Abstract
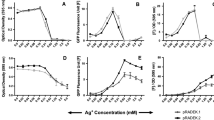
A recombinant E. coli ACV1003 releasing β-galactosidase by a SOS regulon system when it is exposed to a DNA-damaging compound, has been used to detect endocrine disruptors such as tributyltin (TBT) and triphenyltin (TPT). Maximum response ratio by E. coli ACV 1003 (recA::lacZ) – indicating the maximum ratio of enzyme produced against an environmental toxicant to that produced in the absence of a toxicant – was estimated as 6.3 with 1.0 μg TBT ml−1 at 37 °C, which was considerably higher than those with other strains. Extracellular β-galactosidase activity was 51 unit ml−1, which was 5% of that obtained by the conventional Miller's enzyme assay using solvents. Such a low enzyme activity can be rapidly determined, not by the usual time-consuming and tedious enzyme assay, but by an alternative interferometric biosensor. Heavily-doped porous silicon to apply to an interferometer was fabricated by etching to produce a Fabry–Pérot fringe pattern, which caused the change in the refractive index of the medium including β-galactosidase. The change in the effective optical thickness versus β-galactosidase activity showed a sigmoid increase up to the concentration of 250 unit β-galactosidase ml−1.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bryan GW, Gibbs PE (1991) Impact of low concentrations of tributyltin on marine organisms. In: Newman MC, McIntosh AW, eds. Metal Ecotoxicology: Concepts and Applications. Michigan, USA: Lewis Pub. Inc.
Dascãlu D, Brezeanu Gh, Dan PA (1980) Effect of Si dissolution and recrystallization upon ohmic Al/p-Si contacts. Appl. Phys. Lett. 37: 215-217.
Drolet M, Phoenix P, Menael R, Masse F, Liu LF, Crouch RJ (1995) Overexpression of Rnase H partially complements the growth defect of an E. coli ΔtopA mutant. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 92: 3267-3630.
Gu MB, Dhurjati PS, Van Dyk TK, LaRossa RA (1996) A miniature bioreactor for sensing toxicity using recombinant bioluminescent E. coli cells. Biotechnol. Prog. 12: 393-397.
Heitman J, Model P (1991) SOS induction as an in vivo assay of enzyme-DNA interactions. Gene 103: 1-9.
Janshoff A, Dancil K-PS, Steinem C, Greiner DP, Lin VSY, Gurtner C, Motesharci K, Sailor MJ, Ghardiri MR (1998) Macroporous p-type silicon Fabry-Pérot layers. J. Amer. Chem. Soc. 120: 12108-12116.
Jobling S, Nolan M, Tyler CR, Brighty G, Sumpter JP (1998) Widespread sexual disruption in wild fish. Environ. Sci. Technol. 32: 2498-2506.
Lin VS-Y, Moteshaeri K, Dancil KS, Sailor MJ, Ghadiri MR (1997) A porous silicon-based optical interferometric biosensor. Science 278: 840-843.
Miller JH (1972) Experiments in Molecular Genetics. Cold Spring Harbor, NY: Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory Press.
US EPA (1996) 40 CFR (Code of Federal Regulation) Part 180. Environmental Protection Agency, USA.
Vollmer AC, Belkin S, Smulski DR, Van Dyk TK, LaRossa RA (1997) Detection of DNA damage by use of E. coli carrying recA'::lux, uvrA'::lux, or alkA'::lux reporter plasmids. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 63: 2566-2571.
Walker GC (1984) Mutagenesis and inducible responses to deoxyribonucleic acid damage in E. coli. Microbiol. Rev. 48: 60-93.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ryu, CS., Cho, S.M. & Kim, BW. Interferometeric sensing of β-galactosidase released by recombinant E. coli responding to an endocrine disruptor, tributyltin. Biotechnology Letters 23, 653–659 (2001). https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1010308126060
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1010308126060