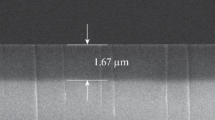
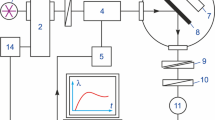
Abstract
Spectroscopic ellipsometry (SE) is a powerful optical tool for non-destructively depth-profiling the dielectric function of samples with a resolution in the Ångstrom range. In this work, the characterization of graded composition layers in transparent materials by SE is described. In modeling studies on the sensitivity limits of the technique, it has been shown that for known index profile shapes, the depth sensitivity can be quite high. For example, diffusion of Na2O into the surface of a vitreous silica sample can be detected for layers as thin as 100Å when the maximum refractive index contrast is only 0.005. The sensitivity of the technique increases as the diffusion depth and refractive index contrast increases. The accuracy of the thickness determination depends on the total thickness of the graded layer; for a given system, the accuracy of the composition measurements do not depend on the surface concentration. Leached alkali-aluminosilicate and modified lead silicate glasses were examined by SE to experimentally confirm the modeling predictions on the composition depth profiling. Extremely good correlation between the SE-determined depth profile and SIMS measurements on similar samples was obtained for the case of the modified lead silicate glass. For the aluminosilicate glass, simultaneous roughening of the glass surface during etching makes composition profiling more difficult.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
A. R. Heyd, Spectroscopic Ellipsometry and its Application to III-V Semiconductors, Ph. D. Thesis, The Pennsylvania State University (1993).
P. G. Snyder, M. C. Rost, G. H. Bu-Abbud, J. A. Woolam, and S. A. Alterovitz, J. Appl. Phys. 60 3293 (1986).
M. Fried, T. Lohner, W. A. M. Aamink, L. J. Hanekamp, and A. Van Silfhout, J. Appl. Phys. 71 2835 (1992).
J. Koh, The Sensitivity Limits of Spectroscopic Ellipsometry for the Characterization of Optical Coatings. M.S. Thesis, The Pennsylvania State University, (1995).
D. V. Mazurin, S. Shvaikovskaya, and M. V. Streltsina, Handbook of Glass Data. Part A. (Elsevier, New York, 1985)
N. P. Bansal and R. H. Doremus, Handbook of Glass Properties. (Academic Press, Orlando, 1986)
I. H. Malitson, J. Opt. Soc. Am. 55 1205 (1965).
A. D’Souza and C. G. Pantano, manuscript accepted by Phys. Chem. Glasses.
Acknowledgments
The support of the National Science Foundation through contract DMR-9308332 is gratefully acknowledged.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Trolier-Mckjnstry, S., Koh, J. Composition Profiling of Graded Dielectric Function Materials by Spectroscopic Ellipsometry. MRS Online Proceedings Library 411, 185–190 (1995). https://doi.org/10.1557/PROC-411-185
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1557/PROC-411-185