Abstract
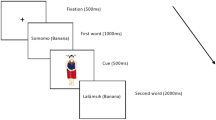
The present study explored bilingual coactivation during natural monolingual sentence-reading comprehension. Native Chinese readers who had learned Japanese as a second language and those who had not learned it at all were tested. The results showed that unrelated Chinese word pairs that shared a common Japanese translation could parafoveally prime each other. Critically, this translation-related preview effect was modulated by the readers’ language-learning experiences. It was found only among the late Chinese–Japanese bilinguals, but not among the monolingual Chinese readers. By setting a novel step, which was testing bilingual coactivation of semantic knowledge in a natural reading scenario without an explicit presentation of L2 words, our results suggest that bilingual word processing can be automatic, unconscious and nonselective. The study reveals an L2-to-L1 influence on readers’ lexical activation during natural sentence reading in an exclusively native context.


Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability and code availability
The datasets generated during and/or analyzed during the current study are available in the OSF repository (https://doi.org/10.17605/OSF.IO/DVM4N).
References
Altarriba, J., Kambe, G., Pollatsek, A., & Rayner, K. (2001). Semantic codes are not used in integrating information across eye fixations in reading: Evidence from fluent Spanish-English bilinguals. Perception & Psychophysics, 63, 875–890. https://doi.org/10.3758/BF03194444
Assche, E. V., Duyck, W., Hartsuiker, R. J. (2012). Bilingual word recognition in a sentence context. Frontiers in Psychology, 3. https://doi.org/10.3389/fpsyg.2012.00174
Bates, D., Kliegl, R., Vasishth, S., & Baayen, R. H. (2015a). Parsimonious mixed models (ar**v:1506.04967 [stat.ME]). Retrieved from https://arxiv.org/abs/1506.04967
Bates, D., Maechler, M., Bolker, B., & Walker, S. (2015b). Fitting linear mixed-effects models using lme4. Journal of Statistical Software, 67, 1–48. https://doi.org/10.18637/jss.v067.i01
Blumenfeld, H. K., & Marian, V. (2007). Constraints on parallel activation in bilingual spoken language processing: Examining proficiency and lexical status using eye-tracking. Language and Cognitive Processes, 22(5), 633–660. https://doi.org/10.1080/01690960601000746
Briihl, D., & Inhoff, A. W. (1995). Integrating information across fixations during reading: The use of orthographic bodies and of exterior letters. Journal of Experimental Psychology: Learning, Memory, and Cognition, 21, 55–67. https://doi.org/10.1037/0278-7393.21.1.55
Christoffels, I. K., De Groot, A. M. B., & Kroll, J. F. (2006). Memory and language skills in simultaneous interpreters: The role of expertise and language proficiency. Journal of Memory and Language, 54, 324–345. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jml.2005.12.004
Costa, A., & Santesteban, M. (2004). Lexical access in bilingual speech production: Evidence from language switching in highly proficient bilinguals and L2 learners. Journal of Memory and Language, 50, 491–511. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jml.2004.02.002
Costa, A., La Heij, W., & Navarrete, E. (2006). The dynamics of bilingual lexical access. Bilingualism: Language and Cognition, 9(2), 137–151. https://doi.org/10.1017/S1366728906002495
Declerck, M., Koch, I., Duñabeitia, J. A., Grainger, J., & Stephan, D. N. (2019). What absent switch costs and mixing costs during bilingual language comprehension can tell us about language control. Journal of Experimental Psychology: Human Perception & Performance, 45(6), 771–789. https://doi.org/10.1037/xhp0000627
Degani, T., Prior, A., & Tokowicz, N. (2011). Bidirectional transfer: The effect of sharing a translation. Journal of Cognitive Psychology, 23, 18–28. https://doi.org/10.1080/20445911.2011.445986
