Abstract
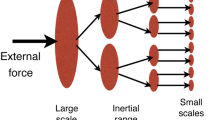
Our objective was to observe a new form of turbulence caused bybiological effects – biological micro-turbulence and explore itsprocess and controlling factors. The methods used were proteusmirabilis CGCs micro-cultured to render the occurrence of the specific movement on micro-organic suspension and its controllingfactors were determined by comparison with the control trials.The results showed that turbulence under the microscope was generally in a mass but partially regular. It was also confirmedthat the turbulence under the microscope exhibited hollow effect,temperature-dependent switching on of occurrence and self-controlof suspension quantity. It is clarified that this new form ofturbulence is a spontaneous and self-control process, which providesan experimental model with controllable conditions for studies ofturbulence and a new way for researches on the mechanism andphysiological functions of the flow of body liquid.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Shapiro, J.A.: Bacteria as multicellular organisms, Scientific American 256 (1998), 82–89.
Mendelson, N.H., Salhi, B. and Sundahl, K.E.: Cytochemical studies of cell viability and gene expression in bacillus subtilis microfibers, Microbiology 143 (1997), 3713–3721.
Rauprich, O., Matsushita, M., Weijer, C.J., et al.: Periodic phenomena in proteus mirabilis swarm colony development, Journal of Bacteriology 178 (1996), 6525–6538.
Dick, H., Murray, R.G.E. and Walmsley, S.: Swarmer cell differentiation of proteus mirabilis in fluid media, Can J Microbiology 31 (1985), 1041–1050.
Henrichsen, J.: Bacterial surface translocation: A survey and a classification, Bacteriol. Rev. 36 (1972), 478–503.
Hu-Fei: Turbulence intermittency and atmospheric surface layer, Scientific Publishing House, Peking, 1995.
Qi-wang Hsu, Jun-kang Liu and Guo-Gang: Population, period and wave of microorganic growth, Ziran Zazhi 15 (1992), 195–197.
Allison, C. and Hughes, C.: Bacterial swarming: An example of prokaryotic differentiation and multi cellular behavior, Science progress 75 (1991), 403–422.
Williams, F.O. and Schwarzhoff, R.H.: Nature of the swarming phenomenon in proteus, Annal. Review of microbiology 32 (1978), 101–122.
Harshey, R.M.: Bees aren't the only ones: Swarming in gram-negative bacteria, Molecular Microbiology 13 (1994), 389–394.
Stahl, S.J., Stewart, K.R. and Williams, F.D.: Extracellular slime associated with proteus mirabilis during swarming, Journal of Bacteriology 154 (1983), 930–937.
Strogats, S.H. and Steuart, I.: Coupled oscillators and biological synchronization, Scientific American 269 (1993), 68–75.
Crutchfield, J.P., Farmer, J.D., Pacard, N.H. and Show, R.S.: Chaos, Scientific American 255 (1986), 38–49.
Ruelle, D.: Five turbulent problems, Physica D 7 (1983), 40–44.
Sirovich, L. and Karlsson, S.: Turbulent drag reduction by passive mechanism, Nature 388 (1997), 753–755.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Liu, Jk., Deng, Gh., Yuan, Zt. et al. Turbulence Under The Microscope. Journal of Biological Physics 26, 77–83 (2000). https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1005293915802
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1005293915802