Abstract
Background:
Although Trastuzumab has improved survival of HER2+ breast cancer patients, resistance to the agent pre-exists or develops through the course of therapy. Here we show that a specific metabolism and autophagy-related cancer cell phenotype relates to resistance of HER2+ breast cancer to Trastuzumab and chemotherapy.
Methods:
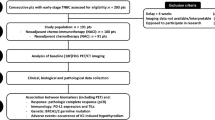
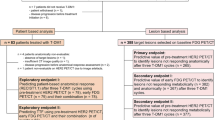
Twenty-eight patients with locally advanced primary breast cancer were prospectively scheduled to received one cycle of Trastuzumab followed by a new biopsy on day 21, followed by taxol/Trastuzumab chemotherapy for four cycles before surgery. FDG PET/CT scan was used to monitor tumour response. Tissue samples were immunohistochemically analysed for metabolism and autophagy markers.
Results:
In pre-Trastuzumab biopsies, the LC3A+/HER2+ cell population was correlated with HIF1α expression (P=0.01), while GLUT1 and LC3B expression were correlated with Ki67 proliferation index (P=0.01 and P=0.01, respectively). FDG PET tumour dimensions before therapy were correlated with LC3B expression (P=0.005). Administration of Trastuzumab significantly reduced clinical and PET-detected tumour dimensions (P<0.01). An inverse association of tumour response with the percentage of cells expressing HIF1α at baseline was documented (P=0.01). Administration of Trastuzumab resulted in a decrease of the proliferation index (P=0.004), GLUT1 (P=0.04) and HER2 (P=0.01) expression. In contrast, the percentage of LC3A+/HER2+ cells was increased (P=0.01). High baseline HIF1α expression was the only parameter associated with poorer pathological response to preoperative chemotherapy (P=0.001).
Conclusions:
As the HER2+/LC3A+ phenotype, which often overexpresses HIF1α, is a major subpopulation increasing after therapy with Trastuzumab, LC3A- and HIF1α-targeting therapies should be investigated for the augmentation of anti-HER2 therapy efficacy.
Similar content being viewed by others
Main
Breast cancer is the most frequent carcinoma in women with a lifetime risk affecting ∼12% of the total population (Siegel et al, 2012). The biology of the disease is heterogeneous and ∼20% of breast carcinomas overexpress the HER2/c-erbB-2 oncoprotein (Gajria and Chandarlapaty, 2011). This receptor, a member of the epidermal growth factor receptor family, has tyrosine kinase activity and is located at the breast cancer cell membrane. This dimerises with all members of the family, when they bind to various cognate ligands. This dimerisation induces autophosphorylation of tyrosine residues and initiates a signalling cascade within the cell. This includes activation of MAP-kinase, phosphoinositide 3-kinase/Akt and protein kinase-C, among others. As a result, tumours with a high percentage of HER2-positive cells assume an aggressive clinical behaviour so that overexpression is linked with poor post-operative outcome and increased resistance to chemotherapy (Gajria and Chandarlapaty, 2011). The introduction into clinical practice of anti-HER2 monoclonal antibodies or specific inhibitors of HER2 tyrosine kinase activity has resulted in important prolongation of overall survival, whether these are used as an adjuvant therapy, a component of chemotherapy for metastatic disease or as a component of neoadjuvant chemotherapy in locally advanced HER2 positive disease (Chang, 2010).
Nevertheless, only 35% of advanced HER2 positive tumours respond to anti-HER2 therapies and 70% of responders will develop disease progression during therapy (Gajria and Chandarlapaty, 2011). Intrinsic resistance of cancer cells is certainly a major determinant of the efficacy of Trastuzumab. PTEN suppression, SRC nonmembrane tyrosine kinase overexpression and constitutive PIK3/Akt activation have been identified as components of intrinsic resistance (Nagata et al, 2004; Narayan et al, 2009; Figure 2A–C. A significant association between LC3A and LC3B was also found (P=0.01, r=0.38).
Linear regression between immunohistochemical variables as assessed before therapy between the percentage of LC3A+/HER2+ and HIF1 α + cells ( A ), the percentage of GLUT1+ and Ki67+ cancer cells ( B ) and the percentage of LC3B+ and Ki67+ cancer cells ( C ) is shown in A – C , respectively. Group analysis between PET dimensions, SUVmax and T-stage, Ki67 proliferation index and LC3B expression is shown in D–F), respectively.
