Abstract
Background
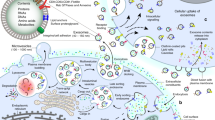
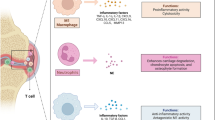
Exosomes are the smallest extracellular vesicles (30–150 nm) secreted by all cell types, including synovial fluid. However, because biological fluids are complex, heterogeneous, and contain contaminants, their isolation is difficult and time-consuming. Furthermore, the pathophysiology of osteoarthritis (OA) involves exosomes carrying complex components that cause macrophages to release chemokines and proinflammatory cytokines. This narrative review aims to provide in-depth insights into exosome biology, isolation techniques, role in OA pathophysiology, and potential role in future OA therapeutics.
Methods
A literature search was conducted using PubMed, Scopus, and Web of Science databases for studies involving exosomes in the osteoarthritis using keywords "Exosomes" and "Osteoarthritis". Relevant articles in the last 15 years involving both human and animal models were included. Studies involving exosomes in other inflammatory diseases were excluded.
Results
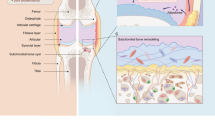
Despite some progress, conventional techniques for isolating exosomes remain laborious and difficult, requiring intricate and time-consuming procedures across various body fluids and sample origins. Moreover, exosomes are involved in various physiological processes associated with OA, like cartilage calcification, degradation of osteoarthritic joints, and inflammation.
Conclusion
The process of achieving standardization, integration, and high throughput of exosome isolation equipment is challenging and time-consuming. The integration of various methodologies can be employed to effectively address specific issues by leveraging their complementary benefits. Exosomes have the potential to effectively repair damaged cartilage OA, reduce inflammation, and maintain a balance between the formation and breakdown of cartilage matrix, therefore showing promise as a therapeutic option for OA.




Similar content being viewed by others
Data Availability
No new data was generated in this article. This review presents comprehensive insights about the already published data.
References
Buratta, S., Tancini, B., Sagini, K., Delo, F., Chiaradia, E., Urbanelli, L., & Emiliani, C. (2020). Lysosomal exocytosis, exosome release and secretory autophagy: The autophagic-and endo-lysosomal systems go extracellular. International journal of molecular sciences., 21(7), 2576.
Shi, R., Wang, P. Y., Li, X. Y., Chen, J. X., Li, Y., Zhang, X. Z., Zhang, C. G., Jiang, T., Li, W. B., Ding, W., & Cheng, S. J. (2015). Exosomal levels of miRNA-21 from cerebrospinal fluids associated with poor prognosis and tumor recurrence of glioma patients. Oncotarget, 6(29), 26971.
Pisitkun, T., Shen, R. F., & Knepper, M. A. (2004). Identification and proteomic profiling of exosomes in human urine. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences., 101(36), 13368–13373.
Zlotogorski-Hurvitz, A., Dayan, D., Chaushu, G., Korvala, J., Salo, T., Sormunen, R., & Vered, M. (2015). Human saliva-derived exosomes: Comparing methods of isolation. Journal of Histochemistry & Cytochemistry., 63(3), 181–189.
Li, Z., Wang, Y., **ao, K., **ang, S., Li, Z., & Weng, X. (2018). Emerging role of exosomes in the joint diseases. Cellular Physiology and Biochemistry., 47(5), 2008–2017.
Liu, S. L., Sun, P., Li, Y., Liu, S. S., & Lu, Y. (2019). Exosomes as critical mediators of cell-to-cell communication in cancer pathogenesis and their potential clinical application. Translational Cancer Research., 8(1), 298.
Mosquera-Heredia, M. I., Morales, L. C., Vidal, O. M., Barcelo, E., Silvera-Redondo, C., Vélez, J. I., & Garavito-Galofre, P. (2021). Exosomes: Potential disease biomarkers and new therapeutic targets. Biomedicines., 9(8), 1061.
Hawker, G. A., & King, L. K. (2022). The burden of osteoarthritis in older adults. Clinics in Geriatric Medicine., 38(2), 181–192.
He, Y., Li, Z., Alexander, P. G., Ocasio-Nieves, B. D., Yocum, L., Lin, H., & Tuan, R. S. (2020). Pathogenesis of osteoarthritis: Risk factors, regulatory pathways in chondrocytes, and experimental models. Biology., 9(8), 194.
