Abstract
Background
Ureteral atresia is the congenital absence of a ureteral opening, resulting in a blind-ended ureter that fails to terminate at the urinary bladder. Consequently, severe hydroureter and hydronephrosis occur ipsilateral to the atresic ureter. However, hydronephrosis contralateral to severe hydroureter, although reported in humans, is not documented in the dog. Additionally, ureteral atresia has not been reported as a cause for lower urinary tract signs directly related to extramural urinary bladder compression. This report aims to describe these unique manifestations of this congenital urinary tract disease, as well as follow-up findings after successful treatment.
Case presentation
A 4-month-old male Husky puppy was evaluated for pollakiuria, stranguria, and urine dribbling of 1-month duration. During the physical examination, a mass was palpated in the mid-abdomen. Diagnostic imaging and cystoscopy findings were diagnostic for right-sided ureteral atresia with secondary hydroureter and hydronephrosis. The severe right hydroureter caused lower urinary tract signs and contralateral hydronephrosis secondary to regional compression of the left distal ureter and urinary bladder. A right-sided ureteronephrectomy was performed, resolving the stranguria and pollakiuria. Significant reduction in the contralateral (left) hydronephrosis also occurred.
Clinical Relevance
Ureteral atresia should be considered as a differential diagnosis for lower urinary tract signs and/or bilateral hydronephrosis in a young dog. Reporting this case expands our knowledge of congenital lower urinary tract disease and the etiology of their manifestations in dogs. Surgical resolution of the congenital ureteral abnormality can result in preservation of renal function in the contralaterally obstructed kidney.
Similar content being viewed by others
Background
Congenital ureteral anatomic anomalies causing obstructive hydroureter and hydronephrosis are rare in veterinary small animal patients, with various etiologies reported [1,2,3,4,5,6,7,8,9,10]. Ureteral atresia, one such anomaly, is the absence of a ureteral opening that results in a blind-ended ureter failing to terminate at the urinary bladder [11]. Hydroureter, hydronephrosis, and a loss in function of the ipsilateral kidney occur secondary to the obstruction. Only one case of ureteral atresia has been recorded in the veterinary literature to date [1].
In humans, hydroureter is a reported cause of contralateral ureteral obstruction and bilateral hydronephrosis; however, to the authors’ knowledge, this has not been reported in the dog [12, 13]. Hydroureter due to ureteral atresia has also not been reported to cause lower urinary tract signs due to extramural urinary bladder compression. In the present case study, we describe both bilateral hydronephrosis and lower urinary tract signs related to ureteral atresia-induced hydroureter in a puppy. We also describe appropriate treatment and follow up for this condition.
Case presentation
A 4-month-old, male intact Siberian Husky weighing 11.8 kg was evaluated because of a 1-month history of stranguria, pollakiuria, and urine dribbling. One week prior to presentation, the referring veterinarian prescribed enrofloxacinFootnote 1 5.8 mg/kg PO q24h for treatment of a lower urinary tract infection diagnosed after finding isosthenuria (specific gravity 1.012) and leukocytes on free-catch dipstick urinalysis. Despite this therapy, the lower urinary tract signs persisted and the dog was referred for evaluation (visit #1).
On physical examination, the dog had a distended abdomen and palpable mid-abdominal mass. Urination resulted in either a weak broken urine stream or infrequent urine dribbling. Hematology and biochemistry yielded no clinically significant abnormalities (creatinine 0.61 mg/dL; reference range, 0.70–1.30 mg/dL). A urine culture was negative for bacterial growth, presumptively due to recent antibiotic administration. Abdominal ultrasonography revealed a 6.2 × 7.8 cm fluid-filled structure consistent with hydronephrosis of the right kidney and severe dilation of the left renal pelvis (1.3 cm; reference range, < 4.0 mm) [14], right ureter (5.5 cm; reference range, < 1.8 mm) [15], and left ureter (1.3 cm; reference range, < 1.8 mm) [15] (Fig. 1a-d). Neither ureter was visualized entering the urinary bladder. A diagnosis of bilateral hydronephrosis and hydroureter, worse on the right was made; however, no cause was identified. Pending availability to perform additional diagnostics, the dog was discharged to return 17 days later. Enrofloxacin was continued at the same dose and frequency as prescribed by the referring veterinarian.