PET vs histology and immunohistochemical variables
Tumour dimensions as assessed by PET imaging ranged from 10 to 68 mm (median 23 mm). In linear regression analysis, PET dimensions were also correlated with advanced T-stage (P=0.01, r=0.21), high histology grade (P=0.05, r=0.38) and with LC3B expression (P=0.005, r=0.27). In group analysis (T1, 2 vs T3, 4), the association of PET dimensions with T-stage did not reach significance (P=0.09; Figure 2D), whereas a strong correlation with high Ki67 proliferation index was documented (P=0.0009; Figure 2E). Similarly, tumours with high LC3B levels were significantly larger in PET images (P=0.05; Figure 2F) No significant association was recorded for the rest of the variables.
SUVmax ranged from 2.1 to 15.7 (median 7.5) and linear regression analysis showed a correlation with PET size (P=0.01, r=0.48). The only other association was a correlation with the percentage of HER2-positive cells (P=0.05, r=0.33). There was no association with T-stage, Ki67 index and LC3B staining (Figure 2D–F) or with any other variable.
Response to Trastuzumab
Administration of Trastuzumab significantly reduced overall tumour dimensions, whether assessed clinically (39.9±2 vs 28.7±22; P=0.01) or with PET (28.7±2 vs 23.2±1; P=0.004); Figure 3A. There was also a significant reduction of the SUV values (7.8±3 vs 4.7±3; P<00001); Figure 3B. Figure 3C shows individual changes of SUVmax, before and after Trastuzumab administration.
Reduction of PET dimensions and of SUVmax after one cycle of Trastuzumab therapy is shown in A, B and C, respectively. Linear regression analysis of reduction of clinical dimensions vs PET dimension reduction, SUVmax reduction and reduction of HF1α-positive cells after trastuzmab is shown in D–F) respectively. Group analysis according to HIF1α status (low vs high) of percentage reduction of PET dimensions is shown in Figure 1G. Group analysis according to HER2 status (low vs high) of percentage reduction of SUVmax is shown in (H). Bars show standard errors and midline the mean value.
The effect of the pathology variables on response to Trastuzumab and on SUVmax was studied. The percentage of clinical or PET-assessed tumour response was calculated as the ratio ‘(initial dimensions−final dimensions)/initial dimensions’. A similar ratio was also calculated for the SUV reduction. Using this ratio, we assessed the percentage of tumour (or SUV) reduction after Trastuzumab administration. Linear regression analysis of response revealed a significant association of the percentage reduction of clinical dimensions with percentage reduction of PET dimension and SUV (Figure 3D and E). A significant inverse association of the baseline percentage of HIF1α+ cells with reduction of clinical dimensions was confirmed (Figure 3F), showing an important association of HIF1α expression with resistance of breast cancer to Trastuzumab therapy. Group analysis, using 50% reduction as a cutoff point to define tumours with low vs high HIF1α reactivity, confirmed a significant association of high HIF1α with resistant tumours (P=0.01); Figure 3G. The association of SUVmax reduction with the percentage of HER2+ cells was not significant (P=0.08; Figure 3H).
Effect of Trastuzumab on the expression of autophagy, proliferation markers and HER2
Tru-cut biopsies obtained on day 21 following administration of Trastuzumab were immunohistochemically analysed. Administration of Trastuzumab resulted in a significant decrease of the proliferation index (29.7±15 vs 24.4±15; P=0.004), and of GLUT1 expression (28±22 vs 13±18; P=0.04); Figure 4A), whereas there was no significant effect on HIF1α expression (42±36 vs 36±35; P=0.75).
Changes of the immunohistochemical profile of tumours after one cycle of Trastuzumab therapy. (A) Ki67 and GLUT1; (B) HER2, LC3A and LC3B; (C) combined HER2/LC3A and HER2/LC3B. Initial pre-therapy content of HIF1α- (D) and of PgR-positive cells (E) according to response to Trastuzumab plus taxol therapy (bars show standard errors and midline the mean value.
