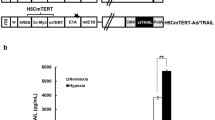
Abstract
TRAIL is a cytokine with a unique ability to induce apoptosis selectively in many transformed cell lines. The instability of TRAIL and the resistance of some cancer cells to TRAIL present the main obstacles for clinical experimentation. We generated an adenovirus expressing full-length TRAIL and tested its efficacy in several cancer cell lines. Ad-TRAIL-infected cancer cells localized full-length TRAIL protein to the cytoplasm and released same-sized TRAIL in the media. Ad-TRAIL was found to induce apoptotic cell death in several cancer cell lines resistant to soluble TRAIL (A549, SKOV3, HT-29 and LNCap) and in TRAIL-sensitive cell lines. Ad-TRAIL, but not soluble TRAIL, induced apoptotic cell death in TRAIL-resistant cell lines, manifested by an increased sub-G1 proportion, caspase-3 activation and PARP cleavage. Ad-TRAIL also induced a media-transferable bystander effect, but only in soluble TRAIL-sensitive cell lines. In conclusion, two novel characteristics of ad-TRAIL were found during this study. First, that ad-TRAIL can induce apoptotic cell death in several cancer cell lines resistant to sTRAIL. Second, that ad-TRAIL induces a media-transferable bystander effect, which is expected to increase its therapeutic value by allowing TRAIL to overcome the locally acting nature and low transduction rate commonly encountered in clinical situation.









Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- TRAIL:
-
Tumor necrosis factor related apoptosis inducing ligand
- Ad-TRAIL:
-
Adenovirus expressing TRAIL
- sTRAIL:
-
soluble TRAIL
- CAR:
-
Coxsackie adenoviral receptor
References
Wiley SR, Schooley K, Smolak PJ, et al. Identification and characterization of a new member of the TNF family that induces apoptosis. Immunity. 1995;3:673–682.
Griffith TS, Lynch DH . TRAIL: a molecule with multiple receptors and control mechanisms. Curr Opin Immunol. 1998;10:559–563.
Pan G, Ni J, Wei YF, Yu G, Gentz R, Dixit VM . An antagonist decoy receptor and a death domain-containing receptor for TRAIL. Science. 1997;277:815–818.
Gura T . How TRAIL kills cancer cells, but not normal cells. Science. 1997;277:768.
Ashkenazi A, Pai RC, Fong S, et al. Safety and antitumor activity of recombinant soluble Apo2 ligand. J Clin Invest. 1999;104:155–162.
Walczak H, Miller RE, Ariail K, Gliniak B, Griffith TS, Kubin M, et al. Tumoricidal activity of tumor necrosis factor-related apoptosis-inducing ligand in vivo. Nat Med. 1999;5:157–163.
Lee SH, Shin MS, Kim HS, et al. Alterations of the DR5/TRAIL receptor 2 gene in non-small cell lung cancers. Cancer Res. 1999;59:5683–5686.
Eggert A, Grotzer MA, Zuzak TJ, Wiewrodt BR, Ikegaki N, Brodeur GM . Resistance to TRAIL-induced apoptosis in neuroblastoma cells correlates with a loss of caspase-8 expression. Med Pediatr Oncol. 2000;35:603–607.
Griffith TS, Chin WA, Jackson GC, Lynch DH, Kubin MZ . Intracellular regulation of TRAIL-induced apoptosis in human melanoma cells. J Immunol. 1998;161:2833–2840.
Leverkus M, Neumann M, Mengling T, et al. Regulation of tumor necrosis factor-related apoptosis-inducing ligand sensitivity in primary and transformed human keratinocytes. Cancer Res. 2000;60:553–559.
Kim K, Fisher MJ, Xu SQ, el-Deiry WS . Molecular determinants of response to TRAIL in killing of normal and cancer cells. Clin Cancer Res. 2000;6:335–346.
Nagane M, Pan G, Weddle JJ, Dixit VM, Cavenee WK, Huang HJ . Increased death receptor 5 expression by chemotherapeutic agents in human gliomas causes synergistic cytotoxicity with tumor necrosis factor-related apoptosis-inducing ligand in vitro and in vivo. Cancer Res. 2000;60:847–853.
