Abstract
Background
Lupus nephritis (LN) is the most common and severe clinical manifestation of systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE). N6-methyladenosine (m6A) is a reversible RNA modification and has been implicated in various biological processes. However, the roles of m6A regulators in LN are not fully demonstrated.
Methods
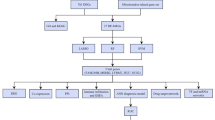
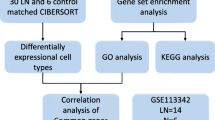
We downloaded the kidney tissue transcriptome dataset of LN patients and normal controls from the GEO database and extracted the expression levels of m6A regulators. We constructed and compared Random Forest (RF) and Support Vector Machine (SVM) models, and subsequently selected featured genes to develop nomogram models. The m6A subtypes were identified based on significantly differentially expressed m6A regulators, and the m6A gene subtypes were identified based on m6A-associated differential genes, and the two m6A modification patterns were comprehensively evaluated.
Results
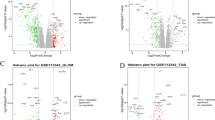
We obtained the GSE32591 and GSE112943 datasets from the GEO database, including 78 LN samples and 36 normal control samples. We extracted the expression levels of 20 m6A regulators. By RF analysis we identified 7 characteristic m6A regulators and constructed nomogramh models with these 7 genes. We identified two m6A subtypes based on these seven important m6A regulators, and the immune cell infiltration levels of the two subtype clusters were significantly different. We identified two more m6A gene subtypes based on m6A-associated DEGs. We calculated the m6A scores using the principal component analysis (PCA) algorithm and found that the m6A scores of m6A cluster A and gene cluster A were lower than those of m6A cluster B and gene cluster B. In addition, we found that the levels of inflammatory factors were also significantly different between m6A clusters and gene clusters.
Conclusion
This study confirms that m6A regulators are involved in the LN process through different modes of action and provide new diagnostic and therapeutic targets for LN.
Similar content being viewed by others
Introduction
Lupus nephritis (LN) is one of the most common and serious complications of systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE) with high morbidity and mortality rates [1]. The global annual incidence of SLE ranges from 1/100,000 to 8.7/100,000, and 40-60% of patients with SLE have LN at the time of onset. approximately 10-20% of patients with LN will eventually develop end-stage renal disease (ESRD) [2]. The treatment of LN is mainly based on glucocorticoids and immunosuppressive agents, but the therapeutic effect is not satisfactory [ The original datasets were downloaded from the Gene Expression Omnibus (https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/geo/). The datasets used and/or analyzed during the current study available from the corresponding author on reasonable request. Lupus nephritis Systemic lupus erythematosus Random Forest Support Vector Machine Principal component analysis End-stage renal disease Differentially expressed genes Gene Ontology Kyoto Encyclopedia of Genes and Genomes Anders HJ, Saxena R, Zhao MH, Parodis I, Salmon JE, Mohan C. Lupus nephritis. Nat Rev Dis Primers. 2020;6(1):7. Hoover PJ, Costenbader KH. Insights into the epidemiology and management of lupus nephritis from the US rheumatologist’s perspective. Kidney Int. 2016;90(3):487–92. **pell M, Lledo GM, Egan AC, et al. From systemic lupus erythematosus to lupus nephritis: the evolving road to targeted therapies. Autoimmun Rev. 2023;22(10):103404. Dominissini D, Moshitch-Moshkovitz S, Schwartz S, et al. Topology of the human and mouse m6A RNA methylomes revealed by m6A-seq. Nature. 2012;485(7397):201–6. Feng L, Du R, Chang B, Li M, Tian J, Wang S. Multilevel regulation of N(6)-methyladenosine RNA modifications: implications in tumorigenesis and therapeutic opportunities. Genes Dis. 2023;10(5):1969–81. Chen XY, Zhang J, Zhu JS. The role of m(6)a RNA methylation in human cancer. Mol Cancer. 2019;18(1):103. Li LJ, Fan YG, Leng RX, Pan HF, Ye DQ. Potential link between m(6)a modification and systemic lupus erythematosus. Mol Immunol. 2018;93:55–63. Li ZX, Zheng ZQ, Yang PY, et al. WTAP-mediated m(6)a modification of lncRNA DIAPH1-AS1 enhances its stability to facilitate nasopharyngeal carcinoma growth and metastasis. Cell Death Differ. 