Dijkstra, A., & Van Heuven, W. J. B. (2002). The architecture of the bilingual word recognition system: From identification to decision. Bilingualism: Language and Cognition, 5, 175–197. https://doi.org/10.1017/S1366728902003012
Dijkstra, T., Wahl, A., Buytenhuijs, F., Van Halem, N., Al-Jibouri, Z., De Korte, M., & Rekké, S. (2019). Multilink: A computational model for bilingual word recognition and word translation. Bilingualism: Language and Cognition, 22, 657–679. https://doi.org/10.1017/S1366728918000287
Engbert, R., & Kliegl, R. (2003). Microsaccades uncover the orientation of covert attention. Vision Research, 43, 1035–1045. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0042-6989(03)00084-1
Ford-Niwa, J., & Kobayashi, N. (1999). SPOT: A test measuring “control” exercised by learners of Japanese. In K. Kazue (Ed.), The acquisition of Japanese as a second language (pp. 53–70). John Benjamins Publishing Company. https://doi.org/10.1075/lald.20.07for
Green, D. W., & Abutalebi, J. (2013). Language control in bilinguals: The adaptive control hypothesis. Journal of Cognitive Psychology, 25(5), 515–530. https://doi.org/10.1080/20445911.2013.796377
Grosjean, F. (1998). Transfer and language mode. Bilingualism: Language and Cognition, 1(3), 175–176. https://doi.org/10.1017/S1366728998000285
Grosjean, F. (2013). Bilingual and monolingual language modes. In C. A. Chapelle (Ed.), The encyclopedia of applied linguistics (p. 658). Blackwell. https://doi.org/10.1002/9781405198431.wbeal0090
Hohenstein, S., & Kliegl, R. (2014). Semantic preview benefit during reading. Journal of Experimental Psychology: Learning, Memory, and Cognition, 40, 166–190. https://doi.org/10.1037/a0033670
Hohenstein, S., Laubrock, J., & Kliegl, R. (2010). Semantic preview benefit in eye movements during reading: A parafoveal fast-priming study. Journal of Experimental Psychology: Learning Memory and Cognition, 36, 1150–1170. https://doi.org/10.1037/a0020233
Hoosain, R. (1991). Psycholinguistic implications for linguistic relativity: A case study of Chinese. Erlbaum. https://doi.org/10.1177/00238309920350030
Inhoff, A. W. (1982). Parafoveal word perception: A further case against semantic preprocessing. Journal of Experimental Psychology: Human Perception and Performance, 8, 137–145. https://doi.org/10.1037/0096-1523.8.1.137
Inhoff, A. W. (1984). Two stages of word processing during eye fixations in the reading of prose. Journal of Verbal Learning and Verbal Behavior, 23, 612–624. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0022-5371(84)90382-7
Inhoff, A. W., & Liu, W. (1998). The perceptual span and oculomotor activity during the reading of Chinese sentences. Journal of Experimental Psychology: Human Perception and Performance, 24(1), 20–34. https://doi.org/10.1037/0096-1523.24.1.20
Inhoff, A. W., & Radach, R. (1998). Definition and computation of oculomotor measures in the study of cognitive processes. In G. Underwood (Ed.), Eye guidance in reading and scene perception (pp. 29–53). UK: Elsevier Science. https://doi.org/10.1016/B978-008043361-5/50003-1
Inhoff, A. W., & Rayner, K. (1980). Parafoveal word perception: A case against semantic preprocessing. Perception & Psychophysics, 27, 457–464. https://doi.org/10.3758/BF03204463
Jiang, N. (2002). Form–meaning map** in vocabulary acquisition in a second language. Studies in Second Language Acquisition, 24(4), 617–637. https://doi.org/10.1017/S0272263102004047
Jiang, N. (2004). Semantic transfer and its implications for vocabulary teaching in a second language. The Modern Language Journal, 88(3), 416–432. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.0026-7902.2004.00238.x
Jouravlev, O., & Jared, D. (2020). Native language processing is influenced by L2-to-L1 translation ambiguity. Language, Cognition and Neuroscience, 35(3), 310–329. https://doi.org/10.1080/23273798.2019.1652764
Kim, J., & Kim, J. H. (2018). Implicit translation during second language lexical processing. The Journal of Cognitive Science, 19, 357–375.