Nimmanapalli R, Perkins CL, Orlando M, O'Bryan E, Nguyen D, Bhalla KN . Pretreatment with paclitaxel enhances apo-2 ligand/tumor necrosis factor-related apoptosis-inducing ligand-induced apoptosis of prostate cancer cells by inducing death receptors 4 and 5 protein levels. Cancer Res. 2001;61:759–763.
Lacour S, Hammann A, Wotawa A, Corcos L, Solary E, Dimanche-Boitrel MT . Anticancer agents sensitize tumor cells to tumor necrosis factorrelated apoptosis-inducing ligand-mediated caspase-8 activation and apoptosis. Cancer Res. 2001;61:1645–1651.
Griffith TS, Anderson RD, Davidson BL, Williams RD, Ratliff TL . Adenoviral-mediated transfer of the TNF-related apoptosis-inducing ligand/Apo-2 ligand gene induces tumor cell apoptosis. J Immunol. 2000;165:2886–2894.
Kagawa S, He C, Gu J, et al. Antitumor activity and bystander effects of the tumor necrosis factor- related apoptosis-inducing ligand (TRAIL) gene. Cancer Res. 2001;61:3330–3338.
He TC, Zhou S, da Costa LT, Yu J, Kinzler KW, Vogelstein B . A simplified system for generating recombinant adenoviruses. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 1998;95:2509–2514.
Kim JY, Lee S, Hwangbo B, et al. NF-kappaB activation is related to the resistance of lung cancer cells to TNF-alpha-induced apoptosis. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2000;273:140–146.
Chinnaiyan AM, Prasad U, Shankar S, et al. Combined effect of tumor necrosis factor-related apoptosis-inducing ligand and ionizing radiation in breast cancer therapy. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 2000;97:1754–1759.
Thakkar H, Chen X, Tyan F, et al. Pro-survival function of Akt/protein kinase B in prostate cancer cells. Relationship with TRAIL resistance. J Biol Chem. 2001;276:38361–38369.
Lin T, Gu J, Zhang L, et al. Targeted expression of green fluorescent protein/tumor necrosis factor-related apoptosis-inducing ligand fusion protein from human telomerase reverse transcriptase promoter elicits antitumor activity without toxic effects on primary human hepatocytes. Cancer Res. 2002;62:3620–3625.
Voelkel-Johnson C, King DL, Norris JS . Resistance of prostate cancer cells to soluble TNF-related apoptosis-inducing ligand (TRAIL/Apo2L) can be overcome by doxorubicin or adenoviral delivery of full-length TRAIL. Cancer Gene Ther. 2002;9:164–172.
Lin T, Huang X, Gu J, et al. Long-term tumor-free survival from treatment with the GFP-TRAIL fusion gene expressed from the hTERT promoter in breast cancer cells. Oncogene. 2002;21:8020–8028.
Zhang L, Gu J, Lin T, Huang X, Roth JA, Fang B . Mechanisms involved in development of resistance to adenovirus-mediated proapoptotic gene therapy in DLD1 human colon cancer cell line. Gene Therapy. 2002;9:1262–1270.
Acknowledgements
This study was supported by a grant (HMP-00-B-20800-0072) of the Good Health R&D Project, Ministry of Health & Welfare, Republic of Korea.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Seol, J., Park, KH., Hwang, CI. et al. Adenovirus-TRAIL can overcome TRAIL resistance and induce a bystander effect. Cancer Gene Ther 10, 540–548 (2003). https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.cgt.7700597
Received:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.cgt.7700597
- Springer Nature America, Inc.
Keywords
This article is cited by
-
Co-delivery of TRAIL and paclitaxel by fibronectin-targeting liposomal nanodisk for effective lung melanoma metastasis treatment
Nano Research (2022)
-
Enhancing the antitumor activity of an engineered TRAIL-coated oncolytic adenovirus for treating acute myeloid leukemia
Signal Transduction and Targeted Therapy (2020)
-
Disulfide bond-disrupting agents activate the tumor necrosis family-related apoptosis-inducing ligand/death receptor 5 pathway
Cell Death Discovery (2019)
-
Regulating the expression of therapeutic transgenes by controlled intake of dietary essential amino acids
Nature Biotechnology (2016)
-
Adeno-associated virus-mediated doxycycline-regulatable TRAIL expression suppresses growth of human breast carcinoma in nude mice
BMC Cancer (2012)