Abstract
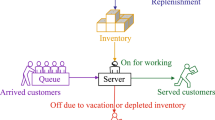
Models of queuing-inventory systems with two inventory replenishment policies (IRPs) are studied: with a fixed supply volume and with a variable supply volume. Inventories can be replenished from two sources with different lead times and inventory delivery costs. If the inventory level drops to the ordering point s, then a regular inventory order is generated to the slow source. If inventory levels fall below a certain threshold r, where r < s, then the system instantly cancels the regular order and an emergency order to the fast source is generated. The system also accepts destructive customers (d-customers), as a result of which inventory levels are instantly reduced. Random variables involved in the formation of the model have exponential distribution functions (dfs) with finite means. The ergodicity conditions for the systems under study are found, their stationary distributions are calculated, and formulas are proposed for finding their characteristics. The problems of minimizing the total cost of the studied systems are solved by choosing the appropriate values of the ordering point s and threshold value r when using different inventory replenishment policies.
Similar content being viewed by others
REFERENCES
M. Schwarz and H. Daduna, “Queuing systems with inventory management with random lead times and with backordering,” Math. Methods Oper. Res. 64, 383–414 (2006).
M. Schwarz, C. Sauer, H. Daduna, R. Kulik, and R. Szekli, “M/M/1 queuing systems with inventory,” Queuing Syst. Theory Appl. 54, 55–78 (2006).
G. B. Rubal’skii, “Stochastic theory of inventory control,” Autom. Remote Control 70, 2098–2108 (2009).
K. Sigman and D. Simchi-Levi, “Light traffic heuristic for an M/G/1 queue with limited inventory,” Ann. Oper. Res. 40, 371–380 (1992).
A. Z. Melikov and A. A. Molchanov, “Stock optimization in transport/storage systems,” Cybernetics 28, 484–487 (1992).
A. Krishnamoorthy, D. Sha**, and W. Narayanan, “Inventory with positive service time: A survey,” in Advanced Trends in Queueing Theory, Vol. 2 of Mathematics and Statistics, Ed. by V. Anisimov and N. Limnios (ISTE, Wiley, London, 2021), pp. 201–238.
R. N. Ramesesh, J. K. Ord, J. C. Hayya, and A. Pan, “Sole versus dual sourcing in stochastic lead-time (s, Q) inventory models,” Manage. Sci. 37, 428–443 (1991).
F. Janssen and T. de Kok, “A two-supplier inventory model,” Int. J. Product. Econ. 59, 395–403 (1999).
C. Kouiki, M. Z. Babai, and S. Minner, “On the benefit of dual-sourcing in managing perishable inventory,” Int. J. Product. Econ. 204 (10), 1–17 (2018).
M. Haughton and K. Isotupa, “A continuous review inventory system with lost sales and emergency orders,” Am. J. Oper. Res. 8, 343–359 (2018). https://doi.org/10.4236/ajor.2018.85020
P. Cao and D. Yao, “Dual sourcing policy for a continuous-review stochastic inventory system,” IEEE Trans. Autom. Control 64, 2921–2928 (2019).
Y. Boulaksil, Y. Hamdouch, K. Ghoudi, and J. C. Fransoo, “Comparing policies for the stochastic multi-period dual sourcing problem from a supply chain perspective,” Int. J. Product. Econ. 232 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijpe.2020.107923
J. Barron, “The continuous (S, s, Se) inventory model with dual sourcing and emergency orders,” Eur. J. Oper. Res. (2021). https:// doi.org/https://doi.org/10.1016/ejor.2021.09.021
S. Minner, “Multiple-supplier inventory models in supply chain management: A review,” Int. J. Product. Econ. 81–82, 265–279 (2003).
M. Yao and S. Minner, “Review of multi-supplier inventory models in supply chain management: An update,” Tech. Rep. SSRN Electron. J. (2017). https://doi.org/10.2139/ssrn.2995134
L. **n and J. A. V. Mieghem, “Dual-sourcing, dual-mode dynamic stochastic inventory models: A review,” SSRN Electron. J. (2021). https://doi.org/10.2139/ssrn.3885147
A. Melikov, A. Krishnamoorthy, and M. O. Shahmaliyev, “Numerical analysis and long run total cost optimization of perishable queuing inventory systems with delayed feedback,” Queuing Models Service Manage. 2, 83–111 (2019).
T. V. Do, “Bibliography on G-networks, negative customers and applications,” Math. Comput. Model. 53, 205–212 (2011).
E. Gelenbe, “Random neural networks with positive and negative signals and product form solution,” Neural Computat. 1, 502–510 (1989).
M. L. Soujanya and P. V. Laxmi, “Analysis on dual supply inventory model having negative arrivals and finite lifetime inventory,” Reliab.: Theory Appl. 16, 295–301 (2021).
M. F. Neuts, Matrix-Geometric Solutions in Stochastic Models: An Algorithmic Approach (John Hopkins Univ. Press, Baltimore, 1981).
A. Z. Melikov, M. O. Shahmaliyev, and S. S. Nair, “Matrix-geometric method to study queuing system with perishable inventory,” Autom. Remote Control 82, 2168–2181 (2021).
A. Krishnamoorthy, R. Manikandan, and B. Lakshmy, “Revisit to queueing-inventory system with positive service time,” Ann. Oper. Res. 233, 221–236 (2015).
Y. Zhang, D. Yue, and W. Yue, “A queueing-inventory system with random order size policy and server vacations,” Ann. Oper. Res. (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10479-020-03859-3
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
The authors declare that they have no conflicts of interest.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Melikov, A.Z., Mirzayev, R.R. & Nair, S.S. Numerical Study of a Queuing-Inventory System with Two Supply Sources and Destructive Customers. J. Comput. Syst. Sci. Int. 61, 581–598 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1134/S1064230722030091
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1134/S1064230722030091