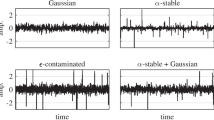
In a number of communication systems, optimum receiver design requires joint demodulation and decoding. The complexity problem arising in practical implementation has led to an interest in iterative receivers. This chapter introduces iterative receiver algorithms based on their graphical models. These consist of representing the factorization of a function of several variables into a product of functions of a lower number of variables. Using this representation, efficient algorithms are derived for computing the a posteriori probabilities to be used for optimal symbol-by-symbol detection of the transmitted data. The unified approach presented here allows one to observe how seemingly different transmission schemes share many common features, and hence solutions that were devised for one problem can easily be adapted to a different one. Our presentation is tutorial in nature and relies heavily on graphical descriptions.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Preview
Unable to display preview. Download preview PDF.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
S. M. Aji, G. B. Horn, and R. J. McEliece, “On the convergence of iterative decoding on graphs with a single cycle,” in Proc. IEEE Int. Symp. Inform. Theory (ISIT 1998), Cambridge, MA, p. 276, August 1998.
S. M. Aji and R. J. McEliece, “The generalized distributive law,” IEEE Trans. Inform. Theory, vol. 46, no. 2, pp. 325–343, March 2000.
A. Anastasopoulos, K. M. Chugg, G. Colavolpe, G. Ferrari, and R. Raheli, “Iterative detection for channels with memory,” Proc. IEEE, vol. 95, no. 6, pp. 1272–1294, June 2007.
M. Bayati, D. Shah, and M. Sharma, “Max–product for maximum weight matching: Convergence, correctness, and LP duality,” IEEE Trans. Inform. Theory, vol. 54, no. 3, pp. 1241–1251, March 2008.
S. Benedetto and E. Biglieri, Principles of Digital Transmission. New York, NY: Kluwer\Plenum, 1999.
E. Biglieri, Coding for Wireless Channels. New York: Springer, 2005.
E. Biglieri, R. Calderbank, A. Constantinides, A. Goldsmith, A. Paulraj, and H. V. Poor, MIMO Wireless Communications. Cambridge, UK: Cambridge University Press, 2007.
E. Biglieri, A. Nordio, and G. Taricco, “Iterative receivers for coded MIMO signaling,” Wireless Commun. Mob. Comput., vol. 4, no. 7, pp. 697–710, November 2004.
E. Biglieri, A. Nordio, and G. Taricco, “MIMO Doubly-iterative receivers: Pre- vs. post-cancellation filtering ,” IEEE Commun. Lett., vol. 9, no. 2, pp. 106–108, February 2005.
E. Biglieri, G. Taricco, and A. Tulino, “Decoding space–time codes with BLAST architectures,” IEEE Trans. Signal Process., vol. 50, no. 10, pp. 2547–2552, October 2002.
J. J. Boutros and G. Caire, “Iterative multiuser joint decoding: Unified framework and asymptotic analysis,” IEEE Trans. Inform. Theory, vol. 48, no. 7, pp. 1772–1793, July 2002.
G. Caire, A. Tulino, and E. Biglieri, “Iterative multiuser joint detection and parameter estimation: A factor-graph approach,” IEEE Information Theory Workshop (ITW2001), Cairns, Australia, September 2–7, 2001.
M. Coates and R. Nowak, “Network for networks: Internet analysis using graphical statistical models,” Proc. IEEE Workshop Neural Netw. Signal Process., vol. 2, pp. 755–764, December 11–13, 2000.
G. Colavolpe and G. Germi, “On the application of factor graphs and the sum-product algorithm to ISI channels,” IEEE Trans. Commun., vol. 53, no. 5, pp. 818–825, May 2005.
R. Drost and A. C. Singer, “Factor graph methods for three-dimensional shape as applied to LIDAR imaging,” J. Opt. Soc. Amer. A, Opt. Image Sc., vol. 21, no. 10, pp. 1855–1868, October 2004.
R. Drost and A. C. Singer, “Factor graph algorithms for equalization,” IEEE Trans. Signal Process., vol. 55, no. 5, pp. 2052–2065, May 2007.