Uivaraseanu, B., Vesa, C. M., Tit, D. M., Abid, A., Maghiar, O., Maghiar, T. A., Hozan, C., Nechifor, A. C., Behl, T., Patrascu, J. M., & Bungau, S. (2022). Therapeutic approaches in the management of knee osteoarthritis. Experimental and Therapeutic Medicine., 23(5), 1–6.
Fan, W. J., Liu, D., Pan, L. Y., Wang, W. Y., Ding, Y. L., Zhang, Y. Y., Ye, R. X., Zhou, Y., An, S. B., & **ao, W. F. (2022). Exosomes in osteoarthritis: Updated insights on pathogenesis, diagnosis, and treatment. Frontiers in Cell and Developmental Biology., 26(10), 949690.
Pan, B. T., & Johnstone, R. M. (1983). Fate of the transferrin receptor during maturation of sheep reticulocytes in vitro: Selective externalization of the receptor. Cell, 33(3), 967–978.
Wolf, P. (1967). The nature and significance of platelet products in human plasma. British Journal of Haematology., 13(3), 269–288.
Johnstone, R. M., Adam, M., Hammond, J. R., Orr, L., & Turbide, C. (1987). Vesicle formation during reticulocyte maturation. Association of plasma membrane activities with released vesicles (exosomes). Journal of Biological Chemistry., 262(19), 9412–9420.
Valenzuela, M. M., Ferguson Bennit, H. R., Gonda, A., Diaz Osterman, C. J., Hibma, A., Khan, S., & Wall, N. R. (2015). Exosomes secreted from human cancer cell lines contain inhibitors of apoptosis (IAP). Cancer Microenvironment., 8, 65–73.
Williams, R. L., & Urbé, S. (2007). The emerging shape of the ESCRT machinery. Nature reviews Molecular cell biology., 8(5), 355–368.
Yue, B., Yang, H., Wang, J., Ru, W., Wu, J., Huang, Y., Lan, X., Lei, C., & Chen, H. (2020). Exosome biogenesis, secretion and function of exosomal miRNAs in skeletal muscle myogenesis. Cell Proliferation., 53(7), e12857.
Kalluri, R., & LeBleu, V. S. (2020). The biology, function, and biomedical applications of exosomes. Science, 367(6478), eaau6977.
Zhang, Y., Bi, J., Huang, J., Tang, Y., Du, S., & Li, P. (2020). Exosome: A review of its classification, isolation techniques, storage, diagnostic and targeted therapy applications. International Journal of Nanomedicine., 22, 6917–6934.
Shu, S. L., Yang, Y., Allen, C. L., Hurley, E., Tung, K. H., Minderman, H., Wu, Y., & Ernstoff, M. S. (2020). Purity and yield of melanoma exosomes are dependent on isolation method. Journal of Extracellular Vesicles., 9(1), 1692401.
Patel, G. K., Khan, M. A., Zubair, H., Srivastava, S. K., Khushman, M. D., Singh, S., & Singh, A. P. (2019). Comparative analysis of exosome isolation methods using culture supernatant for optimum yield, purity and downstream applications. Scientific Reports., 9(1), 5335.
Tang, Y. T., Huang, Y. Y., Zheng, L., Qin, S. H., Xu, X. P., An, T. X., Xu, Y., Wu, Y. S., Hu, X. M., **, B. H., & Wang, Q. (2017). Comparison of isolation methods of exosomes and exosomal RNA from cell culture medium and serum. International Journal of Molecular Medicine., 40(3), 834–844.
Diaz, G., Bridges, C., Lucas, M., Cheng, Y., Schorey, J. S., Dobos, K. M., & Kruh-Garcia, N. A. (2018). Protein digestion, ultrafiltration, and size exclusion chromatography to optimize the isolation of exosomes from human blood plasma and serum. JoVE (Journal of Visualized Experiments)., 134, e57467.
Yu, L. L., Zhu, J., Liu, J. X., Jiang, F., Ni, W. K., Qu, L. S., Ni, R. Z., Lu, C. H., & **ao, M. B. (2018). A comparison of traditional and novel methods for the separation of exosomes from human samples. BioMed Research International., 26, 2018.
Zeringer, E., Barta, T., Li, M., & Vlassov, A. V. (2015). Strategies for isolation of exosomes. Cold Spring Harbor Protocols., 2015(4), 074476.
Momen-Heravi, F., Balaj, L., Alian, S., Trachtenberg, A. J., & Kuo, W. P. (2012). Impact of biofluid viscosity on size and sedimentation efficiency of the isolated microvesicles. Frontiers in Physiology., 29(3), 26975.
