Abstract
Introduction
Integrons are introduced as the most common mechanism for resistance gene dissemination in Pseudomonas aeruginosa.
Aims and tasks
The purpose of the present study was to determine the diversity of the gene cassettes carried with class 1 integrons in clinical isolates of Pseudomonas aeruginosa.
Methods and results
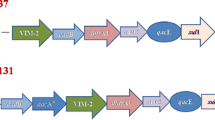
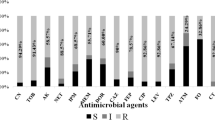
One hundred clinical isolates of Pseudomonas aeruginosa from four hospitals in Northwest of Iran were investigated for antimicrobial susceptibility, presence of class 1 integrons and associated resistance gene cassettes. Seventy-one percent of isolates were multidrug resistant (MDR) and colistin was the most effective antibiotic in this study. Sixty-six isolates (66%) were contained class 1 integrons which all of them carried gene cassettes. There was a strong correlation between integron presence and multidrug resistance phenotype (p < 0.05). Amplification of the internal variable regions of class 1 integrons revealed 10 different arrays ranging in size from 0.6 to 3.5 kb. DNA sequencing analysis of class 1 integrons revealed the presence of several gene cassettes associated with resistance to aminoglycosides (aac and aad), β-lactams (bla OXA), chloramphenicol (cmlA and catB), hypothetical gene cassette encoding a hypothetical protein and an open reading frame with unknown function (orfD). The most prevalent gene cassette found within class 1 integrons was aadB (68.18%), followed by aacA4 (48.48%). To the best of our knowledge, some of the gene cassettes arrays such as aac(3)-Ic-aacA5-cmlA5 and aacA5-aadA1-cmlA5 were first identified in this study. Hospital ward was demonstrated as significant risk factors for the acquisition of class 1 integrons harboring isolates in this study (P < 0.05).
Conclusions
Most of gene cassette arrays in this study are reported for the first time in Iran. These show the role of integrons in dissemination of resistance genes among clinical isolates of P. aeruginosa.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Henrichfreise, B., Wiegand, I., Pfister, W., and Wiedemann, B., Resistance mechanisms of multiresistant Pseudomonas aeruginosa strains from Germany and correlation with hypermutation, Antimicrob. Agents Chemother., 2007, no. 51, pp. 4062–4070.
Morrison, A.J. and Wenzel, R.P., Epidemiology of infections due to Pseudomonas aeruginosa, Rev. Infect. Dis., 1984, no. 6, pp. 627–642.
Livermore, D.M., Multiple mechanisms of antimicrobial resistance in Pseudomonas aeruginosa: Our worst nightmare?, Clin. Infect. Dis., 2002, no. 34, pp. 634–640.
Carmeli, Y., Troillet, N., Eliopoulos, G.M., and Samore, M.H., Emergence of antibiotic-resistant Pseudomonas aeruginosa: Comparison of risks associated with different antipseudomonal agents, Antimicrob. Agents Chemother., 1999, no. 43, pp. 1379–1382.
Stokes, H.W. and Hall, R.M., A novel family of potentially mobile DNA elements encoding site-specific gene-integration functions: Integrons, Mol. Microbiol., 1989, no. 3, pp. 1669–1683.
Collis, C.M., Kim, M.J., Stokes, H.W., and Hall, R.M., Integron-encoded inti integrases preferentially recognize the adjacent cognate attI site in recombination with a 59-be site, Mol. Microbiol., 2002, no. 46, pp. 1415–1427.
Carattoli, A., Importance of integrons in the diffusion of resistance, Vet. Res., 2001, no. 32, pp. 243–259.
Xu, Z., Li, L., Shirtliff, M.E., Alam, M.J., Yamasaki, S., and Shi, L., Occurrence and characteristics of class 1 and 2 integrons in Pseudomonas aeruginosa isolates from patients in southern China, J. Clin. Microbiol., 2009, no. 47, pp. 230–234.
Chen, J., Su, Z., Liu, Y., Wang, S., Dai, X., Li, Y., Peng, S., Shao, Q., Zhang, H., Wen, P., Yu, J., Huang, X., and Xu, H., Identification and characterization of class 1 integrons among Pseudomonas aeruginosa isolates from patients in Zhenjiang, China, Int. J. Infect. Dis., 2009, no. 13, pp. 717–721.
Levesque, C., Piche, L., Larose, C., and Roy, P.H., PCR map** of integrons reveals several novel combinations of resistance genes, Antimicrob. Agents Chemother., 1995, no. 39, pp. 185–191.
Mazel, D., Integrons: agents of bacterial evolution, Nat. Rev. Microbiol., 2006, no. 4, pp. 608–620.
Cambray, G., Guerout, A.M., and Mazel, D., Integrons, Annu. Rev. Genet., 2010, no. 44, pp. 141–166.
Shahcheraghi, F., Badmasti, F., and Feizabadi, M.M., Molecular characterization of class 1 integrons in MDR Pseudomonas aeruginosa isolated from clinical settings in Iran, Tehran, FEMS Immunol. Med. Microbiol., 2010, vol. 58, no. 3, pp. 421–425.