A significant reduction of the HER2+ cell population in the tumours was noted (89±21 vs 70±38; P=0.01; Figure 4B) after exposure to Trastuzumab. The percentage of cells with LC3A expression was significantly increased after therapy (26±21 vs 49±26; P=0.005; Figure 4B). There was no difference in LC3B-positive cells (31±27 vs 27±24; P=0.85; Figure 4B). In double immunostaining, focusing on the total cell population, the percentage of cells expressing simultaneously HER2 and LC3A was increased after the administration of Trastuzumab (30±23 vs 43±29; P=0.01; Figure 4C). Such a difference was not shown for the HER2+/LC3B cell population (45±36 vs 49±35; P=0.16; Figure 4C).
Response to taxol plus Trastuzumab therapy
The response rate (RR) as assessed by comparing the maximal two-dimensional size of post-operative tumour samples with the initial (pre-Trastuzumab) clinically assessed dimensions ranged from 0% to 100%, with a median value of 70%. The RR was calculated as the ratio ‘(initial clinical dimensions−final surgical dimensions)/initial clinical dimensions’. Using this value two groups were formed (low vs high RR). Group analysis revealed a significant association of high-baseline (pre-Trastuzumab) HIF1α expression with low RR (P=0.001) and of high-baseline PgR, but not ER, expression with high RR (P=0.04); Figure 4D and E. No further associations were documented.
Discussion
Identification of molecular pathways involved in resistance of HER2-positive breast cancer to anti-HER2 monoclonal antibodies and molecular targeted therapies is of high clinical relevance. Effective restoration of cancer cell sensitivity would improve survival in a poor prognosis subgroup of breast cancer patients, composing ∼30% of the total patient population. Signalling pathways involving PTEN, SRC, the Akt kinase or the c-met proteins have been identified as major determinants of resistance to anti-HER2 therapies (Nagata et al, 2004; Narayan et al, 2009; Zhang et al, 2011; Minuti et al, 2012).
In the current prospective clinicopathological study we investigated metabolism and autophagy-related tumour features that could influence clinical response to Trastuzumab and to Trastuzumab plus taxol. Immunohistochemical analysis of pre-Trastuzumab tumour biopsies revealed that a tumour subpopulation of HER2+/LC3A+ cells, that is, HER2+ cells with high LC3A autophagic activity, was strongly associated with the overexpression of HIF1α. The direct association between HIF1a and HIF2a expression with HER2 in breast cancer has been previously reported (Bos et al, 2003; Giatromanolaki et al, 2006). HER2 overexpression has been previously shown to directly regulate synthesis of HIF1α and it was shown that HIF1α directly induces mitophagy through BNIP3 (Laughner et al, 2001; Bellot et al, 2009). Of interest, Whelan et al (2013) demonstrate that ERBB2 requires HIF1 for tumour growth and that HIF is a major downstream regulator of HER2, protecting breast cancer cells from anoikis and metabolic stress. HIF1 and LC3 autophagy have been also shown to be involved in cancer–stem cell phenotype induction (Zhu et al, 2013). Overexpression of HIF1 and anaerobic metabolism has been persistently linked with LC3A expression in a large number of studies performed by our group in different tumour types (Giatromanolaki et al, 2010; Giatromanolaki et al, 2011; Giatromanolaki et al, 2013). Thus, there is strong evidence linking anaerobic metabolism, LC3A and HER2 expression in the literature.
Of interest, high expression of LC3B, an additional marker of autophagosomal formation, was associated with high proliferation index; the latter correlated with overexpression of glucose transporter GLUT1. Moreover, increased PET scan tumour dimensions were associated with LC3B overexpression. These are in accordance with a study by Lazova et al (2012) where LC3B was linked with high proliferation in solid tumours including breast cancer. Overall, the findings confirm a close link between hypoxia, glycolytic metabolism and active autophagic pathways in HER2+ breast cancer. However, they indicate that the autophagy pathway may have more complex links because of the heterogeneity of expression and correlations of atg8-related group of homologous proteins, LC3A and B, with the other pathways.
