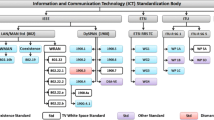
Under utilization of radio spectrum in traditional wireless communication systems [30], along with the increasing spectrum demand from emerging wireless applications, is driving the development of new spectrum allocation policies for wireless communications. These new spectrum allocation policies, which will allow unlicensed users (i.e., secondary users) to access the radio spectrum when it is not occupied by licensed users (i.e., primary users) will be exploited by the cognitive radio (CR) technology. Cognitive radio will improve spectrum utilization in wireless communication systems while accommodating the increasing amount of services and applications in wireless networks. A cognitive radio transceiver is able to adapt to the dynamic radio environment and the network parameters to maximize the utilization of the limited radio resources while providing flexibility in wireless access [45].
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Preview
Unable to display preview. Download preview PDF.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
M. Alicherry, R. Bhatia, and L. (E).Li, “Joint channel assignment and routing for throughput optimization in multi-radio wireless mesh networks,” in Proc. ACM Mobicom’05.
P. Bahl, A. Chandra, and J. Dunagan, “SSCH: Slotted seeded channel hop** for capacity improvement in IEEE 802.11 ad hoc wireless networks,” in Proc. ACM Mobicom’04.
M. M. Buddhikot, “Understanding dynamic spectrum access: Models, taxonomy and challenges,” in Proc. IEEE International Symposium on New Frontiers in Dynamic Spectrum Access Networks (DySPAN), April 2007, pp. 649–663.
S. H. Seyedmehdi, Y. **n, and Y. Lian, “An achievable rate region for the causal cognitive radio,” in Proc. Allerton Conf. Commun. Control and Comp., Monticello, IL, Sept. 2007.
G. Caire and S. Shamai, “On the achievable throughput of a multi-antenna gaussian broadcast channel,” IEEE Trans. Inf. Theory, vol. 49, no. 7, pp. 1691–1705, July 2003.
M. Cao, X. Wang, S. -J. Kim, and M. Madihian, “Multi-hop wireless backhaul networks: A cross-layer design paradigm,” IEEE J. Sel. Areas Commun., vol. 25, no. 4, pp. 738–748, May 2007.
A. Carleial, “Interference channels,” IEEE Trans. Inf. Theory, vol. IT-24, no. 1, pp. 60–70, Jan. 1978.
N. B.Chang and M. Liu, “Optimal channel probing and transmission scheduling for opportunistic spectrum access,” in Proc. ACM Mobicom’07, Sept. 2007.
N. B. Chang and M. Liu, “Competitive analysis of opportunistic spectrum access strategies,” in Proc. IEEE INFOCOM’08, April 2008.
Y. Chen, Q. Zhao, and A. Swami, “Joint design and separation principle for opportunistic spectrum access in the presence of sensing errors,” IEEE Trans. Inf. Theory, vol. 54, no. 5, pp. 2053–2071, May 2008.
P. Cheng, G. Yu, Z. Zhang, H.-H. Chen, and P. Qiu, “On the maximum sum-rate capacity of cognitive multiple access channel,” http://arxiv.org/abs/cs.IT/0612024.
H. Chong, M. Motani, H. Garg, and H. E. Gamal, “On the han-kobayashi region for the interference channel,” To appear in IEEE Trans. Inf. Theory, vol. 54, no. 7, pp. 3188–3195, July 2008.
Y. S. Chow, H. Robbins, and D. Siegmund, Great Expectations: The Theory of Optimal Stop**, Houghton Mifflin Company, Boston, USA, 1971.
T. Clancy, “Achievable capacity under the interference temperature model,” IEEE Conference on Computer Communications (INFOCOM), May 2007.
C. Cordeiro and K. Challapali, “C-MAC: A cognitive MAC protocol for multi-channel wireless networks,” in Proc. DySPAN’07, April 2007.
M. Costa, “Writing on dirty paper,” IEEE Trans. Inf. Theory, vol. IT-29, pp. 439–441, May 1983.
T. Cover and J. Thomas, Elements of Information Theory New York: John Wiley & Sons, 1991.
I. Csiszár and J. Kőrner, Information Theory: Coding Theorems for Discrete Memoryless System. Akadémiai Kiadó, Budapest, Hungary, 1981.
C. da Silva, B. Choi, and K. Kim, “Distributed spectrum sensing for cognitive radio systems,” in Information Theory and Applications ITA Workshop, Feb. 2007.