Sall, I. M., & Flaviu, T. A. (2023). Plant and mammalian-derived extracellular vesicles: a new therapeutic approach for the future. Frontiers in Bioengineering and Biotechnology. https://doi.org/10.3389/fbioe.2023.1215650
Uddin, M. J., Mohite, P., Munde, S., Ade, N., Oladosu, T. A., Chidrawar, V. R., Patel, R., Bhattacharya, S., Paliwal, H., & Singh, S. (2024). Extracellular vesicles: The future of therapeutics and drug delivery systems. Intelligent Pharmacy. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ipha.2024.02.004
Sharma, P., Ludwig, S., Muller, L., Hong, C. S., Kirkwood, J. M., Ferrone, S., & Whiteside, T. L. (2018). Immunoaffinity-based isolation of melanoma cell-derived exosomes from plasma of patients with melanoma. Journal of Extracellular Vesicles., 7(1), 1435138.
Rider, M. A., Hurwitz, S. N., & Meckes, D. G. (2016). ExtraPEG: A polyethylene glycol-based method for enrichment of extracellular vesicles. Scientific Reports., 6(1), 1–4.
Yang, D., Zhang, W., Zhang, H., Zhang, F., Chen, L., Ma, L., Larcher, L. M., Chen, S., Liu, N., Zhao, Q., & Tran, P. H. (2020). Progress, opportunity, and perspective on exosome isolation-efforts for efficient exosome-based theranostics. Theranostics., 10(8), 3684.
Slyusarenko, M., Nikiforova, N., Sidina, E., Nazarova, I., Egorov, V., Garmay, Y., Merdalimova, A., Yevlampieva, N., Gorin, D., & Malek, A. (2021). Formation and evaluation of a two-phase polymer system in human plasma as a method for extracellular nanovesicle isolation. Polymers, 13(3), 458.
Duan, P., Tan, J., Miao, Y., & Zhang, Q. (2019). Potential role of exosomes in the pathophysiology, diagnosis, and treatment of hypoxic diseases. American Journal of Translational Research., 11(3), 1184.
Zhao, K., Ruan, J., & Nie, L. (2023). Effects of synovial macrophages in osteoarthritis. Frontiers in Immunology., 10(14), 1164137.
Zhou, Q., Cai, Y., Jiang, Y., & Lin, X. (2020). Exosomes in osteoarthritis and cartilage injury: Advanced development and potential therapeutic strategies. International Journal of Biological Sciences., 16(11), 1811.
Li, Z., Li, M., Xu, P., Ma, J., & Zhang, R. (2020). Compositional variation and functional mechanism of exosomes in the articular microenvironment in knee osteoarthritis. Cell Transplantation., 20(29), 0963689720968495.
Song, J. E., Kim, J. S., Shin, J. H., Moon, K. W., Park, J. K., Park, K. S., & Lee, E. Y. (2021). Role of synovial exosomes in osteoclast differentiation in inflammatory arthritis. Cells, 10(1), 120.
Nakasa, T., Miyaki, S., Kato, T., Takada, T., Nakamura, Y., Ochi, M. (2012). Exosome derived from osteoarthritis cartilage induces catabolic factor gene expressions in synovium. InORS 2016 Annual Meeting, San Francisco.
Kato, T., Miyaki, S., Ishitobi, H., Nakamura, Y., Nakasa, T., Lotz, M. K., & Ochi, M. (2014). Exosomes from IL-1β stimulated synovial fibroblasts induce osteoarthritic changes in articular chondrocytes. Arthritis Research and Therapy., 16, 1–1.
Mizoguchi, F., Murakami, Y., Saito, T., Miyasaka, N., & Kohsaka, H. (2013). miR-31 controls osteoclast formation and bone resorption by targeting RhoA. Arthritis Research and Therapy., 15, 1–7.
Fushimi, S., Nohno, T., Nagatsuka, H., & Katsuyama, H. (2018). Involvement of miR-140-3p in Wnt3a and TGF β3 signaling pathways during osteoblast differentiation in MC 3T3-E1 cells. Genes to Cells., 23(7), 517–527.
Li, H., Zheng, Q., **e, X., Wang, J., Zhu, H., Hu, H., He, H., & Lu, Q. (2021). Role of exosomal non-coding RNAs in bone-related diseases. Frontiers in Cell and Developmental Biology., 23(9), 811666.
Kolhe, R., Hunter, M., Liu, S., Jadeja, R. N., Pundkar, C., Mondal, A. K., Mendhe, B., Drewry, M., Rojiani, M. V., Liu, Y., & Isales, C. M. (2017). Gender-specific differential expression of exosomal miRNA in synovial fluid of patients with osteoarthritis. Scientific Reports., 7(1), 2029.
