Abstract
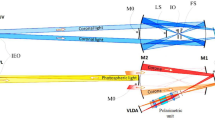
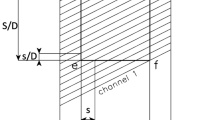
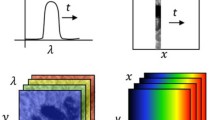
We present the technique and algorithm of numerical modeling of high-resolution spectroscopic equipment. The software is implemented in C++ using nVidia CUDA technology. We report the results of currently developedmodeling of new-generation echelle spectrographs. To validate the algorithms used to construct the mathematical model, we present the results of modeling of NES spectrograph of the 6-m telescope of the Special Astrophysical Observatory of the Russian Academy of Sciences. A comparison of simulated and real images of the spectra acquired with NES spectrograph demonstrates good agreement between the model constructed and experimental data.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
H. Hasan and C. J. Burrows, in Calibrating Hubble Space Telescope, Ed. by J. C. Blades and S. J. Osmer (Space Telescope Science Institute, Baltimore, 1994), p. 395.
F. Diego and D. D. Walker, Monthly Notices Royal Astron. Soc. 217, 347 (1985).
D. D. Walker and F. Diego, Monthly Notices Royal Astron. Soc. 217, 355 (1985).
J. A. Valenti, R. P. Butler, and G. W. Marcy, Publ. Astron. Soc. Pacific 107, 966 (1995).
D. Queloz, IAU Symp. 167, 221 (1995).
P. Ballester and M. R. Rosa, Astron. and Astrophys. Suppl. 126 (1997).
J. Krist, ASP Conf. Ser. 77, 349 (1995).
P. Ghavamian, A. Aloisi, D. Lennon, et al., COS Instrument Sci. rep. 2009-01 (2009).
G. H. Spencer and M. V. R. K. Murty, J. Opt. Soc. America 52, 672 (1962).
C. Palmer, Diffraction grating handbook, 5th ed. (Thermo RGL, New York, 2002).
K. I. Tarasov, Spectral Devices (Mashinostroenie, Moscow, 1977)[In Russian].
A. N. Zaydel, G. V. Ostrovskaya, and Yu. I. Ostrovskii, Methods and practice of spectroscopy (Nauka, Moscow, 1972) [In Russian].
A. A. Boyarchuk, B. M. Shustov, A. A. Moisheev, and M. E. Sachkov, Solar System Research 47, 499 (2013).
V. Panchuk, M. Yushkin, T. Fatkhullin, and M. Sachkov, Astrophys. Space Sci. 354, 163 (2014).
D. J. Schroeder and R. L. Hilliard, Appl.Opt. 19, 2833 (1980).
V. E. Panchuk, V. G. Klochkova, M. V. Yushkin, and I. D. Najdenov, J. Opt. Technol. 76, 87 (2009).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Original Russian Text © M.V. Yushkin, T.A. Fatkhullin, V.E. Panchuk, 2016, published in Astrofizicheskii Byulleten’, 2016, Vol. 71, No. 3, pp. 372–385.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Yushkin, M.V., Fatkhullin, T.A. & Panchuk, V.E. Mathematical model of orbital and ground-based cross-dispersion spectrographs. Astrophys. Bull. 71, 343–356 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1134/S1990341316030081
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1134/S1990341316030081