Fonseca, E.L., Vieira, V.V., Cipriano, R., and Vicente, A.C., Class 1 integrons in Pseudomonas aeruginosa isolates from clinical settings in Amazon region, Brazil, FEMS Immunol. Med. Microbiol., 2005, no. 44, pp. 303–309.
Wu, Y., Li, H., Li, J., and Huang, Z.H., Detection of Pseudomonas aeruginosa carried a new array of gene cassettes within class 1 integron isolated from a teaching hospital in Nan**g, China, J. Microbiol., 2008, no. 46, pp. 687–691.
Naas, T., Poirel, L., Karim, A., and Nordmann, P., Molecular characterization of In50, a class 1 integron encoding the gene for the extended-spectrum beta-lactamase VEB-1 in Pseudomonas aeruginosa, FEMS Microbiol. Lett., 1999, no. 176, pp. 411–419.
Naas, T., Mikami, Y., Imai, T., Poirel, L., and Nordmann, P., Characterization of In53, a class 1 plasmidand composite transposon-located integron of Escherichia coli which carries an unusual array of gene cassettes, J. Bacteriol., 2001, no. 183, pp. 235–249.
Levesque, C., Brassar, S., Lapointe, J., and Roy, P.H., Diversity and relative strength of tandem promoters for the antibiotic-resistance genes of several integrons, Gene, 1994, no. 142, pp. 49–54.
Hall, R.M. and Collis, C.M., Mobile gene cassettes and integrons: Capture and spread of genes by site-specific recombination, Mol. Microbiol., 1995, no. 15, pp. 593–600.
Leverstein-Hall, M.A., Box, A.T., Blok, H.E., Paauw, A., Fluit, A.C., and Verhoef, J., Evidence of extensive interspecies transfer of integron-mediated antimicrobial resistance genes among multidrug-resistant Enterobacteriaceae in a clinical setting, J. Infect. Dis., 2002, no. 186, pp. 49–56.
Forbes, B.A., Sahm, D., and Weissfeld, A., Diagnostic microbiology, St. Louis: Mosby, 2005.
Performance Standards for Antimicrobial Susceptibility Testing, 24th Informational Supplement, M100-S24, Wayne, PA: Clinical and Laboratory Standards Institute, 2014.
Yousefi, S., Nahaei, M., Farajnia, S., Ghojazadeh, M., Akhi, M., Sharifi, Y., Milani, M., and Ghotaslou, R., Class 1 integron and imipenem resistance in clinical isolates of Pseudomonas aeruginosa: Prevalence and antibiotic susceptibility, Iran. J. Microbiol., 2010, no. 2, pp. 115–121.
Cicek, A.C., Saral, A., Duzgun, A.O., Cizmeci, Z., Kayman, T., Balci, P.O., Dal, T., Firat, M., Yazici, Y., and Sancaktar, M., Screening of class 1 and class 2 integrons in clinical isolates of Pseudomonas aeruginosa collected from seven hospitals in Turkey: A multicenter study, Open J. Med. Microbiol., 2013, vol. 3, Art. ID 41014.
Nemec, A., Krizova, L., Maixnerova, M., and Musilek, M., Multidrug-resistant epidemic clones among bloodstream isolates of Pseudomonas aeruginosa in the Czech Republic, Res. Microbiol., 2010, no. 161, pp. 234–242.
Gu, B., Tong, M., Zhao, W., Liu, G., Ning, M., Pan, S., and Zhao, W., Prevalence and characterization of class I integrons among Pseudomonas aeruginosa and Acinetobacter baumannii isolates from patients in Nan**g, China, J. Clin. Microbiol., 2007, no. 45, pp. 241–243.
Poonsuk, K., Tribuddharat, C., and Chuanchuen, R., Class 1 integrons in Pseudomonas aeruginosa and Acinetobacter baumannii isolated from clinical isolates, Southeast Asian J. Trop. Med. Public Health, 2012, no. 43, pp. 376–384.
Kiddee, A., Henghiranyawong, K., Yimsabai, J., Tiloklurs, M., and Niumsup, P.R., Nosocomial spread of class 1 integron-carrying extensively drug-resistant Pseudomonas aeruginosa isolates in a Thai hospital, Int. J. Antimicrob. Agents, 2013, no. 42, pp. 301–306.
Azucena, E. and Mobashery, S., Aminoglycosidemodifying enzymes: Mechanisms of catalytic processes and inhibition, Drug Resist. Updates, 2001, no. 4, pp. 106–117.
Riccio, M.L., Docquier, J.D., Dell’Amico, E., Luzzaro, F., Amicosante, G., and Rossolini, G.M., Novel 3-N-aminoglycoside acetyltransferase gene, aac(3)-Ic, from a Pseudomonas aeruginosa integron, Antimicrob. Agents Chemother., 2003, no. 47, pp. 1746–1748.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
The article is published in the original.
About this article
Cite this article
Goli, H.R., Nahaei, M.R., Rezaee, M.A. et al. Prevalence and molecular characterization of class 1 integrons among clinical isolates of Pseudomonas aeruginosa in Northwest of Iran. Mol. Genet. Microbiol. Virol. 32, 109–115 (2017). https://doi.org/10.3103/S0891416817020057
Received:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.3103/S0891416817020057