N. Devroye, “Information theoretic limits of cooperation and cognition in wireless networks,” Ph.D. dissertation, Harvard, 2007.
N. Devroye, P. Mitran, M. Sharif, S. S. Ghassemzadeh, and V. Tarokh, “Information theoretic analysis of cognitive radio systems,” in Cognitive Wireless Communication Networks, V. Bhargava and E. Hossain, Eds. Springer, 2007.
N. Devroye, P. Mitran, and V. Tarokh, “Achievable rates in cognitive radio channels,” in 39th Annual Conference on Information Sciences and Systems (CISS), Mar. 2005.
N. Devroye, P. Mitran, and V. Tarokh, “Achievable rates in cognitive networks,” in 2005 IEEE International Symposium on Information Theory, Sept. 2005.
N. Devroye, P. Mitran, and V. Tarokh, “Achievable rates in cognitive radio channels,” IEEE Trans. Inf. Theory, vol. 52, no. 5, pp. 1813–1827, May 2006.
N. Devroye, P. Mitran, and V. Tarokh, “Cognitive decomposition of wireless networks,” in Proc. CROWNCOM, Mykonos Island, Greece, Mar. 2006.
N. Devroye and M. Sharif, “The multiplexing gain of MIMO X-channels with partial transmit side-information,” in IEEE International Symposium on Information Theory, June 2007.
N. Devroye and V. Tarokh, “Fundamental limits of cognitive radio networks,” in Cognitive Wireless Networks: Concepts, Methodologies and Vision, F. Fitzek and M. Katz, Eds. Springer, New York, USA, 2007.
R. Etkin, A. Parekh, and D. Tse, “Spectrum sharing for unlicensed bands,” IEEE J. Sel. Areas Commun., vol. 25, no. 3, pp. 517–528, Apr. 2007.
FCC, Spectrum Policy Task Force Report, No. 02-155, Nov. 2002.
G. Ganesan and Y. Li, “Cooperative spectrum sensing in cognitive radio networks,” in New Frontiers in Dynamic Spectrum Access Networks (DYSPAN), Nov. 2005.
M. Gastpar, “On capacity under receive and spatial spectrum-sharing constraints,” IEEE Trans. Inf. Theory, vol. 53, pp. 471–487, Feb. 2007.
S. Geirhofer, L. Tong, and B. M. Sadler, “Dynamic spectrum access in the time domain: Modeling and exploiting whitespace,” IEEE Commun. Mag., vol. 45, no. 5, pp. 66–72, May 2007.
S. Gel’fand and M. Pinsker, “Coding for channels with random parameters,” Probl. Contr. Inf. Theory, vol. 9, no. 1, pp. 19–31, 1980.
A. Ghasemi and E. Sousa, “Collaborative spectrum sensing for opportunistic access in fading environments,” in New Frontiers in Dynamic Spectrum Access Networks (DYSPAN), Nov. 2005.
A. Ghasemi and E. Sousa, “Capacity of fading channels under spectrum-sharing constraints,” in Proc. IEEE Int. Conf. Commun., Istanbul, Turkey, June 2006.
A. Goldsmith, S. Jafar, I. Maric, and S. Srinivasa, “Breaking spectrum gridlock with cognitive radios: An information theoretic perspective,” Proceedings of the IEEE, vol. 97, no. 5, pp. 894–914, May 2009.
P. Grover and A. Sahai, “On the need for knowledge of the phase in exploiting known primary transmissions,” 2nd IEEE Int. Symposium on New Frontiers in Dynamic Spectrum Access Networks, 2007 (DySPAN 2007), pp. 462–471, Dublin, Ireland, 17–20 April 2007.
P. Gupta and P. R. Kumar, “The capacity of wireless networks,” IEEE Trans. Inf. Theory, vol. 46, no. 2, pp. 388–404, Mar. 2000.
B. Hamdaoui and K. G. Shin, “OS-MAC: An efficient MAC protocol for spectrum-agile wireless networks,” IEEE Trans. Mobile Comput., vol. 7, no. 8, pp. 915–930, Aug. 2008.
T. Han and K. Kobayashi, “A new achievable rate region for the interference channel,” IEEE Trans. Inf. Theory, vol. IT-27, no. 1, pp. 49–60, 1981.
