Abstract
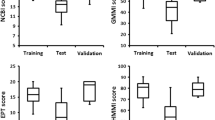
Benthic macroinvertebrates samples were collected in spring and autumn 2000. Fifteen streams in southern Sweden were sampled twice both for chemical, physical, and biological parameters. Eighty-four macroinvertebrate `single' metrics were calculated and tested for their ability of detecting organic pollution of streams. A comparison of the `best' single metrics with two multimetric indices was also done. The Belgian Biotic Index (BBI), the Average Score Per Taxon (ASPT), the Saprobic Index (Zelinka & Marvan), the German Saprobic Index, percentage hypopotamal preferences, the Danish Stream Fauna Index (DSFI) and percentage pelal preferences were found to be good indicators of organic pollution. Both DSFI and ASPT are frequently used for detecting organic pollution in southern Sweden and could be recommended for further use. Although saprobic indices are not commonly used in Sweden, our results indicate that they may be appropriate. BBI, percentage hypopotamal preferences, and percentage pelal preferences are seldom used for detecting organic pollution of Swedish streams, but could maybe prove useful for future uses. Two multimetric indices recently developed for detecting the effects of organic pollution in southern Sweden, the AQEM Type S05 Index and the DJ Index, were compared to the `best' single metrics by determining their responses to total phosphorous concentration, conductivity, and percentage cropland. The comparison showed that the DJ Index proved to be a better indicator of the effects of organic pollution than the single metrics. The other multimetric index, the AQEM Type S05 Index, had slightly lower statistical power, but performed well in comparison to the other metrics.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Alba-Tercedor, J. & A. Sanchez-Ortega, 1988. Un metodo rapido y simple para evaluar la calidad biologica de las aguas corrientes basado en el de Hellawell (1978). Limnetica 4: 51–56.
Armitage, P. D., D. Moss, J. F. Wright & M. T. Furse, 1983. The performance of a new biological water quality score system based on macroinvertebrates over a wide range of unpolluted running-water sites. Wat. Res. 17: 333–347.
AQEM consortium, 2002. Manual for the application of the AQEM system. A comprehensive method to assess European streams using benthic macroinvertebrates, developed for the purpose of the Water Framework Directive. Version 1.0, February 2002.
Barbour, M. T. & C. O. Yoder, 2000. The multimetric approach to bioassessment, as used in the United States of America. In Wright, J. F., D. W. Sutcliffe & M. T. Furse (eds), Assessing the biological quality of fresh waters: RIVPACS and other techniques. Freshwat. Biol., Ambleside, UK: 281–292.
Chandler, J. R., 1970. A biological approach to water quality management. Wat. Pollut. Contr. 69: 415–421.
Dahl, J. & R. K. Johnson, 2003. A multimetric macroinvertebrate index for detecting organic pollution of streams in southern Sweden. Arch. Hydrobiol (submitted).
De Pauw, N. & G. Vanhooren, 1983. Method for biological quality assessment of watercourses in Belgium. Hydrobiologia 100: 153–168.
European Commission, 2000. Directive 2000/60/EC of the European Parliament and of the Council-Establishing a framework for Community action in the field of water policy. Brussels, Belgium, 23 October 2000.
Fore, L. S., J. R. Karr & R. W. Wisseman, 1996. Assessing invertebrate responses to human activities: Evaluating alternative approaches. J. North Am. Benthol. Soc. 15: 212–231.
Friedrich, G., 1990. Eine Revision des Saprobiensystems. Zeitschrift für Wasser und Abwasser Forschung 23: 141–152.
Ghetti, P. F., 1997. Indicie Biotico Esteso (I.B.E.). I macroinvertebrati nel controllo della qualità degli ambienti di acque correnti. Provincia Autonoma di Trento, 222 pp.
Hellawell, J., 1978. Biological surveillance of rivers, a biological monitoring handbook. Water Research Centre, Medmenham and Stevenage, UK, 331 pp.
