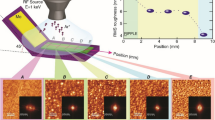
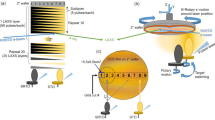
Abstract
Ion-beam sputtering (IBS) has been studied as a means for scalable, mask-less nanopatterning of surfaces. Patterning at the nanoscale has been achieved for numerous types of materials including: semiconductors, metals and insulators. Although much work has been focused on tailoring nanopatterning by systematic ion-beam parameter manipulation, limited work has addressed elucidating on the underlying mechanisms for self-organization of multi-component surfaces. In particular there has been little attention to correlate the surface chemistry variation during ion irradiation with the evolution of surface morphology and nanoscale self-organization. Moreover the role of surface impurities on patterning is not well known and characterization during the time-scale of modification remains challenging. This work summarizes an in-situ approach to characterize the evolution of surface chemistry during irradiation and its correlation to surface nanopatterning for a variety of multi-components surfaces. The work highlights the importance and role of surface impurities in nanopatterning of a surface during low-energy ion irradiation. In particular, it shows the importance of irradiation-driven mechanisms in GaSb(100) nanopatterning by low-energy ions and how the study of these systems can be impacted by oxide formation.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
J. Erlebacher and M. J. Aziz, Phys. Rev. Lett. 82, 2330 (1999).
S. Fascko, T. Dekorsy, C. Koerdt, C. Trappe, H. Kurz, A, Vogt, H. L. Hartnagel, Science 285, 1551 (1998).
T. Bobek, S. Facsko, H. Kurz, T. Dekorsy, M. Xu, and C. Teichert, Phys. Rev. B 68, 085324 (2003).
B. Ziberi, F. Frost, B. Rauschenbach, and Th. Hoche, Appl. Phys. Lett. 87, 033113 (2005).
F. Frost, B. Ziberi, A Schindler, and B. Rauschenbach, Appl. Phys. A 91, 551 (2008).
M. Cornejo, J. Völlner, B. Ziberi, F. Frost and B. Rauschenbach, Fabrication and Characterization in the Micro-Nano Range, in Advanced Structured Materials, 10, Ed. F.A. Lasagni, A.F. Lasagni, Springer-Verlag Berlin, Heidelberg 2011. pp 69–94
J. P. Allain, M. Nieto, M. R. Hendricks, P. Plotkin, S. S. Harilal, and A. Hassanein, Rev. Sci. Instrum. 78, 113105 (2007).
G. Hou, MS Thesis 2010, Purdue University, advisor: J.P. Allain.
O. El-Atwani, J.P. Allain, S. Ortoleva, Nucl. Instrum. Method. B, In Press 2011, doi:10.1016/j.nimb.2011.01.067.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Allain, J.P., El-Atwani, O., Cimaroli, A. et al. Study of scalable IBS nanopatterning mechanisms for III-V semiconductors using in-situ surface characterization. MRS Online Proceedings Library 1354, 203 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1557/opl.2011.1458
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1557/opl.2011.1458