Abstract
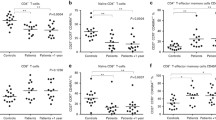
In multiple myeloma (MM) circulating CD19+ cells have been considered as myeloma precursors. As these cells are also possibly a reservoir of treatment resistant disease evaluation of the CD19+ cells during the course of high-dose therapy has to be a major concern. We determined the number of tumor cells in the CD19+ as well as CD19− fractions of PB of eight patients with disease sensitive to VA[I]D chemotherapy, of 10 patients who achieved partial or complete remission post-high-dose therapy (HDT) with peripheral blood stem cell transplantation (PBSCT) and of a further seven patients with disease progression post-transplantation. CD19+ cell fractions were obtained by preparative sequential magnetic and fluorescence activated cell sorting with a median purity of 97.1%. In addition, PB samples of seven patients post-transplantation were sorted for CD20+cells (median purity, 98.7%). The number of tumor cells in the CD19+, the CD19− and the CD20+ fractions were determined using a quantitative CDR3 PCR assay. The number of CD19+ tumor cells in patients in remission post-HDT was similar to those of the patients post-VA[I]D (median, 1.05 vs 0.92 CD19+ tumor cells/ml PB, P = 0.72) providing evidence for the persistence of this tumor cell fraction during the course of HDT. This was in contrast to the CD19−compartment, in which the number of tumor cells was significantly reduced in those patients in remission post-transplantation (median, 53 vs 0 CD19− tumor cells/ml PB; P= 0.006). In patients with progressive disease the number of tumor cells in both cell fractions was significantly higher (CD19+: median, 1.05 vs 21 tumor cells/ml PB, P = 0.05; CD19−: 0 vs 63 tumor cells/ml PB, P = 0.008). While the absolute number of CD19+ cells was reduced in the group of patients after VA[I]D treatment, a polyclonal CD19+ reconstitution had occurred in patients responding to HDT. The tumor cell content in the CD19+ fractions could be confirmed by the results obtained analyzing the CD20+ cell fractions. In conclusion, these results indicate that disease progression after PBSCT in MM is accompanied by an expansion of tumor cells in both the CD19+ and CD19− fractions. Similar numbers of CD19+ clonotypic cells post-HDT suggest that these cells persist and thus, contribute to disease dissemination and relapse.
Similar content being viewed by others
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kiel, K., Cremer, F., Rottenburger, C. et al. Analysis of circulating tumor cells in patients with multiple myeloma during the course of high-dose therapy with peripheral blood stem cell transplantation. Bone Marrow Transplant 23, 1019–1027 (1999). https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.bmt.1701767
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.bmt.1701767
- Springer Nature Limited
Keywords
This article is cited by
-
A multicenter phase I study of inebilizumab, a humanized anti-CD19 monoclonal antibody, in Japanese patients with relapsed or refractory B-cell lymphoma and multiple myeloma
International Journal of Hematology (2019)
-
MicroRNA theragnostics for the clinical management of multiple myeloma
Leukemia (2014)
-
Molecular monitoring of the tumor load predicts progressive disease in patients with multiple myeloma after high-dose therapy with autologous peripheral blood stem cell transplantation
Bone Marrow Transplantation (2001)
-
Evaluation of the kinetics of the bone marrow tumor load in the course of sequential high-dose therapy assessed by quantitative PCR as a predictive parameter in patients with multiple myeloma
Bone Marrow Transplantation (2000)