Hering, D., A. Buffagni, O. Moog, L. Sandin, M. Sommerhäuser, I. Stubauer, C. Feld, R. K. Johnson, P. Pinto, N. Skoulikidis, P. Verdonschot & S. Zahrádková, 2003. The development of a system to assess the ecological quality of streams based on macroinvertebrates-design of the sampling programme within the AQEM project. Int. Rev. Hydrobiol (in press).
Hering, D., O. Moog, L. Sandin & P. F. M. Verdonschot, 2004. Overview and application of the AQEM assessment system. Hydrobiologia 516: 1–20.
Hughes, R. M., 1994. Defining acceptable biological status by comparing with reference conditions. In Davies, W. S. & T. P. Simon (eds), Biological Assessment and Criteria. Tools for water resource planning and decision making. Lewis Publishers, Boca Raton, Fl: 31–48.
Illies, J. (ed.), 1978. Limnofauna Europaea. Gustav Fischer Verlag, Stuttgart.
International Organisation for Standardization (ISO), 1979. Assessment of the biological quality of rivers by a macroinvertebrate 'score'. ISO/TC 147/SC 5/WG 6 N 5, 18 pp.
Johnson, R. K., 1995. The indicator concept in freshwater biomonitoring. Thienemann lecture. In Cranston, P. S. (ed.), Chironomids-from Genes to Ecosystems, Proceedings of the 12th International Symposium in Chironomidae, Canberra, Australia. CSIRO, Melbourne: 11–27.
Johnson, R. K., 1998. Benthic macroinvertebrates. In Wiederholm, T. (ed.), Bedömningsgrunder för miljökvalitet. Sjöar och vattendrag. Bakgrundsrapport 2. Biologiska parametrar. Report 4921, Naturvårdsverket, Uppsala: 85–166.
Johnson, R. K., T. Wiederholm & D. M. Rosenberg, 1993. Freshwater biomonitoring using individual organisms, populations and species assemblages of benthic macroinvertebrates. In Rosenberg, D. M. & V. H. Resh (eds), Freshwater Biomonitoring and Benthic Macroinvertebrates. Chapman and Hall, New York: 40–158.
Karr, J. R., 1981. Assessment of biotic integrity using fish communities. Fisheries 6: 21–27.
Kolkwitz, R. & M. Marsson, 1902. Grundsätse für die biologische Beurteiling des Wassers nach seiner Flora und Fauna. Mitt. Prüfungsanst. Wasserversorg. Abwasserreinig. 1: 33–72.
Metcalfe, J. L., 1989. Biological water-quality assessment of running waters based on macroinvertebrate communities-history and present status in Europe. Envir. Pollut. 60: 101–139.
Moog, O. (ed.), 1995. Fauna Aquatica Austriaca-A comprehensive species inventory of Austrian aquatic organisms with ecological notes, 1st edition. Wasserwirtschaftskataster, Bundesministerium für Land-und Forstwirtschaft, Wien.
Ofenböck, T., O. Moog, J. Gerritsen & M. Barbour, 2004. A stressor specific multimetric approach for monitoring running waters in Austria using benthic macro-invertebrates. Hydrobiologia 516: 251–268.
Polls, I., 1994. How people in the regulated community view biological integrity. J. North Am. Benthol. Soc. 13: 598–604.
Resh, V. H., D. M. Rosenberg & T. B. Reynoldson, 2000. Selection of benthic macroinvertebrate metrics for monitoring water quality of the Frazer River, British Colombia: implications for both multimetric approaches and multivariate models. In Wright, J. F., D. W. Sutcliffe & M. T. Furse (eds), Assessing the Biological Quality of Fresh Waters: RIVPACS and other techniques. Freshwat. Biol., Ambleside, UK: 195–206.
Rosenberg, D. M. & V. H. Resh, 1993. Introduction to freshwater biomonitoring and benthic macroinvertebrates. In Rosenberg, D. M. & V. H. Resh (eds), Freshwater Biomonitoring and Benthic Macroinvertebrates. Chapman & Hall, New York: 1–9.
