Abstract
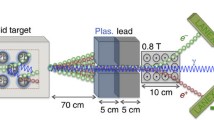
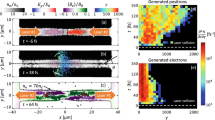
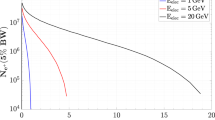
We discuss the necessary requirements to create dense electron-positron plasmas in the laboratory and the possibility of using them to investigate certain aspects of various astrophysical phenomena, such as gamma ray burst engines. Earth-based electron-positron plasmas are created during the interaction of ultra-intense laser pulses im**ing on a solid density target. The fact that positrons can be generated during this interaction has already been demonstrated by Cowan et al. (2000). However, several questions concerning the number, energy, and dynamics of these positrons have yet to be answered. Through insight gathered from PIC simulations, we postulate that the e+e- plasma leaves the creation region in dense jets, with relativistic energies. In order to estimate the number density of the positrons created, we begin by first experimentally measuring the hot electron temperatures and densities of such interactions using a compact electron spectrometer. Once the electron distribution is known, the positron creation rate, Γ, can be estimated. This same experimental diagnostic can also, with minor modification, measure the energy distribution of positrons. Initial estimates are that, with proper target and laser configurations, we could potentially create one of the densest arraignments of positrons ever assembled on earth. This experimental configuration would only last for a few femtoseconds, but would eventually evolve into astrophysically relevant pure electron-positron jets, possibly relevant to e+e- outflow from black holes.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Preview
Unable to display preview. Download preview PDF.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Chen, H., Patel, P.K., Price, D.F., Young, B.K., Springer, P.T., Berry, R., Booth, R., Bruns, C. and Nelson, D.: 2003, Rev. Sci. Instrum. 74, 1551.
Cowan, T.E., Roth, M., Allen, M.M., Johnson, J., Hatchett, S.P., LeSage, G.P. and Wilks, S.C.: 2000, Lawrence Livermore National Lab. Reprint, UCRL-JC-138049: Cowan, T., Hunt, A.W., Johnson, J., Perry, M.D., Fountain, W., Hatchett, S., Key, M.H., Kuehl, T., Parnelli, T., Pennington, D.M., Phillips, T.W., Roth, M., Takahashi, Y. and Wilks, S.C. in High Field Science, Tajima, T., Mima, K. and Baldis, H. (eds.), Kluwer (Academic/Plenum), New York, 2000 pp. 145-156.
Evans, R.B.: 1955, The Atomic Nucleus, McGraw-Hill, New York pp. 695–710.
Gahn, C., Tsakiris, G.D., Pretzler, G., Witte, K.J., Delfin, C., Wahlström, C.-G. and Habs, D.: 2000, Appl. Phys. Lett. 77, 2622.
Greaves, R.G. and Surko, C.M.: 2000, Phys. Rev. Lett. 85, 1883.
Helander, P. and Ward, D.J.: 2003, Phys. Rev. Lett. 90, 135004.
Liang, E., Wilks, S.C. and Tabak, M.: 1998, Phys. Rev. Lett. 81, 4887.
Mackinnon, A., Sentoku, Y., Patel, P.K., Price, D.W., Hatchett, S., Key, M., Anderson, C., Snavely, R. and Freeman, R.R.: 2002, Phys. Rev. Lett., 88, 215006.
Nakashima, K. and Takabe, H.: 2002, Phys. Plasmas 9, 1505.
Norreys, P.: 2003, RAL Annual Report.
Wharton, K.B., Hatchett, S.P., Wilks, S.C., Key, M.H., Moody, J.D., Yanovsky, V., Offenberger, A.A., Hammel, B.A., Perry, M.D. and Joshi, C.: 1998, Phys. Rev. Lett. 81, 822.
Wilks, S.C. and Chen, H.: 2005, accepted Laser and Particle Beams.
Wilks, S.C. and Kruer, W.L.: 1997, IEEE J. Quantum Electronics 33, 1954.
Wilks, S.C., Kruer, W.L., Tabak, M. and Langdon, A.B.: 1992, Phys. Rev. Lett. 69, 1383.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Editor information
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2005 Springer
About this chapter
Cite this chapter
Wilks, S. et al. (2005). Electron-Positron Plasmas Created By Ultra-Intense Laser Pulses Interacting With Solid Targets. In: Kyrala, G. (eds) High Energy Density Laboratory Astrophysics. Springer, Dordrecht. https://doi.org/10.1007/1-4020-4162-4_52
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/1-4020-4162-4_52
Received:
Accepted:
Publisher Name: Springer, Dordrecht
Print ISBN: 978-1-4020-3483-1
Online ISBN: 978-1-4020-4162-4
eBook Packages: Physics and AstronomyPhysics and Astronomy (R0)