherent averaging and it enables scans of various diagnostics. Examples are: i) polarization scans of ECE, ii) wavelength scans of spectrometers, and iii) spatial scans of several diagnostics. The special features of diagnostics for helical systems are described in the following chapters.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Preview
Unable to display preview. Download preview PDF.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
K. Matsuoka, et al., Plasma Physics and Controlled Nuclear Fusion Research, 1988, Vol.2, IAEA, Vienna (1989) 411.
H. Renner, et al., Plasma Phys. Control. Fusion, 31, 1579 (1989).
K. Uo, et al., in Controlled Fusion and Plasma Physics (Proc. 10th Int. Conf. Moscow, 1981),EPS(1981)E-1.
T. Obiki, et al., Nucl. Fusion, 41, 833 (2001).
J. Harris, et al., The Australian & New Zealand Physics, 35, 245 (1988).
D. T. Anderson, et al., J. Plasma Fusion Res. SERIES1, 49 (1998).
O. Motojima, et al., Phys. Plasma6, 1021 (1999).
G Grieger et al., Phys. FluidsB 4, 2081 (1992), F. Wagner, Int. Conf. on Accelerator and Plasma Research, Tae Jeon, Korea, Advanced Fusion Science Research, p. 41 (1995).
H. J. Hartfuss et al., Rev. Sci. Instrum.68, 1244 (1997), and: Diagnostic System for the W7-X Stellarator, this conference.
A. Weller et al., Fusion Engineering and Design34–45, 17 (1997).
A. Werner et al., Fast Ion Loss Diagnostics for the Wendelstein 7-X Stellarator, this conference.
M. S. Jones Jr., et al., Princeton Plasma Phys. Lab. Report., MATT-14 (July, 1959). T. Mizuuchi, et al., Nucl. Fusion 22 (1982) 247.
R. Takahashi, et al., Proc. Int. Stellarator/Heliotron Workshop (IAEA Tech. Committee Meeting) (Kyoto, 1986). Plasma Phys. Lab. Report PPLK-5, 1, 220 (1986).
R. Jaenicke et al., Nuclear Fusion33, 687 (1993).
A. G Dikiji, et al., Sov. J. Plasma Phys.14 (1988) 160. J. V. Gutarev, et al., Proc. Int. Stellarator/Heliotron Workshop (IAEA Tech. Committee Meeting) (Kyoto, 1986). Plasma Phys. Lab. Report PPLK-5, Vol. 1 (1986) 233.
F. Sano, et al., J. Nucl. Mater., 241-243, 961 (1977).
T. Mizuuchi, et al., J. Nucl. Mater., 162-164, 105 (1989).
P. Grigull et al., First Island Divertor Experiments on W7-AS, 28th EPS CFPP, Madeira, Portugal, June, 2001, to be published inPlasma Phys. Control. Fusion.
H. Renner et al., Nucl. Fusion40, 1083 (2000).
V. Erckmann et al., Fusion Engineering and Design53, 365–375 (2001).
K. Watanabe et al, Nuclear Fusion32, 1992 (1992).
K. Narihara, I. Yamada and T. Minami, Proc. 6th International Symposium on Laser-Aided Plasma Diagnostics, Bar Harbor (1993) p.108.
H. Okada et al., Proc. 1996 int. Conf. on Plasma Physics, Vol. 2 (Nagoya, 1996) pp.1434–1435.
A. Weller et al., Rev. Sci. Instr.70, 484 (1999).
A. Weller et al., Physics of Plasmas8, 931 (2001).
S. Sudo et al., 17th Conf. Proceedings of Fusion Energy, IAEA, Yokohama, Japan, EXP1/18 (1998).
S. Kado et al., Jpn. J. Appl. Phys.34, 6492 (1995).
R. Brakel et al., Plasma Phys. Control. Fusion39, B237 (1997).
A. Fujisawa, H. Iguchi, M. Sasao et al., Rev. Sci. Instrum.68, 3393(1992).
A. Fujisawa, H. Iguchi, T. Minami et al. Physics of Plasmas7, 4152(2000).
K. Ida, A. Fujisawa, et al., Phys. Plasmas, 8, 1 (2001).
H. P. Laqua et al., Phys. Rev. Lett.78, 3467 (1997).
H. P. Laqua and H. J. Hartfuss, Phys. Rev. Lett.81, 2060 (1998).
Ch. Fuchs and H. J. Hartfuss, Rev. Sci. Instrum.72, 383 (2001).
F. Volpe and H. P. Laqua, Development of an electron Bernstein emission diagnostic for temperature profiles above the EC-cutoff density at Wendelstein 7-AS Stellarator, 28th EPS CFPP, Madeira, Portugal, June, 2001. See also paper by F. Volpe, Electron Bernstein Wave Diagnostics, at this conference.
Y. Nagayama, et al., Rev. Sci. Instrum.70, 1012 (1999).
P. de Vries, et al., Phys. Plasma.7, 3707 (2000).
T. Ozaki, et al., Rev. Sci. Instrum.72, 2698 (2000).
M. Isobe et al., Rev. Sci. Instrum.70 (1999) 827.
A. Werner et al., Rev. Sci. Instrum.72 (2001) 780.
T. Kondo et al. Nuclear Fusion40 (2000) 1575.
S. Sattler and H. Hartfuss, Phys. Rev. Lett.72, 653 (1994).
H. Hartfuss et al., Plasma Phys. Control. Fusion38, A227 (1996).
F. C. Jobes, D. K. Mansfield: Rev. Sci. Instrum.63, 5154 (1992).
T. Akiyama, E. Sato, T. Nozawa et al: Rev. Sci. Instrum.72, 1073 (2001).
Ch. Fuchs and H. Hartfuss, Phys. Rev. Lett.81, 1626 (1998).
B. J. Peterson et al., Rev. Sci. Instrum.72, 923 (2001).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2002 Springer Science+Business Media New York
About this chapter
Cite this chapter
Sudo, S. et al. (2002). Diagnostics for Helical Systems. In: Stott, P.E., Wootton, A., Gorini, G., Sindoni, E., Batani, D. (eds) Advanced Diagnostics for Magnetic and Inertial Fusion. Springer, Boston, MA. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-1-4419-8696-2_65
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-1-4419-8696-2_65
Publisher Name: Springer, Boston, MA
Print ISBN: 978-1-4613-4669-2
Online ISBN: 978-1-4419-8696-2
eBook Packages: Springer Book Archive