Abstract
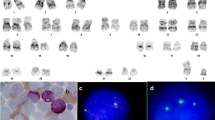
Secondary leukaemia has rarely been reported as a complication of autologous stem cell transplantation for AML. We report two cases of AML who presented with well-characterised cytogenetic abnormalities at presentation: t(8;21) and t(15;17) respectively, and who, after achieving complete morphological and cytogenetic remissions post-autograft, developed MDS/AML associated with monosomy 7. This secondary change is most frequently seen following alkylating agent therapy for solid tumours. The secondary leukaemia seen in our patients may thus be due to exposure of the residual stem cells to the alkylating agents used in the transplant conditioning.
Similar content being viewed by others
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Rege, K., Janes, S., Saso, R. et al. Secondary leukaemia characterised by monosomy 7 occurring post-autologous stem cell transplantation for AML. Bone Marrow Transplant 21, 853–855 (1998). https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.bmt.1701181
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.bmt.1701181
- Springer Nature Limited