Abstract
Background
Dystrophinopathies are the most common X-linked inherited muscle diseases, and the disease-causing gene is DMD. Exonic duplications are a common type of pathogenic variants in the DMD gene, however, 5’ end exonic duplications containing exon 1 are less common. When assessing the pathogenicity of exonic duplications in the DMD gene, consideration must be given to their impact on the reading frame. Traditional molecular methods, such as multiplex ligation-dependent probe amplification (MLPA) and next-generation sequencing (NGS), are commonly used in clinics. However, they cannot discriminate the precise physical locations of breakpoints and structural features of genomic rearrangement. Long-read sequencing (LRS) can effectively overcome this limitation.
Results
We used LRS technology to perform whole genome sequencing on three families and analyze the structural variations of the DMD gene, which involves the duplications of exon 1 and/or exon 2. Two distinct variant types encompassing exon 1 in the DMD Dp427m isoform and/or Dp427c isoform are identified, which have been infrequently reported previously. In pedigree 1, the male individuals harboring duplication variant of consecutive exons 1–2 in the DMD canonical transcript (Dp427m) and exon 1 in the Dp427c transcript are normal, indicating the variant is likely benign. In pedigree 3, the patient carries complex SVs involving exon 1 of the DMD Dp427c transcript showing an obvious phenotype. The locations of the breakpoints and the characteristics of structural variants (SVs) are identified by LRS, enabling the classification of the variants' pathogenicity.
Conclusions
Our research sheds light on the complexity of DMD variants encompassing Dp427c/Dp427m promoter regions and emphasizes the importance of cautious interpretation when assessing the pathogenicity of DMD 5' end exonic duplications, particularly in carrier screening scenarios without an affected proband.
Similar content being viewed by others
Background
Dystrophinopathies are the most common X-linked inherited muscle diseases, and the manifestations range from mild phenotypes of asymptomatic increase in serum concentration of creatine phosphokinase (CK) to severe phenotypes that include Duchenne muscular dystrophy (DMD, MIM 310200), Becker muscular dystrophy (BMD, MIM 300376), and DMD-associated dilated cardiomyopathy (DCM, MIM 302045) [1]. DMD usually presents in early childhood, and affected children are often wheelchair dependent by age 12 years, and few survive beyond the third decade, with respiratory complications and progressive cardiomyopathy being common causes of death. BMD is characterized by later-onset and relatively slow progress, and heart failure from DCM is a common cause of death in BMD [2, 3]. The exact prevalence data of dystrophinopathies are not available. DMD is more common than BMD, and it is reported that the incidence of DMD is 1:4,700 live male births in Canada [4] and 1:3,917 live male births in southeast Norway [5].
The molecular basis of DMD/BMD and DCM is pathogenic variation in the DMD gene (MIM 300377), the largest gene in humans, spanning 2.2 Mb genome sequence at Xp21, consisting of 79 exons. The DMD gene contains at least seven independent, tissue-specific promoters and two polyA-addition sites [6]. Among these, three full-length isoforms share the same number of exons but are derived from three independent promoters (exon 1) in the brain (Dp427c), muscle (Dp427m), and Purkinje cerebellar neurons (Dp427p) [2]. While many variants have been documented within this gene, a majority of them affect the expression of the muscle isoform (Dp427m) [2]. About 65% of DMD gene pathogenic variants are exonic deletions, ~ 10% are exonic duplications, and about 25% are small variants, including point mutations, small insertions/deletions (indels), and others [3].
Numerous molecular genetic methods are available for mutation screening of the DMD gene. Multiple polymerase chain reaction (M-PCR), targeting mutation hotspots, can detect approximately 98% of exonic deletions [7]. Multiplex ligation-dependent probe amplification (MLPA) [8] is more widely used in clinical labs for DMD mutation screening because it can simultaneously detect exonic deletions and duplications. The next-generation sequencing (NGS) technology enables rapid and comprehensive screening of single nucleotide variations (SNVs) and small indels among 79 exons in the DMD gene. Genetic diagnosis could be confirmed in around 98% of DMD/BMD patients by MLPA combined with NGS technology [9]. However, the traditional method of mutation screening for DMD cannot identify the complex structural variants (SVs) of the DMD gene, such as discerning whether DMD exonic duplications occur extragenically or intragenically and whether in tandem or not. This information holds significance for determining the pathogenicity of duplications [10]. Recently, long-read sequencing (LRS) methods have emerged, which can generate genome assemblies of unprecedented quality. Leveraging the advantages of longer reads, LRS has been successfully employed in the genetic testing of monogenic diseases with structural complexity, including thalassemia [11] and congenital adrenal hyperplasia [12].