Abdominal ultrasound findings for a dog with distal ureteral atresia. a Sagittal view of the right kidney showing a complete loss of renal architecture. b Transverse view of the right ureter showing severe dilation. c Sagittal view of the left kidney showing severe dilation of the renal pelvis. d Transverse view of the left ureter showing severe dilation1
At the follow-up evaluation (visit #2), the dog’s lower urinary tract signs persisted of similar severity to visit #1. A recheck ultrasound of the urinary tract revealed progressive hydronephrosis of the right kidney and progressive dilation of the left renal pelvis, right ureter, and left ureter. Suspecting persistent bilateral obstructive disease, an abdominal computed tomography (CT) scanFootnote 2 was performed. It confirmed similar changes to the kidneys and ureters as demonstrated on ultrasound; however, it additionally identified an abrupt, blind ended termination of the right ureter lacking patency with the urinary bladder and extramural compression of the left distal ureter and urinary bladder by the right, severe hydroureter (Fig. 2a-d). No contrastFootnote 3 was excreted by the right kidney. Following the CT scan, a 3.1 mm, 30° rigid cystoscopeFootnote 4 was used to diagnose a left-sided intramural ectopic ureter and an absent right ureteral orifice via a perineal approach as previously described [16]. These findings were consistent with right-sided distal ureteral atresia and hydroureter resulting in extramural compression of the contralateral (left) ureter and urinary bladder. The result of this congenital ureteral abnormality was bilateral hydronephrosis and lower urinary tract signs. Following these procedures, the dog was discharged pending a right-sided ureteronephrectomy. The enrofloxacin, administered for 24 days with no improvement in lower urinary tract signs nor imaging findings, was discontinued.
Abdominal computed tomography findings for a dog with distal ureteral atresia. a Sagittal view showing blind-ended termination of the right ureter (black arrowhead). Secondary hydronephrosis (black star) and hydroureter (pound sign) is also present. b Dorsal view showing compression (white arrowhead) of the urinary bladder (white star) by the dilated atresic ureter (pound sign) and hydronephrotic kidney (black star). The blind-ended termination of the right ureter (black arrowhead) is also present. c Sagittal view showing compression (white arrow) of the left distal ureter (black asterisk) by the dilated atresic ureter (pound sign) and hydronephrotic kidney (black star). d Transverse view showing compression (white arrowhead and arrow) of the left distal ureter (black asterisk) and urinary bladder (white star) by the dilated atresic ureter (pound sign)
Twenty-four hours following discharge, the dog re-presented for inability to urinate. Serum creatinine was within reference interval (0.71 mg/dL; reference range, 0.70–1.30 mg/dL). A red rubber urinary catheter was passed into the urethra with ease and 1100 milliliters of serosanguinous urine containing blood clots was removed from the urinary bladder. A fluoroscopic-assistedFootnote 5 retrograde contrast3 urethrogram revealed an intraluminal filling defect in the pelvic urethra. Flexible urethroscopy performed immediately thereafter using a 2.8 mm ureteroscope4 confirmed mucosal damage and secondary fibrin tags resulting in occlusion of the pelvic urethra, likely iatrogenic from the rigid cystoscopy. An indwelling Foley urinary catheter was placed to allow for urethral healing and clearance of blood clots from the urinary bladder.
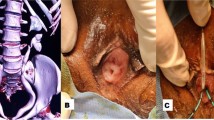
Two days later, a right-sided ureteronephrectomy was performed (Fig. 3). Following a fast overnight, the dog was premedicated with midazolamFootnote 6 0.2 mg/kg IM and hydromorphoneFootnote 7 0.1 mg/kg IM to facilitate intravenous catheter placement. Induction was performed with propofolFootnote 8 3 mg/kg IV to effect. Following endotracheal intubation, the dog was maintained on isoflurane in 100 % oxygen with a fentanylFootnote 9 continuous rate infusion (CRI) at 10 µg/kg/hr. and lactated Ringer’s solution at 5 mL/kg/hr. Anesthetic monitoring included electrocardiography, capnography, pulse oximetry, fractional expired isoflurane, fractional inspired oxygen percentage, and direct arterial blood pressure. Several episodes of systemic hypotension occurred, each responding favorably to a 5 mL/kg bolus of IV fluids.
