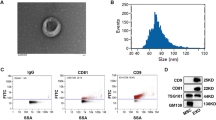
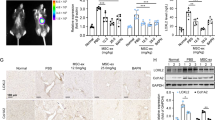
Abstract
Liver fibrosis is a significant health burden, marked by the consistent deposition of collagen. Unfortunately, the currently available treatment approaches for this condition are far from optimal. Lysyl oxidase-like protein 2 (LOXL2) secreted by hepatic stellate cells (HSCs) is a crucial player in the cross-linking of matrix collagen and is a significant target for treating liver fibrosis. Mesenchymal stem cell-derived small extracellular vesicles (MSC-sEVs) have been proposed as a potential treatment option for chronic liver disorders. Previous studies have found that MSC-sEV can be used for microRNA delivery into target cells or tissues. It is currently unclear whether microRNA-4465 (miR-4465) can target LOXL2 and inhibit HSC activation. Additionally, it is uncertain whether MSC-sEV can be utilized as a gene therapy vector to carry miR-4465 and effectively inhibit the progression of liver fibrosis. This study explored the effect of miR-4465-modified MSC-sEV (MSC-sEVmiR-4465) on LOXL2 expression and liver fibrosis development. The results showed that miR-4465 can bind specifically to the promoter of the LOXL2 gene in HSC. Moreover, MSC-sEVmiR-4465 inhibited HSC activation and collagen expression by downregulating LOXL2 expression in vitro. MSC-sEVmiR-4465 injection could reduce HSC activation and collagen deposition in the CCl4-induced mouse model. MSC-sEVmiR-4465 mediating via LOXL2 also hindered the migration and invasion of HepG2 cells. In conclusion, we found that MSC-sEV can deliver miR-4465 into HSC to alleviate liver fibrosis via altering LOXL2, which might provide a promising therapeutic strategy for liver diseases.
摘要
肝纤维化是慢性肝病向肝硬化发展的关键病理过程, 其特征是胶原蛋白的过量沉积。然而, 目前对于肝纤维化仍缺乏有效的治疗方法。肝星状细胞(HSC)分泌的赖氨酰氧化酶样蛋白2(LOXL2)是胶原交联和HSC活化的关键分子, 也是治疗肝纤维化的重要靶点。研究表明, 间质干细胞来源的小细胞外囊泡(MSC-sEV)是治疗慢性肝病的有效方法。MSC-sEV可将miRNA递送到靶细胞或组织中。但目前尚不明确miR-4465是否能够靶向LOXL2抑制HSC活化, 同时MSC-sEV是否可以作为基因治疗载体通过携带miR-4465从而抑制肝纤维化进展也不清楚。本研究探讨了miR-4465对于LOXL2的调控作用及miR-4465修饰的MSC-sEV(MSC-sEVmiR-4465)对LOXL2表达和肝纤维化进展的影响。结果表明, miR-4465可以靶向HSC中LOXL2基因的启动子。此外, MSC-sEVmiR-4465在体外通过下调LOXL2的表达来抑制HSC的活化和胶原的表达。而MSC-sEVmiR-4465注射可减少CCl4诱导的小鼠模型中HSC的活化和胶原沉积。MSC-sEVmiR-4465也能通过调控LOXL2抑制肝癌细胞HepG2的迁移和侵袭。总之, 我们发现MSC-sEV可以通过递送miR-4465到HSC中靶向LOXL2延缓肝纤维化的进展, 有望成为未来肝病治疗的一种新策略。
Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability statement
Data are available on request from the authors.
