Abstract
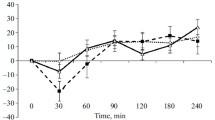
SEVERAL, studies have shown that the narcotic analgesic morphine and morphine-like compounds reduce the release of acetylcholine (ACh) at peripheral cholinergic junctions1–3, but there is relatively little evidence that they have a similar action on the central nervous system. Beleslin and Polak4 have shown that an intraventricular infusion of morphine in the anaesthetized cat leads to a modest decrease in the release of ACh into the cerebrospinal fluid. The morphine antagonists nalorphine (‘Nalline’) and levallorphan (‘Lorfan’) have been shown to reduce ACh released from the ileum of the guinea-pig, but a comparable action on the release of ACh from the brain has not been demonstrated. There is evidence that the brain contains a system of cholinergic neurones with terminals which project to the cerebral cortex5,6 and release ACh at the cortical surface7. If morphine impaired the release of ACh at the cortical level, and if this action was antagonized by narcotic antagonists such as levallorphan, nalorphine and naloxone, such a reversal cf morphine action by the antagonists could yield important information about the neurohumoral changes associated with the hyperactive state which follows the acute withdrawal of morphine in animals and man8. We have therefore investigated the action of morphine on the cortical release of ACh and compared this action with that of morphine antagonists.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Cox, B. M., and Weinstock, M., Brit. J. Pharmacol., 27, 81 (1966).
Gyang, E. A., and Kosterlitz, H. W., Brit. J. Pharmacol., 27, 514 (1966).
Pelikan, E. W., Ann. NY Acad. Sci., 90, 52 (1960).
Beleslin, D., and Polak, L., J. Physiol., 177, 411 (1965).
Shute, C. C. D., and Lewis, P. R., Brain, 90, 497 (1967).
Krnjević, K., and Phillis, J. W., J. Physiol., 166, 296 (1963).
Phillis, J. W., Brain Res., 7, 378 (1968).
Seevers, M. H., and Deneau, G. A., Physiol. Pharmacol., 1, 565 (1963).
Mitchell, J. F., J. Physiol., 165, 98 (1963).
Kosterlitz, H. W., Lees, G. M., and Watt, A. J., Pharmacol. Res. Commun., 1, 42 (1969).
Ramkhen, I. F., Psychopharmacol. Abstracts, 7, 12 (1968).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
JHAMANDAS, K., PINSKY, C. & PHILLIS, J. Effects of Morphine and its Antagonists on Release of Cerebral Cortical Acetylcholine. Nature 228, 176–177 (1970). https://doi.org/10.1038/228176a0
Received:
Revised:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/228176a0
- Springer Nature Limited
This article is cited by
-
Stimulatory effects of opioids on transmitter release and possible cellular mechanisms: Overview and original results
Neurochemical Research (1996)
-
Studies of the role of opioids in control of human pancreatic secretion
Digestive Diseases and Sciences (1988)
-
Effect of endorphins on amylase secretion from rat pancreasIn vivo andIn vitro
Digestive Diseases and Sciences (1985)
-
Brain acetylcholine during morphine withdrawal
Neurochemical Research (1984)
-
Cross-tolerance between morphine and cholinergic blocking agents microinjected into anterior amygdala
Nature (1977)