Intraoperatively, the right ureter was severely distended, resulting in extramural compression and displacement of the urinary bladder (Fig. 4). Additionally, there was no patent connection between the right ureter and urinary bladder, as the blind-ended termination of the ureter was attached via fibrous adhesions to the peritoneum (Fig. 4). Removal of the right kidney and ureter occurred without complication. Postoperative management consisted of lactated Ringer’s solution at 60 mL/kg/day and a fentanyl CRI at 3 µg/kg/hr. Twenty-four hours following surgery, the dog was eating well and pain was well-controlled, prompting transition to acetaminophen with codeineFootnote 10 1 mg/kg PO q8h. The indwelling urinary catheter was left in place for five days following surgery to allow for continued urethral healing. Within six hours following urinary catheter removal, the dog produced a strong, continuous urine stream. No stranguria or pollakiuria were noted. The dog was monitored in-hospital for another twenty-four hours, again during which no stranguria or pollakiuria were reported. The dog was discharged one week after the presentation for urethral obstruction.
Grossly, the right kidney consisted of a thick capsule with no discernable renal tissue and a markedly dilated right ureter that ended in a blind sac. Histologically, the right kidney had scant isolated renal tubules surrounded by haphazardly arranged fibrous tissue and small to moderate numbers of neutrophils and plasma cells. The right ureter had a similar cellular infiltrate as the kidney, with the addition of a diffusely hypertrophied tunica muscularis. The distal blind-ended portion of the ureter contained smooth muscle fibers, confirming ureteral tissue origin. Both gross and microscopic findings were diagnostic of distal ureteral atresia with secondary hydroureter and hydronephrosis. Bacterial cultures of the urine, surgically removed kidney, and fluid within the right hydronephrotic kidney were negative.
At a follow-up recheck four months later (visit #3), the dog was urinating a strong urine stream, with no pollakiuria or stranguria noted. Again, serum creatinine remained within reference interval (0.67 mg/dL; reference range, 0.70–1.30 mg/dL). However, the dog was intermittently dribbling urine, likely the result of the left ectopic ureter. Recheck abdominal ultrasound revealed persistent, but vastly improved left hydronephrosis (6.4 mm; reference range, < 4.0 mm) and hydroureter (4.0 mm; reference range, < 1.8 mm) [14, 15] (Fig. 5a-b). Correction of the left ectopic ureter was not attempted because of the mild nature of the incontinence and owner decision. Now nineteen months after surgery, the dog continues to urinate without stranguria and pollakiuria, and serum creatinine remains within reference interval.
Discussion and conclusions
Ureteral atresia is the congenital absence of a ureteral opening, resulting in a blind-ended ureter that terminates adjacent to the urinary bladder [11]. This anatomical anomaly produces a ureteral obstruction that leads to hydronephrosis, hydroureter, and loss of function of the kidney ipsilateral to the lesion. Ureteral atresia is rare in dogs, as the authors are aware of only one other case being reported [1]. The dog described in that report had right sided hydronephrosis and hydroureter due to distal ureteral atresia with a normal appearing contralateral kidney and ureter. Unique to the dog in this report is obstruction of the contralateral ureter with subsequent hydronephrosis as a result of the dilated atresic ureter. Ureteral obstruction leading to hydronephrosis as a consequence of contralateral hydroureter is also rare in humans [12, 13]. Of clinical importance in the human cases and this report, ureteronephrectomy of the atresic ureter and associated hydronephrotic kidney resulted in a significant reduction of hydronephrosis in the contralateral kidney and preservation of renal function [12, 13].
