Abstract
Both high gain and transconductance at low operating voltages are essential for practical applications of organic field-effect transistors (OFETs). Here, we describe the significance of the double-layer capacitance effect in polar rubbery dielectrics, even when present in a very low ion concentration and conductivity. We observed that this effect can greatly enhance the OFET transconductance when driven at low voltages. Specifically, when the polar elastomer poly(vinylidene fluoride-co-hexafluoropropylene) (e-PVDF-HFP) was used as the dielectric layer, despite a thickness of several micrometers, we obtained a transconductance per channel width 30 times higher than that measured for the same organic semiconductors fabricated on a semicrystalline PVDF-HFP with a similar thickness. After a series of detailed experimental investigations, we attribute the above observation to the double-layer capacitance effect, even though the ionic conductivity is as low as 10–10 S/cm. Different from previously reported OFETs with double-layer capacitance effects, our devices showed unprecedented high bias-stress stability in air and even in water.
Similar content being viewed by others
Introduction
Field-effect transistors (FETs) with both high gain and transconductance are crucial for a broad range of applications1,2,3, including logic circuits, display drivers and sensing4,5,6. High-performance FETs based on organic materials are of particular interest due to their compatibility with low-cost, high-throughput processing and mechanical compliance with soft tissues. However, it has been challenging to realize high transconductance with organic materials due to their relatively low charge carrier mobilities. One effective method is to develop dielectric layers with high capacitances7,8. Halik et al. used an ultra-thin self-assembled monolayer (SAM) dielectric layer9 to achieve a high capacitance of 0.7 μF/cm2 and a transconductance of 0.01–0.04 S/m in vacuum evaporated OTFTs. Ion-doped polymer electrolytes10 and ion gels11,12 have been used as the dielectric layers for OFETs. Their capacitances are high due to the double-layer capacitor effect. The resulting OFETs have been shown to reach transconductances up to 0.5 S/m. However, challenges remain in using the aforementioned systems for practical applications due to the low yield of SAM fabrication, incompatibility of liquid/gel materials with standard manufacturing processes and the high moisture sensitivity of ionic dielectrics6.
Results
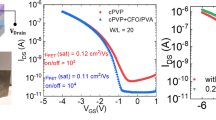
Here, we serendipitously discovered that a polar fluorinated PVDF-HFP elastomer dielectric, despite of a low ion concentration, is able to induce an electric double-layer charging effect under an applied gate voltage. This polymer dielectric is solution-processable with a high static capacitance of ~0.3 μF/cm2, even at a thickness of several micrometers. Devices made from this thick polymer dielectric are capable of operating at low voltages with a transconductance as high as 0.02 Sm−1 for polymer OTFTs and as high as 1.2 Sm−1 for CVD-graphene FET. This polymer dielectric is highly compatible with solution processing of various organic semiconductors. Remarkably, the resulting devices showed both high current output and low bias stress in both ambient and aqueous conditions.
PVDF-HFP polymers are usually semicrystalline when a high molar fraction of PVDF segments are incorporated13. However, a higher molar ratio of the HFP units (45mol% determined by 19F-NMR shown in Supplementary Information Fig. S2) results in an elastic material with a glass transition temperature (Tg) of around −20°C (Fig. S1 and S3). Its dielectric constant is 11 as measured at 1 kHz, a value similar to the previously reported range of 8 to 1314,www.nature.com/nature.
Additional Information
How to cite this article: Wang, C. et al. Significance of the double-layer capacitor effect in polar rubbery dielectrics and exceptionally stable low-voltage high transconductance organic transistors. Sci. Rep. 5, 17849; doi: 10.1038/srep17849 (2015).
References
Sokolov, A. N., Tee, B. C. K., Bettinger, C. J., Tok, J. B. H. & Bao, Z. Chemical and Engineering Approaches To Enable Organic Field-Effect Transistors for Electronic Skin Applications. Accounts of chemical research 45, 361–371 (2011).
Katz, H. E. & Huang, J. Thin-Film Organic Electronic Devices. Annual Review of Materials Research 39, 71–92 (2009).
Coropceanu, V. et al. Charge Transport in Organic Semiconductors. Chemical Reviews 107, 926–952 (2007).
Someya, T., Dodabalapur, A., Huang, J., See, K. C. & Katz, H. E. Chemical and Physical Sensing by Organic Field-Effect Transistors and Related Devices. Advanced Materials 22, 3799–3811 (2010).
Torsi, L. & Dodabalapur, A. Organic Thin-Film Transistors as Plastic Analytical Sensors. Analytical Chemistry 77, 380 A-387 A (2005).