Kim, Y. S., Radach, R., & Vorstius, C. (2012). Eye movements and parafoveal processing during reading in Korean. Reading and Writing, 25, 1053–1078. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11145-011-9349-0
Kliegl, R., Masson, M. E. J., & Richter, E. M. (2010). A linear mixed model analysis of masked repetition priming. Visual Cognition, 18, 655–681. https://doi.org/10.1080/13506280902986058
Kuznetsova, A., Brockhoff, P. B., & Christensen, R. H. B. (2017). lmerTest package: Tests in linear mixed effects models. Journal of Statistical Software, 82, 26. https://doi.org/10.18637/jss.v082.i13
Liu, W., Inhoff, A. W., Ye, Y., & Wu, C. (2002). Use of parafoveally visible characters during the reading of Chinese sentences. Journal of Experimental Psychology: Human Perception and Performance, 28, 1213–1227. https://doi.org/10.1037/0096-1523.28.5.1213
Marian, V. (2019). The language you speak influences where your attention goes. Scientific American.https://blogs.scientificamerican.com/observations/the-language-you-speak-influences-where-your-attention-goes/
Marian, V., & Spivey, M. J. (2003). Competing activation in bilingual language processing: Within- and between-language competition. Bilingualism: Language and Cognition, 6, 97–115. https://doi.org/10.1017/S1366728903001068
Matin, E. (1974). Saccadic suppression: A review and an analysis. Psychological Bulletin, 81(12), 899–917. https://doi.org/10.1037/h0037368
Matuschek, H., Kliegl, R., Vasishth, S., Baayen, H., & Bates, D. (2017). Balancing Type I error and power in linear mixed models. Journal of Memory and Language, 94, 305–315. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jml.2017.01.001
McConkie, G. W., & Rayner, K. (1975). The span of the effective stimulus during a fixation in reading. Perception & Psychophysics, 17, 578–586. https://doi.org/10.3758/BF03203972
Mishra, R. K., & Singh, N. (2016). The influence of second language proficiency on bilingual parallel language activation in Hindi-English bilinguals. Journal of Cognitive Psychology, 28(4), 396–411. https://doi.org/10.1080/20445911.2016.1146725
Miwa, K., Dijkstra, T., Bolger, P., & Baayen, R. H. (2014). Reading English with Japanese in mind: Effects of frequency, phonology, and meaning in different-script bilinguals. Bilingualism: Language and Cognition, 17, 445–463. https://doi.org/10.1017/S1366728913000576
Morford, J. P., Wilkinson, E., Villwock, A., Pinar, P., & Kroll, J. F. (2011). When deaf signers read English: Do written words activate their sign translations? Cognition, 118, 286–292. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cognition.2010.11.006
Orfanidou, E., & Sumner, P. (2005). Language switching and the effects of orthographic specificity and response repetition. Memory & Cognition, 33, 355–369. https://doi.org/10.3758/BF03195323
Pan, J., Shu, H., Wang, Y., & Yan, M. (2015). Parafoveal activation of sign translation previews among deaf readers during the reading of Chinese sentences. Memory & Cognition, 43(6), 964–972. https://doi.org/10.3758/s13421-015-0511-9
Pan, J., Laubrock, J., & Yan, M. (2016). Parafoveal processing in silent and oral reading: Reading mode influences the relative weighting of phonological and semantic information in Chinese. Journal of Experimental Psychology: Learning, Memory and Cognition, 42(8), 1257–1273. https://doi.org/10.1037/xlm0000242
Pan, J., Yan, M., & Yeh, S.-L. (2022). Accessing semantic information from above: Parafoveal processing during the reading of vertically presented sentences in traditional Chinese. Cognitive Science, 46, e13104. https://doi.org/10.1111/cogs.13104
Pan, J., Wang, A., McBride, C., Cho, J.-R., & Yan, M. (2023). Online assessment of parafoveal morphological processing/awareness during reading among Chinese and Korean adults. Scientific Studies of Reading, 27(3), 232–252. https://doi.org/10.1080/10888438.2022.2149335
Philipp, A. M., & Koch, I. (2016). Action speaks louder than words, even in speaking: The influence of (no) overt speech production on language-switch costs. In J. W. Schwieter (Ed.), Cognitive control and consequences in the multilingual mind (pp. 127–144). John Benjamins.