Comparative study of pre-Trastuzumab and post-Trastuzumab tumour biopsies obtained 21 days after administration revealed important transitions of the immunohistochemical profile. Trastuzumab therapy resulted in decrease of HER2 expression in the tumour. This was possibly a result of direct cytotoxic effect on HER2+ cells, which is supported by the reduction on tumour dimensions 21 days post-therapy. The proliferation index was sharply reduced as a result of exposure to Trastuzumab. Of interest, the LC3A and the HER2+/LC3A+ subpopulation was significantly more abundant in the post-Trastuzumab biopsies. Taking into account that the HER2+/LC3A+ cell population increases after Trastuzumab, on a background of an overall decrease of HER2+ total population, we suggest that breast cancer cells expressing LC3A are resistant to Trastuzumab cytotoxic effect and persist in post-therapy biopsies. LC3A-dependent autophagy may therefore define resistance to Trastuzumab. Of interest, two important studies in the literature support the hypothesis that autophagy is involved in breast cancer resistance to HER2-targeted therapies (Vazquez-Martin et al, 2009; Cufi et al, 2012). An additional study supports that macro-autophagy is also involved in the resistance of cancer cells to tamoxifen (Qadir et al, 2008), suggesting that autophagy, and presumably LC3A-targeting agents, may prove to be of importance in both breast cancer chemotherapy and hormonal therapy.
The observation that, in contrast to LC3B, only LC3A is linked with HER2 expression and with resistance of HER2+ cells to Trastuzumab is interesting and demands further investigation. Nevertheless, LC3B is also an important autophagy marker, and was strongly associated with cancer cell proliferation and tumour dimensions, and thus growth. This emerging different biological role of the two LC3s is not surprising. Our group has persistently studied and reported that LC3A and LC3B are not at all identical. Even in normal tissues, according to immunoblotting work, the LC3A protein follows discrete patterns of LC3A-I and LC3A-II changes in liver, lung, kidney and heart tissues of mice, whereas the LC3B protein does not follow the same pattern under stressed conditions, showing a cell type-specific function of these two molecules (Zois et al, 2011). In confocal microscopy in breast and many other cancer cell lines, LC3A and LC3B autophagosomes are not identical and present different subcellular distribution (submitted data). Moreover, a widespread confusion on the role of LC3A vs LC3B autophagy in cancer exists because of the usage of antibodies that either recognise both LC3 forms or erroneously are believed to recognise only LC3B (Koukourakis et al, 2013). In fact, there is growing evidence that the biology behind LC3A-mediated autophagy is not identical to the LC3B one. The observation that LC3A is associated with HER2 in breast cancer as noted in the current study is preliminary and will need further study. On the other hand, LC3B autophagy seems also to be important in breast cancer biology, although rather less related to HER2.
Trastuzumab induced a significant reduction of tumour size in terms of both clinical and PET measurements. SUVmax was also significantly reduced, in accordance to the reduction of tumour proliferation, as assessed with immunohistochemistry. Among the immunohistochemical variables assessed, the overexpression of HIF1α was strongly correlated with the resistance of breast tumours to Trastuzumab. In a recent study HIF1α has been shown to be essential for the growth effect of HER2 activation in breast cancer (Whelan et al, 2013). Blocking HIF1α helped to overcome resistance of hepatoma or lung cancer cells to multikinase or EGFR inhibitors (Minakata et al, 2012; Liang et al, 2013). In our study, HIF1α was further found to be the only important factor predicting poor response of HER2-positive tumours to Trastuzumab plus Taxol, which may a direct effect on increasing intrinsic cancer cell chemoresistance. Indeed, this latter effect of HIF1α has been confirmed for cisplatin and doxorubicin in lung cancer cells (Song et al, 2006). As the HIF1α expression did not change significantly on Trastuzumab, even though the percentage of HER2- and GLUT1 (a HIF1α target gene)-positive cells went down, this implies additional mechanisms besides HER2 or hypoxia driving HIF1α (e.g., other upstream signalling pathways such as Akt and mTOR). The relation of PgR with overall response to Trastuzumab plus Taxol demands further investigation.
The results of the current study, although based on limited material and being certainly of preliminary nature, provide clinical evidence to add to previous experimental data that support a role of autophagy as a contributor to resistance of HER2-positive breast cancer to Trastuzumab. Moreover, the study suggests that HIF1α expression may serve as a baseline biomarker of resistance to Trastuzumab. The HER2+/LC3A+ phenotype, which often overexpressed HIF1α, was revealed as a major subpopulation refractory to Trastuzumab alone. This suggests that LC3A and HIF1α-targeting therapies may prove critical for the augmentation of anti-HER2 therapy efficacy. Further experimental studies are now needed to follow up these observations before scheduling randomised trials investigating the value of autophagy inhibitors in trastuzumab-based chemotherapy.