References
Ahani-Nahayati M, Niazi V, Moradi A, et al., 2022. Umbilical cord mesenchymal stem/stromal cells potential to treat organ disorders; an emerging strategy. Curr Stem Cell Res Ther, 17(2):126–146. https://doi.org/10.2174/1574888x16666210907164046
Albanese M, Chen YFA, Hüls C, et al., 2021. MicroRNAs are minor constituents of extracellular vesicles that are rarely delivered to target cells. PLoS Genet, 17(12):e1009951. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pgen.1009951
Askenase PW, 2021. Exosomes provide unappreciated carrier effects that assist transfers of their miRNAs to targeted cells; I. They are ‘The Elephant in the Room’. RNA Biol, 18(11):2038–2053. https://doi.org/10.1080/15476286.2021.1885189
Asrani SK, Devarbhavi H, Eaton J, et al., 2019. Burden of liver diseases in the world. J Hepatol, 70(1):151–171. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhep.2018.09.014
Cai XP, Cai HQ, Wang J, et al., 2022. Molecular pathogenesis of acetaminophen-induced liver injury and its treatment options. J Zhejiang Univ-Sci B (Biomed & Biotechnol), 23(4):265–285. https://doi.org/10.1631/jzus.B2100977
Chen W, Yang AT, Jia JD, et al., 2020. Lysyl oxidase (LOX) family members: rationale and their potential as therapeutic targets for liver fibrosis. Hepatology, 72(2):729–741. https://doi.org/10.1002/hep.31236
Dixson AC, Dawson TR, di Vizio D, et al., 2023. Context-specific regulation of extracellular vesicle biogenesis and cargo selection. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol, 24(7):454–476. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41580-023-00576-0
Friedman SL, Pinzani M, 2022. Hepatic fibrosis 2022: unmet needs and a blueprint for the future. Hepatology, 75(2):473–488. https://doi.org/10.1002/hep.32285
Ginès P, Krag A, Abraldes JG, et al., 2021. Liver cirrhosis. Lancet, 398(10308):1359–1376. https://doi.org/10.1016/s0140-6736(21)01374-x
Ikenaga N, Peng ZW, Vaid KA, et al., 2017. Selective targeting of lysyl oxidase-like 2 (LOXL2) suppresses hepatic fibrosis progression and accelerates its reversal. Gut, 66(9):1697–1708. https://doi.org/10.1136/gutjnl-2016-312473
Jepsen P, Younossi ZM, 2021. The global burden of cirrhosis: a review of disability-adjusted life-years lost and unmet needs. J Hepatol, 75(S1):S3–S13. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhep.2020.11.042
Jiang WQ, Tan YW, Cai MJ, et al., 2018. Human umbilical cord MSC-derived exosomes suppress the development of CCl4-induced liver injury through antioxidant effect. Stem Cells Int, 2018:6079642. https://doi.org/10.1155/2018/6079642
Kisseleva T, Brenner D, 2021. Molecular and cellular mechanisms of liver fibrosis and its regression. Nat Rev Gastroenterol Hepatol, 18(3):151–166. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41575-020-00372-7
Kostallari E, Valainathan S, Biquard L, et al., 2021. Role of extracellular vesicles in liver diseases and their therapeutic potential. Adv Drug Deliv Rev, 175:113816. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.addr.2021.05.026
Li N, Gu H, Liu L, et al., 2022. Inhibitory effects of LOXL2 knockdown on cellular functions of liver cancer stem cells. Transl Cancer Res, 11 (7):2013–2025. https://doi.org/10.21037/tcr-22-298
Li TF, Yan YM, Wang BY, et al., 2013. Exosomes derived from human umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cells alleviate liver fibrosis. Stem Cells Dev, 22(6):845–854. https://doi.org/10.1089/scd.2012.0395
Li ZH, Rana TM, 2014. Therapeutic targeting of microRNAs: current status and future challenges. Nat Rev Drug Discov, 13(8):622–638. https://doi.org/10.1038/nrd4359
Liu L, Wang P, Wang YS, et al., 2021. MiR-130a-3p alleviates liver fibrosis by suppressing HSCs activation and skewing macrophage to Ly6Clo phenotype. Front Immunol, 12: 696069. https://doi.org/10.3389/fimmu.2021.696069
Magdaleno F, Trebicka J, 2017. Selective LOXL2 inhibition: potent antifibrotic effects in ongoing fibrosis and fibrosis regression. Gut, 66(9):1540–1541. https://doi.org/10.1136/gutjnl-2016-313621
Paik JM, Golabi P, Younossi Y, et al., 2020. Changes in the global burden of chronic liver diseases from 2012 to 2017: the growing impact of NAFLD. Hepatology, 72(5):1605–1616. https://doi.org/10.1002/hep.31173
Psaraki A, Ntari L, Karakostas C, et al., 2022. Extracellular vesicles derived from mesenchymal stem/stromal cells: the regenerative impact in liver diseases. Hepatology, 75(6):1590–1603. https://doi.org/10.1002/hep.32129
Rao DY, Huang DF, Sang CP, et al., 2022. Advances in mesenchymal stem cell-derived exosomes as drug delivery vehicles. Front Bioeng Biotechnol, 9:797359. https://doi.org/10.3389/fbioe.2021.797359
Shao MY, Xu Q, Wu ZR, et al., 2020. Exosomes derived from human umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cells ameliorate IL-6-induced acute liver injury through miR-455-3p. Stem Cell Res Ther, 11:37. https://doi.org/10.1186/s13287-020-1550-0