Like in dogs, ureteral atresia is a rare congenital urinary tract abnormality in humans. It tends to be unilateral, occur most commonly in the distal ureter, be associated with a dysplastic or non-functioning kidney, and diagnosed at a young age [17,18,19,20,21,22]. Although the exact cause is unclear, ureteral atresia is hypothesized to result from ischemic injury to the develo** ureter or a genetic failure of tissue differentiation [23, 24]. During embryological development, the ureter arises from the ureteric bud, the latter of which originates from the mesonephric duct [25]. During ureteral growth, canalization is crucial for the establishment of ureteral patency [25]. Atresia results when this ureteral patency fails to occur, presumably due to one of the aforementioned hypothesized causes. Although the etiology of ureteral atresia in dogs is also uncertain, the numerous similarities between this case and that described in humans would make a common underlying cause plausible [17,18,19,20,21,22]. In this dog, it is unknown if the right kidney was non-functional due to progressive hydronephrosis or true dysplasia; however, the lack of fetal glomeruli and immature tubules make the latter less likely.
Congenital ureteral anatomic anomalies causing obstructive hydronephrosis and hydroureter are rare in veterinary small animal patients. Reported etiologies include duplication, atresia, stricture, stenosis, circumcaval ureter, and ectopic ureter [1,2,3,4,5,6,7,8,9,10]. Classic lower urinary tract clinical signs of hematuria, pollakiuria, and stranguria, when present, were the result of a bacterial lower urinary tract infection [3, 5]. Conversely, the etiology of the lower urinary tract signs in this case was unique, resulting from extramural compression of the urinary bladder by the markedly dilated atresic ureter. The questionable urinary tract infection diagnosis, lack of improvement in clinical signs following extensive (24 days) preoperative antibiotic therapy, negative urine culture during antibiotic treatment, and preoperative ultrasound and CT scan findings provide strong supportive evidence for urinary bladder compression as the cause for the stranguria and pollakiuria reported. Lastly, lower urinary tract clinical signs appear to be uncommon manifestations with any of the congenital urinary tract anatomic abnormalities in small animals [1, 2, 4,5,6,7,8,9].
The decision to pursue ureteronephrectomy was multifactorial, based primarily on the etiology of the lower urinary tract signs as delineated by CT imaging of the abdomen. Additionally, a lack of discernible renal tissue on ultrasound and contrast uptake following CT indicated negligible function remaining in the right kidney. Lastly, surgical removal of the kidney and ureter is the primary treatment modality in humans with ureteral atresia [17, 19, 21, 22], especially if the hydroureter is causing contralateral ureteral obstruction [12, 13]. The rapid resolution of lower urinary tract signs and substantial reduction in contralateral hydronephrosis indicate that surgical removal was the most appropriate clinical decision. The dog, nineteen months following surgery, continues to have a normal serum creatinine value and be lower urinary tract sign free.
In addition to ureteral atresia, a left-sided ectopic ureter was present and likely accounted for the urine dribbling in this dog. Though there was a significant reduction of the left hydroureter and hydronephrosis following surgery, the lack of resolution is explained by the uncorrected ectopic ureter [8, 9]. Ideally, correction of this ectopic ureter would have been pursued; however, owner election against this prevented it from occurring. Furthermore, the dog’s urinary incontinence was very mild.
We acknowledge several potential limitations of this case report. It can be argued that the dog’s lower urinary tract signs were the result of a urinary tract infection and that the upper urinary tract manifestations of hydroureter and hydronephrosis improved on the visit #3 imaging as a result of treatment for an ascending bacterial infection (pyelonephritis). Although possible, we feel these explanations for the findings that make this case report novel are less likely for several reasons. First, the urinary tract infection diagnosis is unconvincing, as it is based solely on the presence of leukocytes found on a free-catch urine dipstick sample. Second, the lower urinary tract signs did not improve despite a duration (24 days) of antibiotic therapy that would be considered sufficient to see improvement in clinical signs. Additionally, the negative urine culture one week into the antibiotic treatment indicated that the enrofloxacin therapy was adequate to sterilize the urine, thus appropriately treating any potential bacterial infection present. Third, dilation of the contralateral (left) kidney and ureter worsened on the visit #2 preoperative ultrasound images following 24 days of antibiotic treatment. Finally, the dog displayed no systemic signs (i.e. lethargy, fever, anorexia) nor had blood work abnormalities (i.e. inflammatory leukogram, renal azotemia) consistent with an ascending infection. In totality, although we cannot exclude the possibility of a concurrent urinary tract infection, these reasons make an infection involving both the lower and upper urinary tract an unlikely contributor to the unique manifestations occurring secondary to the atresic right ureter in this case report.
