Abstract
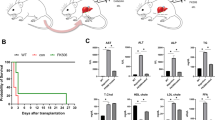
Use and effects of liver specific antigen in orthotopic liver transplantations were researched in this study. Group I: syngeneic control (Wistar-to-Wistar); Group II: acute rejection (SD-to-Wistar); Group III: Thymic inoculation of SD rat LSA day 7 before transplantation. The observation of common situation and survival time, rejection grades, NF-κB activity of splenocytes and IL-2mRNA expression of grafted liver were used to analyze acute rejection severity and immune state of animals in different groups. The common situation of group I was very well after transplantation and no signs of rejection were found. Recipients of group II lost body weight progressively All dead within day 9 to day 13 posttransplantation; median survival time was 10.7 ±0.51 days. It was an optimal acute rejection control. As for group III, 5 out of 6 recipients survived for a long time and common situation was remarkably better than that of group II. Its rejection grades were significantly lower than that of group II(P<0.05). NF-κB activity was only detected in group I at day 5 and day 7 after transplantation, whereas high activity of NF-κB was detected at all time points in groupII and the low NF-κB activity detected in group III was significantly lower than that of group II (P<0.05). No IL-2mRNA expression was detected at any time point in group I, whereas high level expression was detected at all time points in group II and the low level expression only detected at day 3 in group III was significantly lower than that of group II (P<0.05). Conclusion: LSA is an important transplantation antigen which is involved directly in the immunorejection of liver transplantation. We report here for the first time that intrathymic inoculation of LSA can alleviate the rejection of liver allotransplantation; and that grafts can survive for a long time thereby, thus leading to a novel way to achieve liver transplantation immunotolerance.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bishop, G. A., Sun, J., Sheil, A. G. and McCaughan, G. W., 1997. High-dose/activation-associated tolerance: a mechanism for allograft tolerance.Transplantation,64: 1377–1382.
Donaldson, P., Underhill, J., Doherty, D., Hayllar, K., Calne, R., Tan, K. C., O'Grady, J., Wight, D., Portmann, B. and Williams, R., 1993. Influence of human leukocyte antigen matching on liver allograft survival and rejection: “the dualistic effect”.Hepatology,17: 1008–1015.
Doran, T. J., Derley, L., Chapman, J., McCaughan, G., Painter, D., Dorney, S. and Sheil, A. G., 1992. Severity of liver transplantation rejection is associated with recipient HLA type.Transplant Proc,24: 192–193.
Kalli, K., Huntoon, C., Bell, M. and McKean, D. J., 1998. Mechanism responsible for T cell antigen receptor and CD28-or interleukin 1 (IL-1) receptor-initiated regulation of IL-2 gene expression by NF-κB.Mol cell boil,18 (6): 3140–3148.
Kamada, N. and Calne, R. Y., 1983. A surgical experience with five hundred thirty liver transplants in the rat.Surgery,93: 64–69.
Kemnitz, J., Ringe, B., Cohnert, T. R., Gubernatis, G., Choritz, H. and Georgii, A., 1989. Bile duct injury as a part of diagnostic criteria for liver allograft rejection.Hum Pathol,20(2): 132–143.
Kravchenko, V. V., Pan, Z., Han, J., Herbert, J. M., Ulevitch, R. J. and Ye, R. D., 1995. Platelet-activating factor induces NF-kappa B activation through a G protein-coupled pathway.J Biol Chem,270(25): 14928–14934.
Lau, H., Reemtsma, K. and Hardy, M. A. 1983. Pancreatic islet allograft prolongation by donor-specific blood transfusions treated with ultraviolet irradiation.Science,221(4612): 754–756.
Liblau, R. S., Tisch, R., Shokat, K., Yang, X., Dumont, N., Goodnow, C. C. and McDevitt, H. O., 1996. Intravenous injection of soluble antigen induces thymic and peripheral T-cells apoptosis.Proc Natl Acad Sci USA,93: 3031–3036.
Lohse, A. W., Meyer, Z., Buschenfelde, K. H., 1994. Experimental Hepatitis.In: Cohen IR, Miller A, eds. Autoimmune Disease Models: A Guidebook. Academic Press, San Diego, p. 191–199.
Markus, B. H., Duquesnoy, R. J., Gordon, R. D., Fung, JJ., Vanek, M., Klintmalm, G., Bryan, C., Van Thiel, D. and Starzl, T. E., 1988. Histocompatibility and liver transplant outcome. Does HLA exert a dualistic effect?Transplantation,46(3): 372–377.
Oluwole, S. F., Chowdhury, N. C. and **, M. X., 1994. The relative contribution of intrathymic inoculation of donor leukocyte subpopulations in the induction of specific tolerance.Cell Immunol,153: 163–170.
Oluwole, S. F., **, M. X., Chowdhury, N. C. and Ohajekwe, O. A., 1994. Effectiveness of intrathymic inoculation of soluble antigens in the induction of specific unresponsiveness to rat islet allografts without transient recipient immunosuppression.Transplantation,58 (10): 1077–1081.
Patric, A. B. and Devid, B., 1996. NF-κB: ten years after.Cell,87(1): 13–20.
Sharland, A., Shastry, S., Wang, C., Rokahr, K., Sun J., Sheil, A. G., McCaughan, G. W. and Bishop, G. A., 1998. Kinetics of intragraft cytokine expression, cellular infiltration, and cell death in rejection of renal allografts compared with acceptance of liver allografts in a rat model: early activation and apoptosis is associated with liver graft acceptance.Transplantation,65(10): 1370–1377.
Stadlbauer, T. H., Schaub, M., Magee, C. C., Kupiec Weglinski, J. W. and Sayegh, M. H., 2000. Intrathymic immunomodulation in sensitized rat recipients of cardiac allografts: requirements for allorecognition pathways.J Heart Lung Transplant,19(6): 566–575.
Van Antwerp, D. J., Martin, S. J., Kafri, T., Green, D. R. and Verma, I. M., 1996. Suppression of TNF-alpha-induced apoptosis by NF-kappaB.Science,274(5288): 787–789.
Yan, Y. H. and Liu, G. Z., 1998. Transplantation antigens.In: Chenshi, Transplantation Immunology. Hubei Science and Technology Press, Wuhan, p. 45–47 (in Chinese).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Project (NO. 011106206) supported by the Science and Technology Bureau of Zhejiang Province Foundation
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Jia, Ck., Zheng, Ss. & Zhang, Ab. Intrathymic inoculation of donor liver specific antigen alleviates rejection of liver allotransplantation. J. Zhejiang Univ. Sci. A 4, 485–490 (2003). https://doi.org/10.1631/jzus.2003.0485
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1631/jzus.2003.0485