Abstract
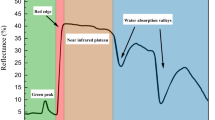
A novel thin film organic bionic leaf was prepared by a solution-casting method to simulate the thermal effect of transpiration and solar spectrum reflection characteristics of plant leaves. The main components of the bionic leaf are polyvinyl alcohol (PVA), lithium chloride (LiCl) and chromium sesquioxide (Cr2O3). The thin film was modified by chemical cross-linking, and its surface was modified by alkylsilane to prevent excessive swelling. The thin film can simulate the thermal effect of natural leaf transpiration because that the hygroscopic PVA and LiCl can absorb and desorb water due to the high and low humidity of the ambient air at night and day, respectively. The thin film has the similar solar spectrum reflection characteristics to those of plant leaves due to the Cr2O3 and the water content of the hygroscopic materials. The measured diurnal maximum radiation temperature difference between the organic bionic leaf and the Osmanthus fragrans leaf was only 0.55 °C. In addition, the solar spectrum reflection measurements revealed that the organic bionic leaf could precisely simulate the key solar spectrum reflection characteristics of plant leaves.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Peng C W, Chang K C, Weng C J, Lai M C, Hsu C H, Hsu S C, Li S Y, Wei Y, Yeh J M. UV-curable nanocasting technique to prepare bio-mimetic super-hydrophobic non-fluorinated polymeric surfaces for advanced anticorrosive coatings. Polymer Chemistry, 2013, 4, 926–932.
Vasiljevic J, Gorjanc M, Tomšic B, Orel B, Jerman I, Mozetic M, Vesel A, Simoncic B. The surface modification of cellulose fibres to create super-hydrophobic, oleophobic and self-cleaning properties. Cellulose, 2013, 20, 277–289.
Liu F, Wang S L, Zhang M, Ma M L, Wang C Y, Li J. Improvement of mechanical robustness of the superhydro-phobic wood surface by coating PVA/SiO2 composite polymer. Applied Surface Science, 2013, 280, 686–692.
Sims D A, Gamon J A. Relationships between leaf pigment content and spectral reflectance across a wide range of species, leaf structures and developmental stages. Remote Sensing of Environment, 2002, 81, 337–354.
Zhang L, Zhou Z G, Zhang G W, Meng Y L, Chen B L, Wang Y H. Monitoring the leaf water content and specific leaf weight of cotton (Gossypium hirsutum L.) in saline soil using leaf spectral reflectance. European Journal of Agronomy, 2012, 41, 103–117.
Paradiso R, Meinen E, Snel J F H, De Visser P, Van Ieperen W, Hogewoning S W, Marcelis L F M. Spectral dependence of photosynthesis and light absorptance in single leaves and canopy in rose. Scientia Horticulturae, 2011, 127, 548–554.
Garrity S R, Eitel J U H, Vierling L A. Disentangling the relationships between plant pigments and the photochemical reflectance index reveals a new approach for remote estimation of carotenoid content. Remote Sensing of Environment, 2011, 115, 628–635.
Féret J B, François C, Gitelson A, Asner G P, Barry K M, Panigada C, Richardson A D, Jacquemoud S. Optimizing spectral indices and chemometric analysis of leaf chemical properties using radiative transfer modeling. Remote Sensing of Environment, 2011, 115, 2742–2750.
Cheng T, Rivard B, Sánchez-Azofeifa A G, Féret J B, Jacquemoud S, Ustin S L. Predicting leaf gravimetric water content from foliar reflectance across a range of plant species using continuous wavelet analysis. Journal of Plant Physiology, 2012, 169, 1134–1142.
Yang Y J, Liu Z M, Hu B R, Man Y H, Wu W J. Bionic composite material simulating the optical spectra of plant leaves. Journal of Bionic Engineering, 2010, 7, S43–S49.
Gates D M. Leaf temperature and transpiration. Agronomy Journal, 1964, 56, 273–277.
Crawford A J, McLachlan D H, Hetherington A M, Franklin K A. High temperature exposure increases plant cooling capacity. Current Biology, 2012, 22, R396–R397.
Ye H, Yuan Z, Zhang S Q. The heat and mass transfer analysis of a leaf. Journal of Bionic Engineering, 2013, 10, 170–176.
Lue S J, Lee D T, Chen J Y, Chiu C H, Hu C C, Jean Y C, Lai J Y. Diffusivity enhancement of water vapor in poly(vinyl alcohol)-fumed silica nano-composite membranes: Correlation with polymer crystallinity and free-volume properties. Journal of Membrane Science, 2008, 325, 831–839.
Zhang L Z, Wang Y Y, Wang C L, **ang H. Synthesis and characterization of a PVA/LiCl blend membrane for air dehumidification. Journal of Membrane Science, 2008, 308, 198–206.
Abuin G C, Cecilia Fuertes M, Corti H R. Substrate effect on the swelling and water sorption of Nafion nanomembranes. Journal of Membrane Science, 2013, 428, 507–515.
Chen G Q, Scholes C A, Qiao G G, Kentish S E. Water vapor permeation in polyimide membranes. Journal of Membrane Science, 2011, 379, 479–487.
Watari T, Wang H Y, Kuwahara K, Tanaka K, Kita H, Okamoto K I. Water vapor sorption and diffusion properties of sulfonated polyimide membranes. Journal of Membrane Science, 2003, 219, 137–147.
Yang T H, Jessie Lue S. UNIQUAC and UNIQUAC-HB models for the sorption behavior of ethanol/water mixtures in a cross-linked polydimethylsiloxane membrane. Journal of Membrane Science, 2012, 415, 534–545.
Liu Z Q, Dong Y, Men H T, Jiang M, Tong J, Zhou J. Post-crosslinking modification of thermoplastic starch/PVA blend films by using sodium hexametaphosphate. Carbohydrate Polymers, 2012, 89, 473–477.
Heydari M, Moheb A, Ghiaci M, Masoomi M. Effect of cross-linking time on the thermal and mechanical properties and pervaporation performance of poly(vinyl alcohol) membrane cross-linked with fumaric acid used for dehydration of isopropanol. Journal of Applied Polymer Science, 2013, 128, 1640–1651.
Park J S, Kim H A, Choi J B, Gwon H J, Shin Y M, Lim Y M, Khil M S, Nho Y C. Effects of annealing and the addition of PEG on the PVA based hydrogel by gamma ray. Radiation Physics and Chemistry, 2012, 81, 857–860.
Nakabayashi S, Nagano K, Nakamura M, Togawa J, Kuro-kawa A. Improvement of water vapor adsorption ability of natural mesoporous material by impregnating with chloride salts for development of a new desiccant filter. Adsorption, 2011, 17, 675–686.
Upadhyay D J, Bhat N V. Separation of azeotropic mixture using modified PVA membrane. Journal of Membrane Science, 2005, 255, 181–186.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ye, H., Gao, Y., Li, S. et al. Bionic Leaves Imitating the Transpiration and Solar Spectrum Reflection Characteristics of Natural Leaves. J Bionic Eng 12, 109–116 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1016/S1672-6529(14)60105-0
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/S1672-6529(14)60105-0