Abstract
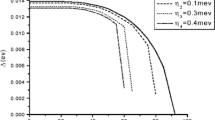
The ratio of nuclear saturation magnetization and superconducting critical field, μ 0 M sat / B S0*≡∈, classifies the strength of mutual influence of nuclear magnetism and superconductivity. In order to investigate the interplay of both phenomena for the three distinct cases ∈ ≪ 1, ∈ ≍ 1, and ∈ ≫ 1 we have measured the ac susceptibility of Al, of the intermetallic compound AuIn 2 , and of the metal hydride TiH 2.07 at ultralow temperatures, 17 μK ≤ T ≤ 1 K, as function of static field 0 ≤ B ≤ 15 mT. For Al, the interplay enables an absolute measurement of the nuclear magnetization. For AuIn 2 , we get a steep decrease of B S (T) and a broadening of the superconducting transition in its nuclear ferromagnetic phase. Surprisingly, the nuclear ferromagnetic state coexists with type-I superconductivity in AuIn 2. The metal hydride TiH 2.07 , which is under present investigation, is a good candidate to show reentrant superconductivity.
Similar content being viewed by others
REFERENCES
V. L. Ginzburg, Sov. Phys. JETP 4, 153 (1957).
B. T. Matthias, H. Suhl, and E. Corenzwit, Phys. Rev. Lett. 1, 92 (1958) and 1, 449 (1958).
O. Fischer, Magnetic Superconductors, Ferromagnetic Materials, Vol. 5, edited by K. H. J. Buschow and E. P. Wohlfarth, Elsevier Science Publishers B. V. 1990, London New York.
M. B. Maple, Physica B 215, 110 (1995).
A. A. Abrikosov and L. P. Gorkov, Sov. Phys. JETP 12, 1243 (1961).
P. Fulde and K. Maki, Phys. Rev. 141, 275 (1966).
L. N. Bulaevskii, A. I. Buzdin, M. L. Kulic, and S. V. Panjukov, Advances in Physics 34, 175 (1984).
W. Wendler, P. Smeibidl, and F. Pobell, J. Low Temp. Phys. 108, 291 (1997).
T. Herrmannsdörfer, P. Smeibidl, B. Schröder-Smeibidl, and F. Pobell, Phys. Rev. Lett. 74, 1665 (1995); T. Herrmannsdörfer and F. Pobell, J. Low Temp. Phys. 100, 253 (1995).
S. Rehmann, T. Herrmannsdörfer, and F. Pobell, Phys. Rev. Lett. 78, 1122 (1997).
Details on AuIn2 will be reported elsewhere.
P. Fulde and R. A. Ferrel, Phys. Rev. 135, 550 (1964).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Herrmannsdörfer, T., Rehmann, S., Seibold, M. et al. Interplay of Nuclear Magnetism and Superconductivity. Journal of Low Temperature Physics 110, 405–410 (1998). https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1022565607158
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1022565607158