2022;29(6):1137–51. Zhao H, Pan S, Duan J, et al. Integrative analysis of m(6)A Regulator-mediated RNA methylation modification patterns and Immune characteristics in Lupus Nephritis. Front Cell Dev Biol. 2021;9:724837. Abdelati AA, Eshak NY, Donia HM, El-Girby AH. Urinary Cellular Profile as a biomarker for Lupus Nephritis. J Clin Rheumatol. 2021;27(8):e469–76. Ding H, Wu T. Insulin-like growth factor binding proteins in Autoimmune diseases. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2018;9:499. Tektonidou MG, Dasgupta A, Ward MM. Risk of end-stage renal disease in patients with Lupus Nephritis, 1971–2015: a systematic review and bayesian Meta-analysis. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2016;68(6):1432–41. Almaani S, Meara A, Rovin BH. Update on Lupus Nephritis. Clin J Am Soc Nephrol. 2017;12(5):825–35. Ren S, Zhang Y, Yang X, et al. N6-methyladenine- induced LINC00667 promoted breast cancer progression through m6A/KIAA1429 positive feedback loop. Bioengineered. 2022;13(5):13462–73. Fattal I, Shental N, Mevorach D, et al. An antibody profile of systemic lupus erythematosus detected by antigen microarray. Immunology. 2010;130(3):337–43. Liu D, Zhou W, Mao L, Cui Z, ** S. Identification of ferroptosis-related genes and pathways in diabetic kidney disease using bioinformatics analysis. Sci Rep. 2022;12(1):22613. Luo Q, Rao J, Zhang L, et al. The study of METTL14, ALKBH5, and YTHDF2 in peripheral blood mononuclear cells from systemic lupus erythematosus. Mol Genet Genomic Med. 2020;8(9):e1298. Cecconi M, Evans L, Levy M, Rhodes A. Sepsis and septic shock. Lancet. 2018;392(10141):75–87. Singer M, Deutschman CS, Seymour CW, et al. The Third International Consensus definitions for Sepsis and septic shock (Sepsis-3). JAMA. 2016;315(8):801–10. Yoo EJ, Oh KH, Piao H, et al. Macrophage transcription factor TonEBP promotes systemic lupus erythematosus and kidney injury via damage-induced signaling pathways. Kidney Int. 2023;104(1):163–80. Chalmers SA, Ayilam Ramachandran R, Garcia SJ et al. The CD6/ALCAM pathway promotes lupus nephritis via T cell-mediated responses. J Clin Invest 2022;132(1). Kwant LE, Vegting Y, Tsang ASMWP, et al. Macrophages in Lupus Nephritis: exploring a potential new therapeutic avenue. Autoimmun Rev. 2022;21(12):103211. Richoz N, Tuong ZK, Loudon KW et al. Distinct pathogenic roles for resident and monocyte-derived macrophages in lupus nephritis. JCI Insight 2022;7(21). Not applicable. This study is supported by Bei**g Hospitals Authority Youth Program (No. QML 20220306 and No. QML 20210303), and Bei**g Association for Science and Technology **qiao Project Seed Fund (Grant No. ZZ22006). MJ and DL analyzed the data and drafted the manuscript. YL, YY, ZH and KZ designed the study, analyzed the data, and revised the manuscript. QS designed and conducted the study, analyzed the data, and drafted and revised the manuscript. All authors contribute to this work and gave final approval of the manuscript. Not applicable. Not applicable. The authors declare no competing interests. Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material. Open Access This article is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License, which permits use, sharing, adaptation, distribution and reproduction in any medium or format, as long as you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons licence, and indicate if changes were made. The images or other third party material in this article are included in the article’s Creative Commons licence, unless indicated otherwise in a credit line to the material. If material is not included in the article’s Creative Commons licence and your intended use is not permitted by statutory regulation or exceeds the permitted use, you will need to obtain permission directly from the copyright holder. To view a copy of this licence, visit http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/. The Creative Commons Public Domain Dedication waiver (http://creativecommons.org/publicdomain/zero/1.0/) applies to the data made available in this article, unless otherwise stated in a credit line to the data. Li, D., Li, Y., Zhu, K. et al. Analysis of m6A-regulated genes and subtype classification in lupus nephritis.
BMC Nephrol 25, 119 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1186/s12882-024-03549-3 Received: Accepted: Published: DOI: https://doi.org/10.1186/s12882-024-03549-3Data availability
Abbreviations
References
Acknowledgements
Funding
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Ethics approval and consent to participate
Consent for publication
Competing interests
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Electronic supplementary material
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Keywords