In this study, we selected three unique families with duplication variants affecting exon 1 and/or exon 2 in the DMD gene to explore the structural characteristics of exonic duplications through LRS. Our investigation aimed to shed light on the pathogenicity of these variants and provide further insights into their implications.
Results
MLPA results
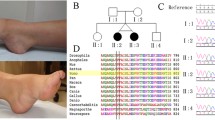
In pedigree 1, the index patient (II4) was identified with a duplication of exon 1–2 in the DMD gene during routine expanded carrier screening (ECS). Subsequently, MLPA was used to confirm that the duplication occurred in exons 1–2 in the Dp427m isoform and exon 1 in the Dp427c isoform of the DMD gene. Further investigation of the family demonstrated that the other three females (II2, II3, and III8) were heterozygous duplication carriers. Unexpectedly, three male members (I1, III3, III5) harbored the same hemizygous duplication variants, without clinical manifestations of DMD/BMD and abnormal biochemical indicators (I1, III3). The lack of genotype–phenotype cosegregation suggested that the duplication variant affecting exons 1–2 in the Dp427m isoform and exon 1 in the Dp427c isoform of the DMD gene was likely benign. (See Fig. 1B and Supplementary Fig. 1).
Genetic analysis of the DMD gene in Pedigree 1. A and B show the family pedigree and DMD gene analysis results detected by MLPA, male members I1, III3, and III5 had hemizygous duplication variants of consecutive DMD exons 1–2 in Dp427m and exon 1 in Dp427c, and female members II2, II3, II4 and III8 were heterozygous. C shows a critical breakpoint from a screenshot of the integrative genomics viewer (IGV) based on LRS data analysis. D Schematic diagram shows the location of the breakpoint and architectural features of the duplication variant. E is the result of Sanger sequencing verification for the critical breakpoint. The red dashed line indicates the breakpoints and the red single arrow indicates the same critical breakpoint
In pedigree 2, the affected boy (II1) presented with a duplication variant involving exon 2 in the DMD gene, displaying the characteristic clinical phenotype of DMD. His sister (II2, index patient) carried the heterozygous duplication of exon 2, with mild phenotype of abnormal biochemical indicators. Their mother (I2) was identified as a carrier of the heterozygous duplication variant of exon 2 in the DMD gene, without abnormal phenotype. (See Fig. 2B).
Genetic analysis of the DMD gene in Pedigree 2. A and B show the family pedigree and DMD gene analysis results detected by MLPA, affected boy (II1) had a hemizygous duplication variant of exon 2 in the DMD gene, and his mother and sisiter were heterozygous. C shows a critical breakpoint from a screenshot of the integrative genomics viewer (IGV) based on LRS data analysis. D Schematic diagram shows the locations of breakpoints and architectural features of the duplication variants. E is the result of Sanger sequencing verification for the critical breakpoint. The red dashed line indicates the breakpoints and the red single arrow indicates the same critical breakpoint
In pedigree 3, the proband exhibited a duplication variant involving exon 1 in Dp427c, displaying typical clinical phenotypes of DMD. His pregnant mother was identified as a carrier of the heterozygous variant. (See Fig. 3A).
Genetic analysis of the DMD gene in Pedigree 3. A shows the family pedigree and DMD gene analysis results detected by MLPA. The proband (II1) had hemizygous duplication variants of exon 1 of the Dp427c transcript in the DMD gene, and his mother was heterozygous. B shows critical breakpoints from screenshots of the integrative genomics viewer (IGV) based on LRS data analysis, and corresponding verification results by Sanger sequencing. From top to bottom are the joints of fragments a and c, fragments c and e, fragments e and a (indicated in C). The red single arrows indicate the breakpoints. C Schematic diagram shows the locations of breakpoints and architectural features of the duplication variant. The red dashed lines indicate the breakpoints involved in recombination, and the coordinates of the breakpoints in the genome are shown next to them
Breakpoints and architectural features identification by LRS and validation
Whole genome LRS was performed to identify the breakpoints, and the sequencing data parameters were described in Supplementary Table 2. In the index patient (II4) in pedigree 1, LRS revealed that the duplication variant was located at chrX:33,019,224–33,822,717. This duplication encompassed a contiguous segment of approximately 803.5 kb, spanning consecutive DMD exons 1–2 within the Dp427m transcript and exon 1 within the Dp427c transcript. The duplication occurred in a tandem arrangement. The critical breakpoint was confirmed by Sanger sequencing. (See Fig. 1C\D\E).