Change history
29 April 2014
This paper was modified 12 months after initial publication to switch to Creative Commons licence terms, as noted at publication
References
Bellot G, Garcia-Medina R, Gounon P, Chiche J, Roux D, Pouysségur J, Mazure NM (2009) Hypoxia-induced autophagy is mediated through hypoxia-inducible factor induction of BNIP3 and BNIP3L via their BH3 domains. Mol Cell Biol 29: 2570–2581.
Bos R, van der Groep P, Greijer AE, Shvarts A, Meijer S, Pinedo HM, Semenza GL, van Diest PJ, van der Wall E (2003) Levels of hypoxia-inducible factor-1alpha independently predict prognosis in patients with lymph node negative breast carcinoma. Cancer 97: 1573–1581.
Chang HR (2010) Trastuzumab-based neoadjuvant therapy in patients with HER2-positive breast cancer. Cancer 116: 2856–2867.
Cufi S, Vazquez-Martin A, Oliveras-Ferraros C, Corominas-Faja B, Urruticoechea A, Martin-Castillo B, Menendez JA (2012) Autophagy-related gene 12 (ATG12) is a novel determinant of primary resistance to HER2-targeted therapies: utility of transcriptome analysis of the autophagy interactome to guide breast cancer treatment. Oncotarget 3: 1600–1614.
Gajria D, Chandarlapaty S (2011) Review HER2-amplified breast cancer: mechanisms of Trastuzumab resistance and novel targeted therapies. Expert Rev Anticancer Ther 11: 263–275.
Giatromanolaki A, Sivridis E, Fiska A, Koukourakis MI (2006) Hypoxia-inducible factor-2 alpha (HIF-2 alpha) induces angiogenesis in breast carcinomas. Appl Immunohistochem Mol Morphol 14: 78–82.
Giatromanolaki AN, Charitoudis GS, Bechrakis NE, Kozobolis VP, Koukourakis MI, Foerster MH, Sivridis EL (2011) Autophagy patterns and prognosis in uveal melanomas. Mod Pathol 24: 1036–1045.
Giatromanolaki A, Koukourakis MI, Pouliliou S, Gatter KC, Pezzella F, Harris AL, Sivridis E (2013) Overexpression of LC3A autophagy protein in follicular and diffuse large B-cell lymphomas. Hematol Oncol Stem Cell Ther 6: 20–25.
Giatromanolaki A, Koukourakis MI, Harris AL, Polychronidis A, Gatter KC, Sivridis E (2010) Prognostic relevance of light chain 3 (LC3A) autophagy patterns in colorectal adenocarcinomas. J Clin Pathol. 63: 867–872.
Koukourakis MI, Giatromanolaki A, Zois CE, Sivridis E (2013) LC3 immunostaining pitfalls. Histopathology 62: 962–963.
Laughner E, Taghavi P, Chiles K, Mahon PC, Semenza GL (2001) HER2 (neu) signaling increases the rate of hypoxia-inducible factor 1alpha (HIF-1alpha) synthesis: novel mechanism for HIF-1-mediated vascular endothelial growth factor expression. Mol Cell Biol 21: 3995–4004.
Lazova R, Camp RL, Klump V, Siddiqui SF, Amaravadi RK, Pawelek JM (2012) Punctate LC3B expression is a common feature of solid tumors and associated with proliferation, metastasis, and poor outcome. Clin Cancer Res 18: 370–379.
Liang Y, Zheng T, Song R, Wang J, Yin D, Wang L, Liu H, Tian L, Fang X, Meng X, Jiang H, Liu J, Liu L (2013) Hypoxia-mediated sorafenib resistance can be overcome by EF24 through Von Hippel-Lindau tumor suppressor-dependent HIF-1α inhibition in hepatocellular carcinoma. Hepatology 57: 1847–1857.
Minakata K, Takahashi F, Nara T, Hashimoto M, Tajima K, Murakami A, Nurwidya F, Yae S, Koizumi F, Moriyama H, Seyama K, Nishio K, Takahashi K (2012) Hypoxia induces gefitinib resistance in non-small-cell lung cancer with both mutant and wild-type epidermal growth factor receptors. Cancer Sci 103: 1946–1954.