Z. J. Hass and J. Deng, “Dual busy tone multiple access (DBTMA) – A multiple access control scheme for ad hoc networks,” IEEE Trans. Commun., vol. 50, no. 6, pp. 975–985, Jun. 2002.
S. Haykin, “Cognitive radio: Brain-empowered wireless communications,” IEEE J. Sel. Areas Commun., vol. 23, no. 2, pp. 201–220, Feb. 2005.
C. Heegard and A. E. Gamal, “On the capacity of computer memories with defects,” IEEE Trans. Inf. Theory, vol. 29, pp. 731–739, Sept. 1983.
S.-C. Hong, M. Vu, and V. Tarokh, “Cognitive sensing based on side information,” Sarnoff Conf., Apr. 2008.
N. Hoven and A. Sahai, “Power scaling for cognitive radio,” Int Conf. Wireless Netw., Comm. Mobile Comput., vol. 1, pp. 250–255, Jun. 2005.
A. C. C. Hsu, D. S. L. Wei, and C.-C. J. Kuo, “A cognitive MAC protocol using statistical channel allocation for wireless ad-hoc networks,” in Proc. IEEE WCNC’07.
J. Huang, R. Berry, and M. Honig, “Distributed interference compensation for wireless networks,” IEEE J. Sel. Areas Commun., vol. 24, no. 5, pp. 1074–1084, May 2006.
J. Huang, R. Berry, and M. Honig, “Auction-based spectrum sharing,” ACM/Kluwer J. Mobile Netw. Appl. (MONET), vol. 11, no. 3, pp. 405–418, Jun. 2006.
S. Huang, X. Liu, and Z. Ding, “Opportunistic spectrum access in cognitive radio networks,” in Proc. IEEE INFOCOM 2008, Apr. 2008.
T. Hunter, A. Hedayat, M. Janani, and A. Nostratinia, “Coded cooperation with space-time transmission and iterative decoding,” in WNCG Wireless, Oct. 2003.
M. Islam, Y.-C. Liang, and A. T. Hoang, “Joint power control and beamforming for secondary spectrum sharing,” in Proc. of IEEE 66th Vehicular Technology Conference (VTC), Oct. 2007.
S. A. Jafar and S. Srinivasa, “Capacity limits of cognitive radio with distributed and dynamic spectral activity,” IEEE J. Sel. Areas Commun., vol. 25, pp. 529–537, Apr. 2007.
S. Jafar and S. Shamai, “Degrees of freedom region for the MIMO X channel,” IEEE Trans. Inf. Theory, vol. 54, no. 1, pp. 151–170, Jan. 2008.
S.-W. Jeon, N. Devroye, M. Vu, S.-Y. Chung, and V. Tarokh, “Cognitive networks achieve throughput scaling of a homogeneous network,” IEEE Trans. Info. Theory, submitted Mar 2008.
J. Jia, Q. Zhang, and X. Shen, “HC-MAC: A hardware-constrained cognitive MAC for efficient spectrum management,” IEEE J. Sel. Areas Commun., vol. 26, no. 1, pp. 106–117, Jan. 2008.
J. Jiang and X. **n, “On the achievable rate regions for interference channels with degraded message sets,” submitted to IEEE Trans. Inf. Theory, vol. 54, no. 10, pp. 4707–4712, Apr. 2007.
J. Jiang, X. **n, and H. Garg, “Interference channels with common information,” submitted to IEEE Trans. Inf. Theory, vol. 54, no. 1, pp. 171–187, Jan. 2008.
A. Jovicic and P. Viswanath, “Cognitive radio: An information-theoretic perspective,” Proc. IEEE ISIT 2006, Seattle, USA, July 9–14, 2006.
A. Karnik, A. Iyer, and C. Rosenberg, “Throughput-optimal configuration of fixed wireless networks,” IEEE/ACM Trans. Networking, vol. 16, no. 5, pp. 1161–1174, Oct. 2008.
S. M. Kay, Fundamentals of Statistical Signal Processing, Volume 2: Detection Theory. Prentice Hall, New Jersey, USA, 1998.
F. P. Kelly, A. Maulloo, and D. Tan, “Rate control for communication networks: Shadowing prices, proportional fairness, and stability,” J. Oper. Res. Soc., vol. 49, no. 3, pp. 237–252, Mar. 1998.