Pollatsek, A., Lesch, M., Morris, R. K., & Rayner, K. (1992). Phonological codes are used in integrating information across saccades in word identification and reading. Journal of Experimental Psychology: Human Perception and Performance, 18(1), 148–162. https://doi.org/10.1037/0096-1523.18.1.148
R Development Core Team. (2020). R: A language and environment for statistical computing. R Foundation for Statistical Computing.
Rayner, K. (1975). The perceptual span and peripheral cues during reading. Cognitive Psychology, 7, 65–81. https://doi.org/10.1016/0010-0285(75)90005-5
Rayner, K. (2009). Eye movements and attention in reading, scene perception, and visual search. Quarterly Journal of Experimental Psychology, 62, 1457–1506. https://doi.org/10.1080/17470210902816461
Rayner, K., Balota, D. A., & Pollatsek, A. (1986). Against parafoveal semantic preprocessing during eye fixations in reading. Canadian Journal of Psychology, 40(4), 473–483. https://doi.org/10.1037/h0080111
Rayner, K., Schotter, E. R., & Drieghe, D. (2014). Lack of semantic parafoveal preview benefit in reading revisited. Psychonomic Bulletin & Review, 21, 1067–1072. https://doi.org/10.3758/s13423-014-0582-9
Reynolds, M. G., Schlöffel, S., & Peressotti, F. (2016). Asymmetric switch costs in numeral naming and number word reading: Implications for models of bilingual language production. Frontiers in Psychology, 6, 2011. https://doi.org/10.3389/fpsyg.2015.02011
Santesteban, M., & Schwieter, J. (2020). Lexical selection and competition in bilinguals. In R. Heredia & A. Cieślicka (Eds.), Bilingual lexical ambiguity resolution (pp. 126–156). Cambridge University Press. https://doi.org/10.1017/9781316535967.007
Schotter, E. R. (2013). Synonyms provide semantic preview benefit in English. Journal of Memory and Language, 69, 619–633. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jml.2013.09.002
Simpson, G. B., & Burgess, C. (1985). Activation and selection processes in the recognition of ambiguous words. Journal of Experimental Psychology: Human Perception and Performance, 11(1), 28–39. https://doi.org/10.1037/0096-1523.11.1.28
Thierfelder, P., Wigglesworth, G., & Tang, G. (2020). Orthographic and phonological activation in Hong Kong deaf readers: An eye-tracking study. Quarterly Journal of Experimental Psychology, 73(12), 2217–2235. https://doi.org/10.1177/1747021820940223
Thierry, G., & Wu, Y. (2007). Brain potentials real unconscious translation during foreign-language comprehension. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences, 104(30), 12530–12535. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.0609927104
Thomas, M. S. C., & Allport, A. (2000). Language switching costs in bilingual visual word recognition. Journal of Memory and Language, 43(1), 44–66. https://doi.org/10.1006/jmla.1999.2700
Tsai, J.-L., Lee, C.-Y., Tzeng, O. J. L., Hung, D. L., & Yen, N.-S. (2004). Use of phonological codes for Chinese characters: Evidence from processing of parafoveal preview when reading sentences. Brain and Language, 91, 235–244. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bandl.2004.02.005
Tsai, J.-L., Kliegl, R., & Yan, M. (2012). Parafoveal semantic information extraction in traditional Chinese reading. Acta Psychologica, 141, 17–23. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.actpsy.2012.06.004
Tsang, Y. K., & Chen, H.-C. (2013). Early morphological processing is sensitive to morphemic meanings: Evidence from processing ambiguous morphemes. Journal of Memory and Language, 68(3), 223–239. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jml.2012.11.003
Van Hell, J. G., & Dijkstra, T. (2002). Foreign language knowledge can influence native language performance in exclusively native contexts. Psychonomic Bulletin & Review, 9(4), 780–789. https://doi.org/10.3758/bf03196335