Sohrabi B, Dayeri B, Zahedi E, et al., 2022. Mesenchymal stem cell (MSC)-derived exosomes as novel vehicles for delivery of miRNAs in cancer therapy. Cancer Gene Ther, 29(8–9):1105–1116. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41417-022-00427-8
Sun J, Tian X, Lu SQ, et al., 2017. MicroRNA-4465 suppresses tumor proliferation and metastasis in non-small cell lung cancer by dilectly targeting the oncogene EZH2. Biomed Pharmacother, 96:1358–1362. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biopha.2017.11.070
Tan YW, Huang Y, Mei R, et al., 2022. HucMSC-derived exosomes delivered BECN1 induces ferroptosis of hepatic stellate cells via regulating the xCT/GPX4 axis. Cell Death Dis, 13(4):319. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41419-022-04764-2
Toh WS, Lai RC, Zhang B, et al., 2018. MSC exosome works through a protein-based mechanism of action. Biochem Soc Trans, 46(4):843–853. https://doi.org/10.1042/bst20180079
Wang XK, Wu SL, Yang Y, et al., 2022. LncRNA CARMN affects hepatocellular carcinoma prognosis by regulating the miR-192-5p/LOXL2 axis. Oxid Med Cell Longev, 2022: 9277360. https://doi.org/10.1155/2022/9277360
Wu SF, **ng XX, Wang YH, et al., 2021. The pathological significance of LOXL2 in pre-metastatic niche formation of HCC and its related molecular mechanism. Eur J Cancer, 147:63–73. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ejca.2021.01.011
Xu YZ, Fan P, Liu L, et al., 2023. Novel perspective in transplantation therapy of mesenchymal stem cells: targeting the ferroptosis pathway. J Zhejiang Univ-Sci B (Biomed & Biotechnol), 24(2):115–129. https://doi.org/10.1631/jzus.B2200410
Yan YM, Xu WR, Qian H, et al., 2009. Mesenchymal stem cells from human umbilical cords ameliorate mouse hepatic injury in vivo. Liver Int, 29(3):356–365. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1478-3231.2008.01855.x
Yuan XQ, Li TF, Shi L, et al., 2021. Human umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cells deliver exogenous miR-26a-5p via exosomes to inhibit nucleus pulposus cell pyroptosis through METTL14/NLRP3. Mol Med, 27:91. https://doi.org/10.1186/s10020-021-00355-7
Zhang TP, Hu JJ, Wang XM, et al., 2019. MicroRNA-378 promotes hepatic inflammation and fibrosis via modulation of the NF-κB-TNFα pathway. J Hepatol, 70(1):87–96. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhep.2018.08.026
Zhang WD, Ren WZ, Han DX, et al., 2022. LncRNA-m18as1 competitively binds with miR-18a-5p to regulate follicle-stimulating hormone secretion through the Smad2/3 pathway in rat primary pituitary cells. J Zhejiang Univ-Sci B (Biomed & Biotechnol), 23(6):502–514. https://doi.org/10.1631/jzus.B2101052
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 82272421), the Jiangsu Provincial Key Research and Development Program (No. BE2021690), the Changzhou’s 14th Five-year Plan Project to Train Highlevel Health Professionals (No. 2022CZLJ027), the Scientific Project of Jiangsu Health Commission (No. Z2020038), and the Changzhou Sci & Tech Program (No. CJ20220164), China.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Yan** WANG, Yifei CHEN, and Fuji YANG contributed to investigation, validation, formal analysis, and writing–original draft. **aolong YU, Ying CHU, and **g ZHOU performed methodology and software. Jianbo XI and Yongmin YAN contributed to conceptualization, funding acquisition, and writing–review & editing. All authors have read and approved the final manuscript, and therefore, have full access to all the data in the study and take responsibility for the integrity and security of the data.
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Yan** WANG, Yifei CHEN, Fuji YANG, **aolong YU, Ying CHU, **g ZHOU, Yongmin YAN, and Jianbo XI declare that they have no conflict of interest.
All institutional and national guidelines for the care and use of laboratory animals were followed. The animal study protocol followed the ethical policies and procedures approved by the Jiangsu University Ethics Committee (Approval No. UJS-IACUC-AP-2020033127).
Additional information
Materials and methods
Detailed methods are provided in the electronic supplementary materials of this paper.
Supplementary information
Materials and methods
Electronic supplementary material
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wang, Y., Chen, Y., Yang, F. et al. MiR-4465-modified mesenchymal stem cell-derived small extracellular vesicles inhibit liver fibrosis development via targeting LOXL2 expression. J. Zhejiang Univ. Sci. B (2024). https://doi.org/10.1631/jzus.B2300305
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1631/jzus.B2300305
Key words
- Mesenchymal stem cell (MSC)
- Small extracellular vesicle (sEV)
- MicroRNA-4465 (miR-4465)
- Hepatic stellate cell (HSC)
- Liver fibrosis