D. I. Kim, L. Le, and E. Hossain, “Joint rate and power allocation for cognitive radios in dynamic spectrum access environment,” IEEE Trans. Wireless Commun., vol. 7, no. 12, pp. 5517–5527, Dec. 2008.
P. J. Kolodzy, “Interference temperature: A metric for dynamic spectrum utilization,” Int. J. Netw. Manag., vol. 16, no. 2, pp. 103–113, Mar. 2006.
O. Koyluoglu and H. Gamal, “On power control and frequency re-use in the two-user cognitive channel,” submitted to IEEE Trans. Wireless Commun., 2007.
S. Kulkarni and C. Rosenberg, “Opportunistic scheduling: Generalizations to include multiple constraints, multiple Interfaces, and short term fairness,” ACM/Kluwer Wireless Netw. J. (WINET), vol. 11, no. 5, pp. 557–569, Sept. 2005.
A. Kusnetsov and B. Tsybakov, “Coding in a memory with defective cells,” Prob. Pered. Inform., vol. 10, pp. 52–60, Apr.–Jun. 1974.
L. Le and E. Hossain, “OSA-MAC: A MAC protocol for opportunistic spectrum access in cognitive radio networks,” in Proc. IEEE WCNC’08, Mar.–Apr. 2008.
L. Le and E. Hossain, “Resource allocation for spectrum underlay in cognitive radio networks,” IEEE Trans. Wireless Commun., vol. 7, no. 12.
J. Li, C. Blake, D. S. J. D. Couto, H. I. Lee, and R. Morris, “Capacity of ad hoc wireless networks,” in Proc. ACM Mobicom’01.
Y. Liang, A. Somekh-Baruch, H. V. Poor, S. S. (Shitz), and S.Verdú, “Capacity of cognitive interference channels with and without secrecy,” submitted to IEEE Trans. Inf. Theory, vol. 55, no. 2, pp. 604–619, Feb. 2009.
Y. C. Liang, Y. Zeng, E. C. Y. Peh, and A. T. Hoang, “Sensing-throughput tradeoff for cognitive radio networks,” IEEE Trans. Wireless Commun., vol. 7, no. 4, pp. 1326–1337, Apr. 2008.
X. Liu, E. K. P. Chong, and N. B. Shroff, “Opportunistic transmission scheduling with resource-sharing constraints in wireless networks,” IEEE J. Sel. Areas Commun., vol. 19, no. 10, pp. 2053–2065, Oct. 2001.
X. Luo and K. Kar, “Joint scheduling and power allocation in multi-channel access point networks under QoS constraints,” in Proc. IEEE ICC’08, May 2008.
L. Ma, X. Han, and C. C. Shen, “Dynamic open spectrum sharing MAC protocol for wireless ad hoc networks,” in Proc. DySPAN’05, Nov. 2005.
M. Maddah-Ali, A. Motahari, and A. Khandani, “Signaling over MIMO multi-base systems: combination of multi-access and broadcast schemes,” in 2006 IEEE International Symposium on Information Theory, Jul. 2006.
M. Marcus, “Unlicensed cognitive sharing of TV spectrum: The controversy at the federal communications commission,” IEEE Comm. Mag., vol. 43, no. 5, pp. 24–25, May 2005.
I. Maric, R. Yates, and G. Kramer, “Capacity of interference channels with partial transmitter cooperation,” IEEE Trans. Inf. Theory, vol. 53, pp. 3536–3548, Oct. 2007.
S. M. Mishra, A. Sahai, and R. W. Brodersen, “Cooperative sensing among cognitive radios,” in Proc. IEEE Int. Conf. Commun., Istanbul, Turkey, Jun. 2006.
J. Mitola, “Cognitive radio,” Ph.D. dissertation, Royal Institute of Technology (KTH), 2000.
P. Mitran, N. Devroye, and V. Tarokh, “On compound channels with side-information at the transmitter,” IEEE Trans. Inf. Theory, vol. 52, no. 4, pp. 1745–1755, Apr. 2006.
J. Mo, H.-S.W. So, and J. Walrand, “Comparison of multichannel MAC protocols,” IEEE Trans. Mobile Comput., vol. 7, no. 1, pp. 50–65, Jan. 2008.
J. Mo and J. Walrand, “Fair end-to-end window-based congestion control,” IEEE/ACM Trans. Netw., vol. 8, no. 5, pp. 556–567, Oct. 2000.