Veldre, A., & Andrews, S. (2016). Semantic preview benefit in English: Individual differences in the extraction and use of parafoveal semantic information. Journal of Experimental Psychology: Learning, Memory, and Cognition, 42(6), 837–854. https://doi.org/10.1037/xlm0000212
Verhoef, K., Roelofs, A., & Chwilla, D. J. (2009). Role of inhibition in language switching: Evidence from event-related brain potentials in overt picture naming. Cognition, 110(1), 84–99. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cognition.2008.1
Von Studnitz, R. E., & Green, D. W. (1997). Lexical decision and language switching. International Journal of Bilingualism, 1(1), 3–24. https://doi.org/10.1177/136700699700100102
Wang, A., Yeon, J., Zhou, W., Shu, H., & Yan, M. (2016). Cross-language parafoveal semantic processing: Evidence from Korean-Chinese bilinguals. Psychonomic Bulletin & Review, 23(1), 285–290. https://doi.org/10.3758/s13423-015-0876-6
Weber, A., & Cutler, A. (2004). Lexical competition in non-native spoken-word recognition. Journal of Memory and Language, 50(1), 1–25. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0749-596X(03)00105-0
Wickham, H. (2016). ggplot2: Elegant graphics for data analysis (2nd ed.). Springer. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-319-24277-4
Yan, M., & Kliegl, R. (2023). Chinese offers a test for universal cognitive processes. Behavioral and Brain Sciences, 46, e258. https://doi.org/10.1017/S0140525X23000663
Yan, M., Richter, E. M., Shu, H., & Kliegl, R. (2009). Chinese readers extract semantic information from parafoveal words during reading. Psychonomic Bulletin & Review, 16, 561–566. https://doi.org/10.3758/PBR.16.3.561
Yan, M., Zhou, W., Shu, H., & Kliegl, R. (2012). Lexical and sub-lexical semantic preview benefits in Chinese reading. Journal of Experimental Psychology: Learning, Memory and Cognition, 38, 1069–1075. https://doi.org/10.1037/a0026935
Yan, M., Zhou, W., Shu, H., & Kliegl, R. (2015). Perceptual span depends on font size during the reading of Chinese sentences. Journal of Experimental Psychology: Learning, Memory and Cognition, 41, 209–219. https://doi.org/10.1037/a0038097
Yan, M., Wang, A., Song, H., & Kliegl, R. (2019). Parafoveal processing of phonology and semantics during the reading of Korean sentences. Cognition, 193, 104009. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cognition.2019.104009
Yang, J., Wang, S., Tong, X., & Rayner, K. (2012). Semantic and plausibility effects on preview benefit during eye fixations in Chinese reading. Reading and Writing, 25, 1031–1052. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11145-010-9281-8
Yen, M.-H., Tsai, J.-L., Tzeng, O.J.-L., & Hung, D. L. (2008). Eye movements and parafoveal word processing in reading Chinese. Memory & Cognition, 36, 1033–1045. https://doi.org/10.3758/MC.36.5.1033
Funding
This research was supported by a Fundo para o Desenvolvimento das Ciências e da Tecnologia (FDCT) grant from the Macao Science and Technology Development Fund (Project Code: 0015/2021/ITP).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflicts of interest
None.
Ethics approval
All experimental procedures were reviewed and approved by the Ethics Committee of the Department of Psychology, University of Macau (SONA-2022-06).
Consent to participate and for publication
All participants gave their written informed consent to participate in the experiment and to publish their data.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Hao, Y., Luo, Y., Lin-Hong, K.Hy. et al. Shared translation in second language activates unrelated words in first language. Psychon Bull Rev 31, 1245–1255 (2024). https://doi.org/10.3758/s13423-023-02405-z
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.3758/s13423-023-02405-z