A. W. Eckford and S. Pasupathy, “Iterative multiuser detection with graphical modeling,” IEEE Int. Conf. Personal Wireless Communications, Hyderabad, India, pp. 454–458, December 17–20, 2000.
G. J. Foschini, “Layered space–time architecture for wireless communication in a fading environment when using multi-element antennas,” Bell Labs. Tech. J., vol. 1, no. 2, pp. 41–59, Autumn 1996.
B. Frey, Graphical Models for Machine Learning and Digital Communication. Cambridge, MA: MIT Press, 1998.
B. J. Frey, R. Koetter, and A. C. Singer, “ ‘Codes’ on images and iterative phase unwrap**,” in Proc. IEEE Inform. Theory Workshop, Cairns, Australia, pp. 9–11, September 2–7, 2001.
Q. Guo, L. **, and H.-A. Loeliger, “Turbo equalization based on factor graphs,” in Proc. IEEE Int. Symp. Information Theory, Adelaide, Australia, September 4–9, 2005, pp. 2021–2025.
C. Herzet, N. Noels, V. Lottici, H. Wymeersch, M. Luise, M. Moeneclaey, and L. Vandendorpe, “Code-aided turbo synchronization,” Proc. IEEE, vol. 95, no. 6, pp. 1255–1271, June 2007.
R. Koetter, A. C. Singer, and M. Tüchler, “Turbo equalization,” IEEE Signal Process. Mag., Vol. 21, no. 1, pp. 67–80, January 2004.
F. R. Kschischang, B. J. Frey, and H.-A. Loeliger, “Factor graphs and the sum–product algorithm,” IEEE Trans. Inform. Theory, vol. 47, no. 2, pp. 498–519, February 2001.
H.-A. Loeliger, “Leat squares and Kalman filtering,” in Codes, Graphs, and Systems, R. Blahut and R. Koetter, Eds. Boston, MA: Kluwer, 2002, pp. 113–135.
H.-A. Loeliger, “An introduction to factor graphs,” IEEE Signal Proc. Mag., pp. 28–41, January 2004.
H.-A. Loeliger, J. Dauwels, J. Hu, S. Korl, L. **, and F. R. Kschischang, “The factor graph approach to model-based signal processing,” Proc. IEEE, vol. 95, no. 6, pp. 1295–1322, June 2007.
H.-A. Loeliger, J. Dauwels, V. M. Koch, and S. Korl, “Signal processing with factor graphs: Examples,” in Proc. First Int. Symp. on Control, Communications and Signal Processing, Hammamet, Tunisia, March 21–24, 2004, pp. 571–574.
J. Pearl, Probabilistic Reasoning in Intelligent Systems: Networks of Plausible Inference. San Francisco, CA: Morgan Kaufmann, 1988.
T. Richardson and R. Urbanke, Modern Coding Theory. New York, NY: Cambridge University Press, 2008.
M. Tüchler, R. Koetter, and A. C. Singer, “Turbo equalization: Principles and new results,” IEEE Trans. Commun., vol. 50, no. 5, pp. 754–766, May 2002.
M. Tüchler, S. ten Brink, and J. Hagenauer, “Masures for tracing convergence of iterative decoding algorithms,” in Proc. 4th IEEE/ITG Conf. Source and Channel Coding, Berlin, Germany, pp. 53–60, January 2002.
N. Wiberg, Codes and Decoding on General Graphs, Ph.D. Dissertation 440, Univ. Linkö**, Linkö**, Sweden, Linkö** Studies in Science and Technology, 1996.
A. P. Worthen and W. E. Stark, “Unified design of iterative receivers using factor graphs,” IEEE Trans. Inform. Theory, vol. 47, no. 2, pp. 843–849, February 2001.
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by the Spanish Ministery of Education and Science under Project TEC2006-01428/TCM
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2009 Springer-Verlag US
About this chapter
Cite this chapter
Biglieri, E. (2009). Iterative receivers and their graphical models. In: Tarokh, V. (eds) New Directions in Wireless Communications Research. Springer, Boston, MA. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-1-4419-0673-1_5
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-1-4419-0673-1_5
Published:
Publisher Name: Springer, Boston, MA
Print ISBN: 978-1-4419-0672-4
Online ISBN: 978-1-4419-0673-1
eBook Packages: EngineeringEngineering (R0)