In pedigree 2, the fresh lymphocyte sample was unavailable from the affected boy (II1), but a fresh sample was obtained from II2. LRS on II2 indicated the duplication variant was ~ 71.0 kb, located at chrX:32,999,023–33,070,000. This duplication involved a single exon 2 of the DMD gene and was arranged in tandem, potentially disrupting the reading frame of the DMD gene. We conducted Sanger sequencing to validate the critical breakpoint. (See Fig. 2C\D\E).
In pedigree 3, the proband (II1) exhibited a complex duplication spanning approximately 688.9 kb within the DMD gene, as identified by LRS. This duplication involved an inverted single exon 1 of the Dp427c transcript. The initial tandem duplication segment was potentially substantial (~ 6.3 Mb), ranging from chrX:33,154,365 to chrX:39,474,769. Additionally, two internal deletions were observed either following or occurring simultaneously with the tandem duplication. These deletions encompassed fragments b (chrX:33,202,989–33,283,460) and d (chrX:33,523,779–39,074,862), respectively. Furthermore, an inversion (fragment c, chrX:33,283,460–33,523,779) was also detected. These complex genomic rearrangements result in an out-of-frame variant. Three critical breakpoints were verified by Sanger sequencing. (See Fig. 3 B\C).
No pathogenic SNVs and indels were identified in any of the subjects based on nanopore sequencing data. The size of duplication variants revealed by LRS was consistent with those determined by CNV-Seq using NGS with a resolution of 100 kb. (See Supplementary Fig. 2).
Sequence characteristics of breakpoints
In the three pedigrees examined in this study, repeat sequences were observed surrounding most of the breakpoints. These include various types of repeat elements, such as short interspersed nuclear elements (SINE), long interspersed nuclear elements (LINE), long terminal repeat elements (LTR), and low complexity repeats. Detailed information can be found in Supplementary Fig. 3.
Discussion
Exonic duplications are a frequent type of pathogenic variant in the DMD gene [3, 7, 13], and duplication of exon 2 is the most prevalent duplication variant among DMD patients [13]. While MLPA and NGS methods are commonly employed in clinical settings to detect exonic duplication variants in DMD, they often fail to discern the precise physical locations of breakpoints and structural characteristics of genomic rearrangements. However, LRS overcomes the limitations associated with assembly problems encountered when dealing with long and complex sequences. Kubota et al. [14] reported a DMD patient with complex genomic rearrangements involving exon 2 duplication through LRS, and simultaneously detected the normal intact DMD gene sequence, suggesting a mosaic nature in the patient. For individuals clinically diagnosed with DMD or BMD, long-read whole-genome sequencing presents a valuable approach for identifying potential structural variants within the DMD gene when conventional methods are unable to confirm the genetic diagnosis. **, detection of variants
Raw data in fastq format were obtained by capturing the electrical signal generated by PromethION. Guppy basecalling software (v5.0.16) was employed during this process. To maintain analysis accuracy and data integrity, NanoFilt (v2.8.0, https://github.com/wdecoster/nanofilt) was applied to eliminate low-quality reads (Qphred < = 7) and short reads (< 1000 bp) from the raw data. Additionally, a total of 50 bp bases from both the head and tail ends of the reads were trimmed. Minimap2 (https://github.com/lh3/minimap2) was employed to align the reads to the reference genomes hg19 (GRCh37) accurately. Subsequently, samtools (v1.2, https://github.com/samtools/samtools) was used to convert the resulting SAM file to the BAM format for further processing and analysis. Sniffles2 (https://github.com/fritzsedlazeck/Sniffles) was utilized to process the BAM files to detect structural variations (SVs) in the genomic data. To refine the results, screening based on high-quality variant reads was conducted, and the karyotype diagnosis report was examined. By combining these analyses, preliminary SV results with improved accuracy and reliability were obtained. To examine single nucleotide variants (SNVs) and indels from samples, PEPPER-Margin-DeepVariant (r0.8-gpu, https://github.com/kishwarshafin/pepper) was employed by providing the BAM file as input.
