Abstract
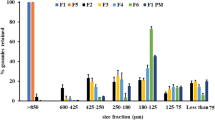
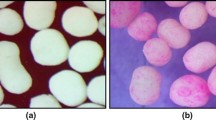
Amelt solidification technique has been developed to obtain sustained-release waxy beads of flurbiprofen. Low glass transition temperature (t g) and shear-induced crystallization of flurbiprofen made it a suitable candidate for melt solidification technique. The process involved emulsification and solidification of flurbiprofen-cetyl alcohol melt at significantly low temperature (5°C). The effect of variables, namely, the amount of cetyl alcohol and the speed of agitation, was studied using 32 factorial design. The technique and the beads were evaluated on the basis of process and desired yield, surface topography, Fourier-transform infrared (FT-IR), differential scanning calorimetry (DSC), particle size distribution, crushing strength, and drug release. Average values for process and desired yields were 97% wt/wt and 26% wt/wt, respectively. No interaction was observed between drug and excipient. Multiple regression analysis was carried out, and response surfaces were obtained. A curvilinear relationship was observed between percentage of desired yield and the amount of cetyl alcohol. Linear decrease in crushing strength was observed with increase in the amount of cetyl alcohol. Drug released from the beads followed zero order kinetics. Burst release was shown to a greater extent in beads containing a lower amount of cetyl alcohol. Response surfaces of time required for certain percentage of drug (t D%) showed that after critical concentration of about 20% of cetyl alcohol (400 mg/batch), no significant release retardant effect was observed.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bodmeier R, Wang J, Bhagwatwar, H. Process and formulation variables in the preparation of wax microparticles by melt dispersion technique for water insoluble drugs.J Microcapsul. 1992;9:89–98.
Schaefer T, Holm P, Kristensen HG. Melt granulation in a laboratory scale high shear mixer.Drug Dev Ind Pharm. 1990;16:1249–1277.
Nadia P, Beatrice A, Cristina C, Lorenzo R. Preparation and characterisation of iburprofen-poloxamer 188 granules obtained by melt granulation.Eur J Pharm Sci. 2002;15:71–78.
Gokonda SR, Hileman GA, Upadrastha SM. Development of matrix controlled release beads by extrusion-spheronozation techniques technology using a statistical screening design.Drug Dev Ind Pharm. 1994;20:279–292.
Kim JW, Ulrich J. Prediction of degree of deformation and crystallization time of molten droplets in pastillations process.Int J Pharm. 2003;257:205–215.
Barthelemy P, Laforet JP, Farah N, Joachim J. Compritol 888 ATO: an innovative hot melt coating agent for prolonged drug formulations.Eur J Pharm Biopharm. 1999;47:87–90.
Adeyeye CM, Price JC. Development and evaluation of sustained release ibuprofen-wax microspheres I: effect of formulation variables on physical characteristics.Pharm Res. 1991;8:1377–1383.
Adeyeye CM, Price JC. Development and evaluation of sustained release ibuprofen-wax microspheres II: in vitro dissolution studies.Pharm Res. 1994;11:575–579.
Paradkar AR, Maheshwari M, Ketkar AR, Chauhan B. Preparation and evaluation of ibuprofen beads by melt solidification techniques.Int J Pharm. 2003;255:33–42.
Maheshwari M, Ketkar AR, Chauhan B, Patil VB, Paradkar AR. Preparation and characterization of ibuprofen-cetyl alcohol beads by melt solidification technique: effect of variables.Int J Pharm. 2003;261:57–67.
Gilman AG, Rall TW, Taylor P.Goodman and Gillman's the Pharmacological Basis of Therapeutics. New York, NY: Pergamon Press, 1990.
Jarosz PJ, Parrott EJ. Comparison of granule strength and tablet strength.J Pharm Sci. 1983;72:530–535.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Paradkar, A., Maheshwari, M., Tyagi, A.K. et al. Preparation and characterization of flurbiprofen beads by melt solidification technique. AAPS PharmSciTech 4, 65 (2003). https://doi.org/10.1208/pt040465
Received:
Accepted:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1208/pt040465