Roberts, M. E. et al. Water-stable organic transistors and their application in chemical and biological sensors. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences 105, 12134–12139 (2008).
Veres, J., Ogier, S., Lloyd, G. & de Leeuw, D. Gate Insulators in Organic Field-Effect Transistors. Chemistry of Materials 16, 4543–4555 (2004).
Ortiz, R. P., Facchetti, A. & Marks, T. J. High-k Organic, Inorganic and Hybrid Dielectrics for Low-Voltage Organic Field-Effect Transistors. Chemical Reviews 110, 205–239 (2009).
Halik, M. et al. Low-voltage organic transistors with an amorphous molecular gate dielectric. Nature 431, 963–966 (2004).
Panzer, M. J. & Frisbie, C. D. Polymer Electrolyte Gate Dielectric Reveals Finite Windows of High Conductivity in Organic Thin Film Transistors at High Charge Carrier Densities. Journal of the American Chemical Society 127, 6960–6961 (2005).
Lee, J., Panzer, M. J., He, Y., Lodge, T. P. & Frisbie, C. D. Ion Gel Gated Polymer Thin-Film Transistors. Journal of the American Chemical Society 129, 4532–4533 (2007).
Cho, J. H. et al. Printable ion-gel gate dielectrics for low-voltage polymer thin-film transistors on plastic. Nature materials 7, 900–906 (2008).
Lee, K. H. et al. “Cut and Stick” Rubbery Ion Gels as High Capacitance Gate Dielectrics. Adv. Mater. 24, 4457–4462 (2012).
Kim, S. H., Choi, J. K. & Bae, Y. C. Mechanical properties and ionic conductivity of gel polymer electrolyte based on poly(vinylidene-fluoride-co-hexafluoropropylene). J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 81, 948–956 (2001).
**e, H. et al. PVDF-HFP composite polymer electrolyte with excellent electrochemical properties for Li-ion batteries. J. Solid State Electrochem. 12, 1497–1502 (2008).
Matthews, J. R. et al. Scalable Synthesis of Fused Thiophene-Diketopyrrolopyrrole Semiconducting Polymers Processed from Nonchlorinated Solvents into High Performance Thin Film Transistors. Chem. Mat. 25, 782–789 (2013).
Li, J., Sun, Z. & Yan, F. Solution Processable Low-Voltage Organic Thin Film Transistors with High-k Relaxor Ferroelectric Polymer as Gate Insulator. Advanced Materials 24, 88–93 (2012).
Halik, M. et al. Low-voltage organic transistors with an amorphous molecular gate dielectric. Nature 431, 963–966 (2004).
Klauk, H., Zschieschang, U. & Halik, M. Low-voltage organic thin-film transistors with large transconductance. J. Appl. Phys. 102, 074514 (2007).
Cho, J. H. et al. Printable ion-gel gate dielectrics for low-voltage polymer thin-film transistors on plastic. Nature Materials 7, 900–906 (2008).
Gray, F. M. Solid polymer electrolytes: fundamentals and technological applications. (VCH, New York, NY; 1991).
Armand, M., Endres, F., MacFarlane, D. R., Ohno, H. & Scrosati, B. Ionic-liquid materials for the electrochemical challenges of the future. Nature materials 8, 621–629 (2009).
Cho, J. H. et al. High-Capacitance Ion Gel Gate Dielectrics with Faster Polarization Response Times for Organic Thin Film Transistors. Advanced Materials 20, 686–690 (2008).
Riande, E. & Díaz-Calleja,R. . Electrical properties of polymers. (Marcel Dekker, New York; 2004).
Kolb, R. E. S. P., MN) (Minnesota Mining and Manufacturing Company (Saint Paul, MN), United States; 1981).
Seki, M., Sato, K. & Yosomiya, R. Polyurethane elastomer-LiClO4 complexes as a polymeric solid electrolyte. Die Makromolekulare Chemie 193, 2971–2978 (1992).
Ratner, M. A. & Shriver, D. F. Ion transport in solvent-free polymers. Chemical Reviews 88, 109–124 (1988).
Sirringhaus, H. Reliability of Organic Field-Effect Transistors. Advanced Materials 21, 3859–3873 (2009).
Laiho, A., Herlogsson, L., Forchheimer, R., Crispin, X. & Berggren, M. Controlling the dimensionality of charge transport in organic thin-film transistors. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences 108, 15069–15073 (2011).
Kim, D. H. et al. Liquid-Crystalline Semiconducting Copolymers with Intramolecular Donor−Acceptor Building Blocks for High-Stability Polymer Transistors. Journal of the American Chemical Society 131, 6124–6132 (2009).