Sandin, L., J. Dahl & R. K. Johnson, 2004. Assessing acid stress in Swedish boreal and alpine streams using benthic macroinvertebrates. Hydrobiologia 516: 129–148.
Schmidt-Kloiber, A. & R. C. Nijboer, 2004. The effect of taxonomic resolution on the assessment of ecological water quality classes. Hybrobiologia 516: 269–283.
Skoulikidis, N. Th., K. C. Gritzalis, T. Kouvarda & A. Buffagni, 2004. The development of an ecological quality assessment and classification system for Greek running waters based on benthic macroinvertebrates. Hydrobiologia 516: 149–160.
Skriver, J., N. Friberg & J. Kirkegaard, 2000. Biological assessment of running waters in Denmark: Introduction of the Danish Stream Fauna Index (DSFI). Verh. Int. Ver. Limnol. 27: 1822–1830.
Sladeček, V., H. A. Hawkes, J. S. Alabaster, I. Daubner, I. Nötlich, J. F. d. Solbé & D. Uhlman, 1982. Biological examination. In Suess, M. J. (ed.), Examination of Water for Pollution Control. A Reference Handbook, Vol. 3. Biological, Bacteriological and Virological Examination. Pergamon Press, Oxford, 531 pp.
Stanner, D. & P. Bordeau, 1995. Europe's Environment: The Dobris Assessment. European Environment Agency, Luxembourg, 712 pp.
Suter, G. W., 1993. A critique of ecosystem health concepts and indexes. Environ. Toxicol. Chem. 12: 1533–1539.
ter Braak, C. J. F. & I. C. Prentice, 1988. A theory of gradient analysis. Adv. Ecol. Res. 18: 271–317.
Vlek H. E., P. F. M. Verdonschot & R. C. Nijboer, 2004. Towards a multimetric index for the assessment of Dutch streams using benthic macroinvertebrates. Hydrobiologia 516: 173–189.
Whitton, B. A., 1979. Algae and higher plants as indicators of river pollution. In James, A. & L. Evison (eds), Biological Indicators of Water Quality. John Wiley, Chichester, 597 pp.
Wiederholm, T., 1980. Use of benthos in lake monitoring. J. Wat. Pollut. Cont. Fed. 52: 537–547.
Wiederholm, T. & R. K. Johnson, 1997. Monitoring and assessment of lakes and watercourses in Sweden. In Ottens, J. J., F. A. M. Claessen et al. (eds), Monitoring Tailor-made II. Information Strategies in Water Management. Proceedings from an international workshop, 1996, Nunspeet, The Netherlands: 317–329.
Wilander, A., R. K. Johnson, W. Goedkoop & L. Lundin, 1998. Riksinventering 1995. En synoptisk studie av vattenkemi och bottenfauna i svenska sjöar och vattendrag. Report 4813, Naturvårdsverket, Stockholm, 191 pp.
Wilander, A., R. K. Johnson & W. Goedkoop, 2003. Riksinventering 2000. En synoptisk studie av vattenkemi och bottenfauna i svenska sjöar och vattendrag. Report 2003:1, Department of Environmental Assessment, SLU, Uppsala, 181 pp.
Woodiwiss, F., 1964. The biological system of stream classification used by the Trent River Board. Chem. Industry 14: 443–447.
Zelinka, M. & P. Marvan, 1961. Zur Präzisierung der biologischen Klassifikation der Reinheit fließender Gewässer. Arch. Hydrobiol. 57: 389–407.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Dahl, J., Johnson, R.K. & Sandin, L. Detection of organic pollution of streams in southern Sweden using benthic macroinvertebrates. Hydrobiologia 516, 161–172 (2004). https://doi.org/10.1023/B:HYDR.0000025264.35531.cb
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1023/B:HYDR.0000025264.35531.cb