Analysis of sequence characteristics near breakpoints
A manual analysis of the flanking sequences at each breakpoint was performed to investigate the presence of repetitive elements, and 100 or 200-base pair reads both upstream and downstream of each breakpoint were extracted. The "Repeat Masker" program from the UCSC Genome Browser was employed to conduct a comprehensive search for repetitive elements within these extracted reads.
NGS sequencing and copy number variants (CNVs) analysis
Approximately 50 ng of genomic DNA (gDNA) underwent fragmentation using the DNA Fragment kit (KT100804248, Yikon, China), followed by library preparation using the DNA library prepare kit (XK038, Yikon, China). The quality of the resulting library was assessed using the Agilent 2100 Bioanalyzer (Agilent, USA). Subsequently, DNA libraries were subjected to sequencing on the Nextseq500 system (Illumina, USA). Copy number quantification across the genome was performed using NGS reads, following established protocols.
PCR and Sanger sequencing validation
The breakpoints of the DMD gene identified by nanopore sequencing were confirmed by PCR and Sanger sequencing. PCR primers were designed using MFEprimer-3.1 (https://mfeprimer3.igenetech.com/), and primer sequences were listed in Supplementary Table 1. Template gDNA was amplified using 25 ul 2 × GoldStar Best MasterMix (CW0655M, Cwbio, China), 2 ul forward primer, and 2 ul reverse primer to obtain around 1 kb PCR products. PCR products were confirmed on agarose gels and sequenced on an ABI Prism 3730xl Genetic Analyser (Applied Biosystems) and analyzed with Chromas software (Technelysium, Australia).
Availability of data and materials
The data that support the findings of this study have been deposited into the CNGB Sequence Archive (CNSA) of China National GeneBank DataBase (CNGBdb) with accession number CNP0004854. (https://db.cngb.org/search/project/CNP0004854/).
References
Fratter C, Dalgleish R, Allen SK, Santos R, Abbs S, Tuffery-Giraud S, et al. EMQN best practice guidelines for genetic testing in dystrophinopathies. Eur J Hum Genet. 2020;28:1141–59.
Muntoni F, Torelli S, Ferlini A. Dystrophin and mutations: one gene, several proteins, multiple phenotypes. Lancet Neurol. 2003;2:731–40.
Ferlini A, Neri M, Gualandi F. The medical genetics of dystrophinopathies: molecular genetic diagnosis and its impact on clinical practice. Neuromuscul Disord. 2013;23:4–14.
Dooley J, Gordon KE, Dodds L, MacSween J. Duchenne muscular dystrophy: a 30-year population-based incidence study. Clin Pediatr (Phila). 2010;49:177–9.
Tangsrud SE, Halvorsen S. Child neuromuscular disease in southern Norway. The prevalence and incidence of Duchenne muscular dystrophy. Acta Paediatr Scand. 1989;78:100–3.
Doorenweerd N, Mahfouz A, van Putten M, Kaliyaperumal R, Hoen PACT, Hendriksen JGM, et al. Timing and localization of human dystrophin isoform expression provide insights into the cognitive phenotype of Duchenne muscular dystrophy. Sci Rep. 2017;7:12575.
Beggs AH, Koenig M, Boyce FM, Kunkel LM. Detection of 98% of DMD/BMD gene deletions by polymerase chain reaction. Hum Genet. 1990;86:45–8.
Schwartz M, Duno M. Improved molecular diagnosis of dystrophin gene mutations using the multiplex ligation-dependent probe amplification method. Genet Test. 2004;8:361–7.
Kong X, Zhong X, Liu L, Cui S, Yang Y, Kong L. Genetic analysis of 1051 Chinese families with Duchenne/Becker Muscular Dystrophy. BMC Med Genet. 2019;20:139.
Bai Y, Liu J, Xu J, Sun Y, Li J, Gao Y, et al. Long-Read Sequencing Revealed Extragenic and Intragenic Duplications of Exons 56–61 in DMD in an Asymptomatic Male and a DMD Patient. Front Genet. 2022;13:878806.