Kim, J. et al. The Origin of Excellent Gate-Bias Stress Stability in Organic Field-Effect Transistors Employing Fluorinated-Polymer Gate Dielectrics. Advanced Materials 26, 7241–7246 (2014).
Zschieschang, U., Weitz, R. T., Kern, K. & Klauk, H. Bias stress effect in low-voltage organic thin-film transistors. Appl. Phys. A 95, 139–145 (2009).
Mei, J., Kim, D. H., Ayzner, A. L., Toney, M. F. & Bao, Z. Siloxane-Terminated Solubilizing Side Chains: Bringing Conjugated Polymer Backbones Closer and Boosting Hole Mobilities in Thin-Film Transistors. Journal of the American Chemical Society 133, 20130–20133 (2011).
Cheng, X. Y. et al. Air Stable Cross-Linked Cytop Ultrathin Gate Dielectric for High Yield Low-Voltage Top-Gate Organic Field-Effect Transistors. Chem. Mater. 22, 1559–1566 (2010).
Yoon, M. H., Yan, H., Facchetti, A. & Marks, T. J. Low-voltage organic field-effect transistors and inverters enabled by ultrathin cross-linked polymers as gate dielectrics. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 127, 10388–10395 (2005).
Klauk, H. et al. High-mobility polymer gate dielectric pentacene thin film transistors. J. Appl. Phys. 92, 5259–5263 (2002).
Sirringhaus, H., Tessler, N. & Friend, R. H. Integrated optoelectronic devices based on conjugated polymers. Science 280, 1741–1744 (1998).
McCulloch, I. et al. Liquid-crystalline semiconducting polymers with high charge-carrier mobility. Nature Materials 5, 328–333 (2006).
Matthews, J. R. et al. Scalable Synthesis of Fused Thiophene-Diketopyrrolopyrrole Semiconducting Polymers Processed from Nonchlorinated Solvents into High Performance Thin Film Transistors. Chem. Mater. 25, 782–789 (2013).
Acknowledgements
G. S. acknowledges postdoctoral fellowship support from the David and Alice van Buuren Funds of the Belgian American Educational Foundation (B.A.E.F.) and from the Fulbright Foundation (Fulbright Research Scholar Fellow). Z. B. acknowledges partial support from the Air Force Office of Scientific Research (FA9550-15-1-0106) and Samsung Electronics. R. P. acknowledges support from the Marie Curie Fellowship, TECNIOSPRING. T.H.L. acknowledges support from ILJU foundation in South Korea and Toshiba Corporation through CIS-FMA.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
C.W., W.-Y.L., D.K., R.P. and Z.B. conceived, designed and directed the project. C.W. and Z.B. designed the polymer. C.W. and R.N. screened the processing techniques. W.-Y.L., D.K., R.P., R.N., G.S., C.L., R.N. and H.-C.W. fabricated and tested the devices; J.M. tested the thermal properties and purification of the dielectric material. D.K., R.P., T.H.L. and Y.N. measured the dielectric capacitance. J.L. did theoretical calculation of the e-PVDF-HFP dielectric. Y.D. and X.G. measured and analyzed X-ray absorption patterns and GIXD patterns. S.H. and A.S. measured and analyzed the temperature-dependent properties. W.N., J.R.M and M.H. synthesized the PTDPPTFT4 semiconductive polymers.
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing financial interests.
Electronic supplementary material
Rights and permissions
This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License. The images or other third party material in this article are included in the article’s Creative Commons license, unless indicated otherwise in the credit line; if the material is not included under the Creative Commons license, users will need to obtain permission from the license holder to reproduce the material. To view a copy of this license, visit http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/
About this article
Cite this article
Wang, C., Lee, WY., Kong, D. et al. Significance of the double-layer capacitor effect in polar rubbery dielectrics and exceptionally stable low-voltage high transconductance organic transistors. Sci Rep 5, 17849 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1038/srep17849
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/srep17849
- Springer Nature Limited
This article is cited by
-
Stretchable transistors and functional circuits for human-integrated electronics
Nature Electronics (2021)
-
Fully stretchable active-matrix organic light-emitting electrochemical cell array
Nature Communications (2020)
-
Inkjet-printed stretchable and low voltage synaptic transistor array
Nature Communications (2019)
-
Long-range crystal alignment with polymer additive for organic thin film transistors
Journal of Polymer Research (2019)
-
Printable elastic conductors by in situ formation of silver nanoparticles from silver flakes
Nature Materials (2017)