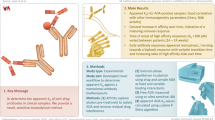
Abstract
Non-neutralizing anti-idiotype antibodies against a therapeutic monoclonal antibody (mAb) play a crucial role in the creation of total pharmacokinetic (PK) assays and total target engagement (TE) assays during both pre-clinical and clinical development. The development of these anti-idiotype antibodies is challenging. In this study, we utilized a hybridoma platform to produce a variety of anti-idiotype antibodies against GSK2857914, a humanized IgG1 anti-BCMA monoclonal antibody. The candidate clones were evaluated using surface plasmon resonance (SPR) and bio-layer interferometry (BLI) for binding affinity, binding profiling, matrix interference, and antibody pairing determination. We discovered that three anti-idiotype antibodies did not prevent BCMA from binding to GSK2857914. All three candidates demonstrated high binding affinities. One of the three exhibited minimal matrix inference and could pair with the other two candidates. Additionally, one of the three clones was biotinylated as a capture reagent for the total PK assay, and another was labeled with ruthenium as a detection reagent for both the total PK assay and total TE assay. The assay results clearly show that these reagents are genuine non-neutralizing anti-idiotypic antibodies and are suitable for total PK and TE assay development. Based on this and similar studies, we conclude that the hybridoma platform has a high success rate for generating non-neutralizing anti-idiotype antibodies. Our methodology for develo** and characterizing non-neutralizing anti-idiotype antibodies to therapeutic antibodies can be generally applied to any antibody-based drug candidate’s total PK and total TE assay development.
Graphical Abstract








Similar content being viewed by others
References
Nelson AL, Dhimolea E, Reichert JM. Development trends for human monoclonal antibody therapeutics. Nat Rev Drug Discov. 2010;9(10):767–74. https://doi.org/10.1038/nrd3229.
Nissim A, Chernajovsky Y. Historical development of monoclonal antibody therapeutics. Handb Exp Pharmacol. 2008;181:3–18. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-540-73259-4_1.
Mahmood I, Green MD. Pharmacokinetic and pharmacodynamic considerations in the development of therapeutic proteins. Clin Pharmacokinet. 2005;44(4):331–47. https://doi.org/10.2165/00003088-200544040-00001.
Roskos LK, Schneider A, Vainshtein I, Schwickart M, Lee R, Lu H, et al. PK-PD modeling of protein drugs: implications in assay development. Bioanalysis. 2011;3(6):659–75. https://doi.org/10.4155/bio.11.28.
DeSilva B, Smith W, Weiner R, Kelley M, Smolec J, Lee B, et al. Recommendations for the bioanalytical method validation of ligand-binding assays to support pharmacokinetic assessments of macromolecules. Pharm Res. 2003;20(11):1885–900. https://doi.org/10.1023/b:pham.0000003390.51761.3d.
Chin SE, Ferraro F, Groves M, Liang M, Vaughan TJ, Dobson CL. Isolation of high-affinity, neutralizing anti-idiotype antibodies by phage and ribosome display for application in immunogenicity and pharmacokinetic analyses. J Immunol Methods. 2015;416:49–58. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jim.2014.10.013.
Goodman J, Agoram B. Analytical assay platforms for soluble target engagement biomarkers: old favorites and emerging technologies. Bioanalysis. 2013;5(23):2919–31. https://doi.org/10.4155/bio.13.262.
Zheng S, McIntosh T, Wang W. Utility of free and total target measurements as target engagement and efficacy biomarkers in biotherapeutic development–opportunities and challenges. J Clin Pharmacol. 2015;55(Suppl 3):S75-84. https://doi.org/10.1002/jcph.357.
Lee JW, Kelley M, King LE, Yang J, Salimi-Moosavi H, Tang MT, et al. Bioanalytical approaches to quantify “total” and “free” therapeutic antibodies and their targets: technical challenges and PK/PD applications over the course of drug development. AAPS J. 2011;13(1):99–110. https://doi.org/10.1208/s12248-011-9251-3.
Fairman D, Tang H. Best practices in mAb and soluble target assay selection for quantitative modelling and qualitative interpretation. AAPS J. 2023;25(1):23. https://doi.org/10.1208/s12248-023-00788-4.
