Abstract
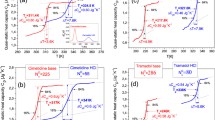
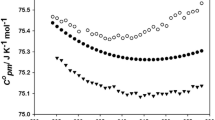
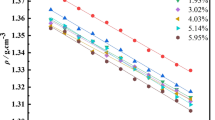
1,8-Diazabicyclo[5,4,0]undec-7-ene (DBU) was neutralized by a range of Bransted acids with a wide variation in the ΔpKa values of their constituent acids and base. The salts exhibited properties characteristic of an ionic liquid, such as high thermal stability and liquidity near ambient temperature. Analyses of thermal behaviors and temperature dependencies of density, viscosity (η), and ionic conductivity were made to correlate the physicochemical properties with the ΔpKa value of the obtained protic ionic liquids (PILs). Differential thermal analyses (DTA) revealed that PILs with high ΔpKa values underwent thermal decomposition resembling their aprotic counterparts; however, PILs with a low ΔpKa exhibited the evaporation of neutral species progressively generated from the shifting of the equilibrium toward neutral components during the weight loss process. The ionicity of the PILs, determined from Walden plots utilizing density, conductivity, and viscosity data, was found to decrease as temperature increased, and this effect was more pronounced for low ΔpKa values, possibly because of the shifting of the equilibrium and the imbalance between strong hydrogen bonds and Coulombic interactions. Fragility, estimated from plots of log(η) versus the scaled temperature Tg/T was found to be lower for PILs than for DBU owing to neutralization. [DBU]-based PILs exhibit intermediate fragility in nature, but this fragility becomes more prominent for PILs with low ΔpKa values.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
S-Y. Lee, A. Ogawa, M. Kanno, H. Nakamoto, T. Yasuda, and M. Watanabe, J. Am. Chem. Soc., 132, 9767(2010).
M. A. B. H. Susan, A. Noda, S. Mitsushima, and M. Watanabe, Chem. Commun., 2003, 938.
H. Nakamoto and M. Watanabe, Chem. Commun., 2007, 2539.
A. Noda, M. A. B. H. Susan, K. Kudo, S. Mitsushima, K. Hayamizu, and M. Watanabe, J. Phys. Chem. B, 107, 4024 (2003).
M. Yoshizawa, W. Xu, and C. A. Angell, J. Am. Chem. Soc., 125, 15411 (2003).
M. S. Miran, H. Kinoshita, T. Yasuda, M. A. B. H. Susan, and M. Watanabe, Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys., 14, 5178 (2012); Chem. Commun., 47, 12676(2011).
H. Luo, G. A. Baker, J. S. Lee, R. M. Pagni, and S. Dai, J. Phys. Chem. B, 113, 4182 (2009).
H. Tokuda, K. Hayamizu, K. Ishii, M. A. B. H. Susan, and M. Watanabe, J. Phys. Chem. B, 108, 16593 (2004); H. Tokuda, S. Tsuzuki, M. A. B. H. Susan, K. Hayamizu, and M. Watanabe J. Phys. Chem. B, 110, 19593(2006).
C. A. Angell, in “ Relaxations in Complex Systems,” edited by K. L. Ngai and G. B. Wright, NRL, Washington D. C., 1985, p. 3.
K. Ueno, Z. Zhao, M. Watanabe, and C. A. Angell, J. Phys. Chem. B., 116, 63 (2012).
K. Ueno, H. Tokuda, and M. Watanabe, Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys., 12, 1649 (2010).
H. Kashyap, H. Annapureddy, and C. Margulis, J. Phys. Chem. B., 115, 13212 (2011).
L-M. Wang, C. A. Angell, and R. Richert, J. Chem. Phys., 125, 74506 (2006).
J.-P. Belieres and C. A. Angell, J. Phys. Chem. B, 111, 4936 (2007).
Acknowledgments
This research was supported by a NEDO Technology Research Grant.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Miran, M.S., Kinoshita, H., Yasuda, T. et al. Protic Ionic Liquids Based on a Super-Strong Base: Correlation between Physicochemical Properties and ΔpKa. MRS Online Proceedings Library 1473, 1–6 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1557/opl.2012.1133
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1557/opl.2012.1133