Liang Q, Gu W, Chen P, Li Y, Liu Y, Tian M, et al. A More Universal Approach to Comprehensive Analysis of Thalassemia Alleles (CATSA). J Mol Diagn. 2021;23:1195–204.
Liu Y, Chen M, Liu J, Mao A, Teng Y, Yan H, et al. Comprehensive Analysis of Congenital Adrenal Hyperplasia Using Long-Read Sequencing. Clin Chem. 2022;68:927–39.
White SJ, Aartsma-Rus A, Flanigan KM, Weiss RB, Kneppers AL, Lalic T, et al. Duplications in the DMD gene. Hum Mutat. 2006;27:938–45.
Kubota A, Ishiura H, Porto KJL, Tanaka M, Mitsui J, Unuma A, et al. DMD exon 2 duplication due to a complex genomic rearrangement is associated with a somatic mosaicism. Neuromuscul Disord. 2022;32:263–9.
**e Z, Sun C, Zhang S, Liu Y, Yu M, Zheng Y, et al. Long-read whole-genome sequencing for the genetic diagnosis of dystrophinopathies. Ann Clin Transl Neurol. 2020;7:2041–6.
He W, Meng G, Hu X, Dai J, Liu J, Li X, et al. Reclassification of DMD Duplications as Benign: Recommendations for Cautious Interpretation of Variants Identified in Prenatal Screening. Genes (Basel). 2022;13:1972.
Nallamilli BRR, Chaubey A, Valencia CA, Stansberry L, Behlmann AM, Ma Z, et al. A single NGS-based assay covering the entire genomic sequence of the DMD gene facilitates diagnostic and newborn screening confirmatory testing. Hum Mutat. 2021;42:626–38.
Chen JM, Cooper DN, Ferec C, Kehrer-Sawatzki H, Patrinos GP. Genomic rearrangements in inherited disease and cancer. Semin Cancer Biol. 2010;20:222–33.
Ling C, Dai Y, Fang L, Yao F, Liu Z, Qiu Z, et al. Exonic rearrangements in DMD in Chinese Han individuals affected with Duchenne and Becker muscular dystrophies. Hum Mutat. 2020;41:668–77.
Hu P, Tan J, Yu F, Shao B, Zhang F, Zhang J, et al. A capillary electrophoresis-based multiplex PCR assay for expanded carrier screening in the eastern Han Chinese population. NPJ Genom Med. 2022;7:6.
Acknowledgements
The authors would like to thank all patients and their families who participated in this study.
Funding
This work was supported by the National Key Research and Development Program of China (2022YFC2703200, 2021YFC2700600), and the National Natural Science Foundation of China (82171839).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
JS and FD were involved in project conception and funding acquisition. JS, TD, and FD designed this project. TD, XS, JW, MG, HX, and JX developed the methodology. JS, JY, YZ, and FW interpreted and analyzed the results. JS and TD wrote the main manuscript text and all authors reviewed the manuscript.
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Ethics approval and consent to participate
Informed consent was obtained from all subjects and/or their legal guardian(s). This study was approved by the Institutional Review Board of the First Affiliated Hospital of Nan**g Medical University (No. 2023-SR-454).
Consent for publication
Not applicable.
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Open Access This article is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License, which permits use, sharing, adaptation, distribution and reproduction in any medium or format, as long as you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons licence, and indicate if changes were made. The images or other third party material in this article are included in the article's Creative Commons licence, unless indicated otherwise in a credit line to the material. If material is not included in the article's Creative Commons licence and your intended use is not permitted by statutory regulation or exceeds the permitted use, you will need to obtain permission directly from the copyright holder. To view a copy of this licence, visit http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/. The Creative Commons Public Domain Dedication waiver (http://creativecommons.org/publicdomain/zero/1.0/) applies to the data made available in this article, unless otherwise stated in a credit line to the data.
About this article
Cite this article
Shen, J., Ding, T., Sun, X. et al. Comprehensive analysis of genomic complexity in the 5’ end coding region of the DMD gene in patients of exons 1–2 duplications based on long-read sequencing. BMC Genomics 25, 292 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1186/s12864-024-10224-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1186/s12864-024-10224-2