This is the first case report in any animal species of a congenital ureteral anatomic abnormality causing lower urinary tract signs and contralateral ureteral obstruction and hydronephrosis due to extramural compression of the contralateral ureter and urinary bladder. This report expands our understanding of congenital lower urinary tract disease in dogs; albeit rare, this abnormality is an important differential diagnosis in a young dog with bilateral hydronephrosis and lower urinary tract signs, especially if a bacterial urinary tract infection has been ruled out. Furthermore, this case demonstrates that ureteronephrectomy represents a viable long-term treatment option, despite contralateral hydronephrosis being a sequalae of the original anatomic abnormality. Lastly, the diagnostic workup in this case illustrates how CT is becoming incrementally more important for in the diagnosis and treatment of some congenital urogenital diseases.
Availability of data and materials
All data generated or analyzed during this study are included in this published article.
Notes
Baytril®, Bayer Healthcare, Shawnee Mission, Kansas
Toshiba Aquilon 16, Toshiba American Medical Systems, Tustin, California
Omnipaque 300 mgI/mL, GE Healthcare, Marlborough, Massachusetts
Karl Storz Endoscopy-America, El Segundo, California
CombiDiagnost R90, Philips Medical Systems, Nashville, Tennessee
Versed®, West-Ward Pharmaceutical, Eatontown, New Jersey
Dilaudid®, Hospira, Lake Forest, Illinois
Diprivan®, Zoetis, Kalamazoo, Michigan
Sublimaze®, Hospira, Lake Forest, Illinois
Tylenol® with Codeine 3, Janssen Pharmaceutical, Titusville, New Jersey
Abbreviations
- PO:
-
Per os
- CT:
-
Computed tomography
- IM:
-
Intramuscular
- IV:
-
Intravenous
- CRI:
-
Continuous rate infusion
References
Rousset N, Abbondati E, Posch B, Owen LJ, Herrtage M. Unilateral hydronephrosis and hydroureter secondary to ureteric atresia, and uterus unicornis in a young terrier. J Small Anim Pract. 2011;52:441–44.
Zotti A, Poser H, Chiavegato D. Asymptomatic double ureteral stricture in an 8-month-old Maine Coon cat: an imaging-based case report. J Feline Med Surg. 2004;6:371–75.
Esterline ML, Biller DS, Sicard GK. Ureteral duplication in a dog. Vet Radiol Ultrasound. 2005;46:485–89.
Pullium JK, Dillehay DL, Webb S, Pinter MJ. Congenital bilateral ureteral stenosis and hydronephrosis in a neonatal puppy. Contemp Top Lab Anim Sci. 2000;39:34–6.
Lam NK, Berent AC, Weisse CW, Bryan C, Mackin AJ, Bagley DH. Endoscopic placement of ureteral stents for treatment of congenital ureteral stenosis in a dog. J Am Vet Med Assoc. 2012;140:983–90.
Doust RT, Clarke SP, Hammond G, Paterson C, King A. Circumcaval ureter associated with an intrahepatic portosystemic shunt in a dog. J Am Vet Med Assoc. 2006;228:389–91.
D’Ippolito P, Nicoli S, Zatelli A. Proximal ureteral ectopia causing hydronephrosis in a kitten. J Feline Med Surg. 2006;8:420–23.
Berent AC, Mayhew PD, Porat-Mosenco Y. Use of cystoscopic-guided laser ablation for treatment of intramural ureteral ectopia in male dogs: four cases (2006–2007). J Am Vet Med Assoc. 2008;232:1026–34.
Cannizzo KL, McLoughlin MA, Mattoon JS, Samii VF, Chew DJ, DiBartola SP. Evaluation of transurethral cystoscopy and excretory urography for diagnosis of ectopic ureters in female dogs: 25 cases (1992–2000). J Am Vet Med Assoc. 2003;223:475–81.
Ioannidi OM, Papazoglou LG, Psalla D, Papadopoulou P, Papazoglou D, Tsampa N, Mylonakis ME. Topics in Companion An Med. 2019;26:22–4.
Slater GS. Ureteral atresia producing giant hydroureter. J Urol. 1957;78:135–37.