Liang M, Klakamp SL, Funelas C, Lu H, Lam B, Herl C, et al. Detection of high- and low-affinity antibodies against a human monoclonal antibody using various technology platforms. Assay Drug Dev Technol. 2007;5(5):655–62. https://doi.org/10.1089/adt.2007.089.
Staack RF, Stracke JO, Stubenrauch K, Vogel R, Schleypen J, Papadimitriou A. Quality requirements for critical assay reagents used in bioanalysis of therapeutic proteins: what bioanalysts should know about their reagents. Bioanalysis. 2011;3(5):523–34. https://doi.org/10.4155/bio.11.16.
Tornetta M, Fisher D, O’Neil K, Geng D, Schantz A, Brigham-Burke M, et al. Isolation of human anti-idiotypic antibodies by phage display for clinical immune response assays. J Immunol Methods. 2007;328(1–2):34–44. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jim.2007.08.008.
Lowe DC, Gerhardt S, Ward A, Hargreaves D, Anderson M, Ferraro F, et al. Engineering a high-affinity anti-IL-15 antibody: crystal structure reveals an alpha-helix in VH CDR3 as key component of paratope. J Mol Biol. 2011;406(1):160–75. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmb.2010.12.017.
Groves MA, Nickson AA. Affinity maturation of phage display antibody populations using ribosome display. Methods Mol Biol. 2012;805:163–90. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-1-61779-379-0_10.
Kohler G, Milstein C. Continuous cultures of fused cells secreting antibody of predefined specificity. Nature. 1975;256(5517):495–7. https://doi.org/10.1038/256495a0.
An Y, Zhang Y, Mueller HM, Shameem M, Chen X. A new tool for monoclonal antibody analysis: application of IdeS proteolysis in IgG domain-specific characterization. MAbs. 2014;6(4):879–93. https://doi.org/10.4161/mabs.28762.
Kilpatrick KE, Wring SA, Walker DH, Macklin MD, Payne JA, Su JL, et al. Rapid development of affinity matured monoclonal antibodies using RIMMS. Hybridoma. 1997;16(4):381–9. https://doi.org/10.1089/hyb.1997.16.381.
Caterson B, Christner JE, Baker JR. Identification of a monoclonal antibody that specifically recognizes corneal and skeletal keratan sulfate. Monoclonal antibodies to cartilage proteoglycan. J Biol Chem. 1983;258(14):8848–54.
Hendriks J, Schasfoort RBM, Huskens J, Saris DF, Karperien M. Kinetic characterization of SPR-based biomarker assays enables quality control, calibration free measurements and robust optimization for clinical application. Anal Biochem. 2022;658: 114918. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ab.2022.114918.
Carle K, Kellie JF, Gunn GR, Jiang Y. Determination of label efficiency and label degree of critical reagents by LC-MS and native MS. Anal Biochem. 2023;664: 115033. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ab.2022.115033.
Oquendo E, Lin X, Ye S, Coble K, Grimaldi C. Using multiple platforms for critical reagents selection process to support pharmacokinetic ligand-binding assay development. Bioanalysis. 2021;13(10):761–9. https://doi.org/10.4155/bio-2020-0257.
Bio-Rad Ready-made Anti-Biotherapeutic Antibodies 2023. Antibodies for Bioanalysis & Drug Monitoring | Bio-Rad. https://www.bio-rad-antibodies.com/biotherapeutic-antibodies-bioanalysis-drug-monitoring.html?
Funding
This study was sponsored by GSK., Upper Providence, PA, USA.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
All authors listed have made a substantial, direct, and intellectual contribution to the work (writing, review, and editing) and approved it for publication.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing Interests
The research was supported by GSK Research and Development. The authors are employees of GSK and may be eligible for GSK stock options or have stock ownership. The authors have no other relevant affiliations or financial involvement with any organization or entity with a financial interest in or financial conflict with the subject matter or materials discussed in the manuscript apart from those disclosed.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Liu, V., McGrath, K., Albert, J. et al. Screening Non-neutralizing Anti-idiotype Antibodies Against a Drug Candidate for Total Pharmacokinetic and Target Engagement Assay. AAPS J 26, 18 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1208/s12248-024-00892-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1208/s12248-024-00892-z