Minuti G, Cappuzzo F, Duchnowska R, Jassem J, Fabi A, O'Brien T, Mendoza AD, Landi L, Biernat W, Czartoryska-Arłukowicz B, Jankowski T, Zuziak D, Zok J, Szostakiewicz B, Foszczyńska-Kłoda M, Tempińska-Szałach A, Rossi E, Varella-Garcia M (2012) Increased MET and HGF gene copy numbers are associated with Trastuzumab failure in HER2-positive metastatic breast cancer. Br J Cancer 107: 793–799.
Nagata Y, Lan KH, Zhou X, Tan M, Esteva FJ, Sahin AA, Klos KS, Li P, Monia BP, Nguyen NT, Hortobagyi GN, Hung MC, Yu D (2004) PTEN activation contributes to tumor inhibition by Trastuzumab, and loss of PTEN predicts Trastuzumab resistance in patients. Cancer Cell 6: 117–127.
Narayan M, Wilken JA, Harris LN, Baron AT, Kimbler KD, Maihle NJ (2009) Trastuzumab-induced HER reprogramming in ‘resistant’ breast carcinoma cells. Cancer Res 69: 2191–2194.
Qadir MA, Kwok B, Dragowska WH, To KH, Le D, Bally MB, Gorski SM (2008) Macroautophagy inhibition sensitizes tamoxifen-resistant breast cancer cells and enhances mitochondrial depolarization. Breast Cancer Res Treat 112: 389–403.
Siegel R, DeSantis C, Virgo K, Stein K, Mariotto A, Smith T, Cooper D, Gansler T, Lerro C, Fedewa S, Lin C, Leach C, Cannady RS, Cho H, Scoppa S, Hachey M, Kirch R, Jemal A, Ward E (2012) Cancer treatment and survivorship statistics, 2012. CA Cancer J Clin 62: 220–241.
Song X, Liu X, Chi W, Liu Y, Wei L, Wang X, Yu J (2006) Hypoxia-induced resistance to cisplatin and doxorubicin in non-small cell lung cancer is inhibited by silencing of HIF-1alpha gene. Cancer Chemother Pharmacol 58: 776–784.
Vazquez-Martin A, Oliveras-Ferraros C, Menendez JA (2009) Autophagy facilitates the development of breast cancer resistance to the anti-HER2 monoclonal antibody Trastuzumab. PloS One 4: e6251.
Whelan KA, Schwab LP, Karakashev SV, Franchetti L, Johannes GJ, Seagroves TN, Reginato MJ (2013) The oncogene HER2/neu (ERBB2) requires the hypoxia-inducible factor HIF-1 for mammary tumor growth and anoikis resistance. J Biol Chem 288: 15865–15877.
Zhang S, Huang WC, Li P, Guo H, Poh SB, Brady SW, **ong Y, Tseng LM, Li SH, Ding Z, Sahin AA, Esteva FJ, Hortobagyi GN, Yu D (2011) Combating Trastuzumab resistance by targeting SRC, a common node downstream of multiple resistance pathways. Nat Med 17: 461–469.
Zois CE, Giatromanolaki A, Sivridis E, Papaiakovou M, Kainulainen H, Koukourakis MI (2011) ‘Autophagic flux’ in normal mouse tissues: focus on endogenous LC3A processing. Autophagy 7: 1371–1378.
Zhu H, Wang D, Liu Y, Su Z, Zhang L, Chen F, Zhou Y, Wu Y, Yu M, Zhang Z, Shao G (2013) Role of the Hypoxia-inducible factor-1 alpha induced autophagy in the conversion of non-stem pancreatic cancer cells into CD133+ pancreatic cancer stem-like cells. Cancer Cell Int 13: 119.
Acknowledgements
The study has been financially supported by the Tumour and Angiogenesis Research Group, ARCO Onlus (Cremona-Italy), Cancer Research UK and the Breast Cancer Research Foundation.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Additional information
This work is published under the standard license to publish agreement. After 12 months the work will become freely available and the license terms will switch to a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-Share Alike 3.0 Unported License.
Rights and permissions
From twelve months after its original publication, this work is licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-Share Alike 3.0 Unported License. To view a copy of this license, visit http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc-sa/3.0/
About this article
Cite this article
Koukourakis, M., Giatromanolaki, A., Bottini, A. et al. Prospective neoadjuvant analysis of PET imaging and mechanisms of resistance to Trastuzumab shows role of HIF1 and autophagy. Br J Cancer 110, 2209–2216 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1038/bjc.2014.196
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/bjc.2014.196
- Springer Nature Limited