Khattar M, Dorairagan LN, Kumar S, Pal BC, Elangovan S, Nayak P. Giant obstructive megaureter causing contralateral ureteral obstruction and hydronephrosis: A first-time report. Urology. 2009;74:1306–08.
Yu M, Ma G, Ge Z, Lu R, Deng Y, Guo Y. Unilateral congenital giant megaureter with renal dysplasia compressing contralateral ureter and causing bilateral hydronephrosis: a case report and literature review. BMC Urol. 2016;16:7.
D’Anjou MA, Bédard A, Dunn ME. Clinical significance of renal pelvic dilation on ultrasound in dogs and cats. Vet Radiol Ultrasound. 2011;52:88–94.
Neuwirth L, Mahaffey M, Crowell W, Selcer B, Barsanti J, Cooper R, Brown J. Comparison of excretory urography and ultrasonography for detection of experimentally induced pyelonephritis in dogs. Am J Vet Res. 1993;54:660–69.
Tong K, Weisse C, Berent AC. Rigid urethrocystoscopy via a percutaneous fluoroscopic-assisted perineal approach in male dogs: 19 cases (2005–2014). J Am Vet Med Assoc. 2016;249:918–25.
Bleve CB, Conighi ML, Fasoli L, Bucci V, Battaglino F, Chiarenza SF. Proximal ureteral atresia, a rare congenital anomaly-incidental finding: a case report. Transl Pediatr. 2017;6:67–71.
Ashimine S, Miyazato M, Hayashi E, Morozumi M, Sugaya K, Ogawa Y. Distal ureteral atresia: recovery of renal function after relief of obstruction at ten months old. Int J Urol. 2005;12:578–80.
Bhattacharjee PK, Sushil G, Sharma GD. Distal ureteric atresia presenting as an abdominal lump in an adult. Indian J Surg. 2004;66:175–77.
Wu S, Xu R, Zhu X, Zhao X. Distal ureteral atresia with ureteropelvic junction obstruction in a female child: a rare case. Int J Clin Exp Med. 2015;8:1472–74.
Bagnara V, Castorina S, Nappo SG, Privitera G, Luca T, Caione P. Hypothesis on etiopathogenesis, congenital or acquired, of an imperforate distal ureter: a case report. J Med Case Rep. 2015;9:227.
Sinha RS, Saha K, Bhattacharjee P, Majhi TK, Sarkar R. Distal ureteric atresia-a case report. J Indian Assoc Pediatr Surg. 2002;7:156–58.
Louw JH, Barnard CN. Congenital intestinal atresia; observations on its origin. Lancet. 1955;269:1065–67.
Airik R, Kispert A. Down the tube of obstructive uropathies: the important of tissue interactions during ureter development. Kidney Int. 2007;72:1459–67.
Ruanto-Gill D, Coco-Payeras A, Tejedo-Mateu A. Obstruction and normal recanalization of the ureter in the human embryo. Its relation to congenital ureteric obstruction. Eur Urol. 1975;1:287–93.
Acknowledgements
Not applicable.
Funding
Not applicable.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
MZ was the responsible student on the case and wrote the manuscript. RS gathered, optimized, and labeled all the images. TB was the responsible clinician and revised the manuscript. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethics approval and consent to participate
Owner consent was obtained.
Consent for publication
Informed consent for publication of the clinical details was obtained from the dog’s owner.
Competing interests
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Open Access This article is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License, which permits use, sharing, adaptation, distribution and reproduction in any medium or format, as long as you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons licence, and indicate if changes were made. The images or other third party material in this article are included in the article's Creative Commons licence, unless indicated otherwise in a credit line to the material. If material is not included in the article's Creative Commons licence and your intended use is not permitted by statutory regulation or exceeds the permitted use, you will need to obtain permission directly from the copyright holder. To view a copy of this licence, visit http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/. The Creative Commons Public Domain Dedication waiver (http://creativecommons.org/publicdomain/zero/1.0/) applies to the data made available in this article, unless otherwise stated in a credit line to the data.
About this article
Cite this article
Zalek, M., Shah, R. & Bolton, T. A case of congenital ureteral atresia causing rare upper and lower urinary tract manifestations in a puppy: a case report. BMC Vet Res 17, 73 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1186/s12917-021-02780-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1186/s12917-021-02780-6