D. Niyato and E. Hossain, “Competitive spectrum sharing in cognitive radio networks: A dynamic game approach,” IEEE Trans. Wire less Commun., vol. 7, no. 7, pp. 2651–2660, Jul. 2008.
M. Oner and F. Jondral, “On the extraction of the channel allocation information in spectrum pooling systems,” IEEE J. Sel. Areas Commun., vol. 25, no. 3, pp. 558–565, Apr. 2007.
P. Popovski, H. Yomo, K. Nishimori, R. D. Taranto, and R. Prasad, “Opportunistic interference cancellation in cognitive radio systems,” in Proc. 2nd IEEE International Symposium on Dynamic Spectrum Access Networks (DySPAN), Dublin, Ireland, Apr. 2007.
A. Sabharwal, A. Khoshnevis, and E. Knightly, “Opportunistic spectral usage: Bounds and a multi-band CSMA/CA protocol,” IEEE/ACM Trans. Netw., vol. 15, no. 3, pp. 533–545, Jun. 2007.
Y. Shi and Y. T. Hou, “A distributed optimization algorithm for multi-hop cognitive radio networks,” in Proc. INFOCOM’08, Apr. 2008.
O. Simeone, Y. Bar-Ness, and U. Spagnolini, “Stable throughput of cognitive radios with and without relaying capability,” IEEE Trans. Commun., vol. 55, no. 12, pp. 2351–2360, Dec. 2007.
R. Smallwood and E. Sondik, “The optimal control of partially observable Markov processes over a finite horizon,” Oper. Res., vol. 21, no. 5, pp. 1071–1088, Sept.–Oct. 1973.
J. So and N. Vaidya, “Multi-channel MAC for ad hoc networks: Handling multi-channel hidden terminals using a single transceiver,” in Proc. ACM Mobihoc’04.
S. Srinivasa, S. Jafar, and N. **dal, “On the capacity of the cognitive tracking channel,” Proc. IEEE Int. Symp. Inf. Theory, July 2006.
Y. Steinberg and N. Merhav, “Identification in the presence of side information with application to watermarking,” IEEE Trans. Inf. Theory, vol. 47, pp. 1410–1422, May 2001.
H. Su and X. Zhang, “Channel-hop** based single transceiver MAC for cognitive radio networks,” in Proc. CISS’08, Mar. 2008.
H. Su and X. Zhang, “Cross-layer based opportunistic MAC protocols for QoS provisionings over cognitive radio wireless networks,” IEEE J. Sel. Areas Communs., vol. 26, no. 1, pp. 118–129, Jan. 2008.
J. Sun, E. Modiano, and L. Zheng, “Wireless channel allocation using an auction algorithm,” IEEE J. Sel. Areas Commun., vol. 24, no. 5, pp. 1085–1096, May 2006.
R. Tandra and A. Sahai, “SNR walls for signal detection,” IEEE J. Sel. Areas Commun., vol. 2, no. 1, pp. 4–17, Feb. 2008.
A. Tkachenko, “Testbed design for cognitive radio spectrum sensing experiments,” Ph.D. dissertation, Berkeley, 2007.
J. Unnikrishnan and V. V. Veeravalli, “Cooperative sensing for primary detection in cognitive radio,” IEEE J. Sel. Signal Process., vol. 2, no. 1, pp. 18–27, Feb. 2008.
S. Verdú, Multiuser Detection. Cambridge University Press, Cambridge, UK, 2003.
P. Viswanath, D. Tse, and R. Laroia, “Opportunistic beamforming using dumb antennas,” IEEE Trans. Inf. Theory, vol. 48, no. 6, pp. 1277–1294, Jun., 2002.
M. Vu, N. Devroye, and V. Tarokh, “On the primary exclusive regions in cognitive networks,” submitted to IEEE Trans. Wireless Comm., to appear.
M. Vu, S. S. Ghassemzadeh, and V. Tarokh, “Interference in a cognitive network with beacon,” IEEE Wireless Comm. Netw. Conf., Mar. 2008.
M. Vu and V. Tarokh, “Scaling laws of single-hop cognitive networks,” submitted to IEEE Trans. Wireless Comm., to appear.
F. Wang, M. Krunz, and S. Cui, “Price-based spectrum management in cognitive radio network,” IEEE J. Sel. Signal Process., vol. 2, no. 1, pp. 74–87, Feb. 2008.
H. Weingarten, Y. Steinberg, and S. Shamai, “The capacity region of the Gaussian MIMO broadcast channel,” submitted to IEEE Trans. Inf. Theory, vol. 52, no. 9, pp. 3936–3964, Sept. 2006.
W. Weng, T. Peng, and W. Wang, “Optimal power control under interference temperature constraints in cognitive radio network,” in Proc. of IEEE Wireless Communications and Networking Conference, Hong Kong, Mar. 2007.
W. Wu, S. Vishwanath, and A. Arapostathis, “Capacity of a class of cognitive radio channels: Interference channels with degraded message sets,” IEEE Trans. Inf. Theory, vol. 53, no. 11, pp. 4391–4399, Jun. 2007.
W. Wu, S. Vishwanath, and A. Aripostathis, “On the capacity of interference channel with degraded message sets,” submitted to IEEE Trans. Inf. Theory, vol. 53, no. 11, pp. 4391–4399, 2007.
Y. **ng, C. Marthur, M. Haleem, R. Chandramouli, and K. Subbalakshmi, “Dynamic spectrum access with QoS and interference temperature constraints,” IEEE Trans. Mobile Comput., vol. 6, no. 4, pp. 423–433, Apr. 2007.
R. Yeung, A First Course in Information Theory. Springer, New York, USA, 2002.
S. Yiu and M. Vu, “Interference reduction by beamforming in cognitive networks,” submitted to Proc. IEEE Global Telecommun. Conf., pp. 1–6, Nov. 30–Dec. 4.
L. Zhang, Y. -C. Liang, and Y. **n, “Joint beamforming and power allocation for multiple access channels in cognitive radio networks, IEEE J. Sel. Areas Commun., vol. 26, no. 1, pp. 38–51, Jan. 2008.
L. Zhang, Y.-C. Liang, Y. **n, and H. V. Poor, “Robust cognitive beamforming with partial channel state information,” http://front.math.ucdavis.edu/0711.4414.
L. Zhang, Y. **n, and Y.-C. Liang, “Power allocation for multi-antenna multiple access channels in cognitive radio networks,” in Annual Conference on Information Sciences and Systems (CISS), Mar. 2007.
R. Zhang and Y. Liang, “Exploiting multi-antennas for opportunistic spectrum sharing in cognitive radio networks,” http://front.math.ucdavis.edu/0711.4414.
Q. Zhao and B. M. Sadler, “A survey of dynamic spectrum access,” IEEE Signal Process. Mag., vol. 24, no. 3, pp. 79–89, May, 2007.
Q. Zhao, L. Tong, A. Swami, and Y. Chen, “Decentralized cognitive MAC for opportunistic spectrum access in ad hoc networks: A POMDP framework,” IEEE J. Sel. Areas Commun., vol. 25, no. 3, pp. 589–600, Apr. 2007.
Additional Readings
K. R. Chowdhury and I. F. Akyildiz, “Cognitive wireless mesh networks with dynamic spectrum access,” IEEE J. Sel. Areas Communs., vol. 26, no. 1, pp. 168–181, Jan. 2008.
M. Gandetto and C. Regazzoni, “Spectrum sensing: A distributed approach for cognitive terminals,” IEEE J. Sel. Areas Commun., vol. 25, no. 3, pp. 546–546, Apr. 2007.
S. Geirhofer, L. Tong, and B. M. Sadler, “Cognitive medium access: Constraining interference based on experimental models,” IEEE J. Sel. Areas Commun., vol. 26, no. 1, pp. 95–105, Jan. 2008.
D. Niyato, E. Hossain, and L. Le, “Competitive spectrum sharing and pricing in cognitive wireless mesh networks,” in Proc. IEEE WCNC'08, Mar.–Apr. 2008.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2009 Springer-Verlag US
About this chapter
Cite this chapter
Hossain, E., Le, L., Devroye, N., Vu, M. (2009). Cognitive Radio: From Theory to Practical Network Engineering. In: Tarokh, V. (eds) New Directions in Wireless Communications Research. Springer, Boston, MA. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-1-4419-0673-1_10
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-1-4419-0673-1_10
Published:
Publisher Name: Springer, Boston, MA
Print ISBN: 978-1-4419-0672-4
Online ISBN: 978-1-4419-0673-1
eBook Packages: EngineeringEngineering (R0)