Mao, G., Zhang, Z., Hu, S., Zhang, Z., Chang, Z., Huang, Z., Liao, W., & Kang, Y. (2018). Exosomes derived from miR-92a-3p-overexpressing human mesenchymal stem cells enhance chondrogenesis and suppress cartilage degradation via targeting WNT5A. Stem Cell Research and Therapy., 9, 1–3.
Inoue, Y., Kumagai, K., Ishikawa, K., Kato, I., Kusaba, Y., Naka, T., Nagashima, K., Choe, H., Ike, H., Kobayashi, N., & Inaba, Y. (2024). Increased Wnt5a/ROR2 signaling is associated with chondrogenesis in meniscal degeneration. Journal of Orthopaedic Research: official Publication of the Orthopaedic Research Society. https://doi.org/10.1002/jor.25825
Mao, G., Hu, S., Zhang, Z., Wu, P., Zhao, X., Lin, R., Liao, W., & Kang, Y. (2018). Exosomal miR-95-5p regulates chondrogenesis and cartilage degradation via histone deacetylase 2/8. Journal of Cellular and Molecular Medicine., 22(11), 5354–5366.
Varela-Eirín, M., Carpintero-Fernández, P., Guitián-Caamaño, A., Varela-Vázquez, A., García-Yuste, A., Sánchez-Temprano, A., Bravo-López, S. B., Yañez-Cabanas, J., Fonseca, E., Largo, R., & Mobasheri, A. (2022). Extracellular vesicles enriched in connexin 43 promote a senescent phenotype in bone and synovial cells contributing to osteoarthritis progression. Cell Death and Disease., 13(8), 681.
Molnar, V., Matišić, V., Kodvanj, I., Bjelica, R., Jeleč, Ž, Hudetz, D., Rod, E., Čukelj, F., Vrdoljak, T., Vidović, D., & Starešinić, M. (2021). Cytokines and chemokines involved in osteoarthritis pathogenesis. International Journal of Molecular Sciences., 22(17), 9208.
Bodmer, J. L., Schneider, P., & Tschopp, J. (2002). The molecular architecture of the TNF superfamily. Trends in Biochemical Sciences., 27(1), 19–26.
Zhao, C., Chen, J. Y., Peng, W. M., Yuan, B., Bi, Q., & Xu, Y. J. (2020). Exosomes from adipose-derived stem cells promote chondrogenesis and suppress inflammation by upregulating miR-145 and miR-221. Molecular Medicine Reports., 21(4), 1881–1889.
Zhang, J., Rong, Y., Luo, C., & Cui, W. (2020). Bone marrow mesenchymal stem cell-derived exosomes prevent osteoarthritis by regulating synovial macrophage polarization. Aging (Albany NY)., 12(24), 25138.
Tao, S. C., Yuan, T., Zhang, Y. L., Yin, W. J., Guo, S. C., & Zhang, C. Q. (2017). Exosomes derived from miR-140-5p-overexpressing human synovial mesenchymal stem cells enhance cartilage tissue regeneration and prevent osteoarthritis of the knee in a rat model. Theranostics., 7(1), 180.
Qiu, M., Liu, D., & Fu, Q. (2021). MiR-129-5p shuttled by human synovial mesenchymal stem cell-derived exosomes relieves IL-1β induced osteoarthritis via targeting HMGB1. Life Sciences., 15(269), 118987.
**, Z., Ren, J., & Qi, S. (2019). RETRACTED: human bone mesenchymal stem cells-derived exosomes overexpressing microRNA-26a-5p alleviate osteoarthritis via down-regulation of PTGS2. International Immunopharmacology, 78, 105946.
Zhou, Y., Ming, J., Li, Y., Li, B., Deng, M., Ma, Y., Chen, Z., Zhang, Y., Li, J., & Liu, S. (2021). Exosomes derived from miR-126-3p-overexpressing synovial fibroblasts suppress chondrocyte inflammation and cartilage degradation in a rat model of osteoarthritis. Cell Death Discovery., 7(1), 37.
Zhao, X., Zhao, Y., Sun, X., **ng, Y., Wang, X., & Yang, Q. (2020). Immunomodulation of MSCs and MSC-derived extracellular vesicles in osteoarthritis. Frontiers in Bioengineering and Biotechnology., 29(8), 575057.
Wang, Y., Yu, D., Liu, Z., Zhou, F., Dai, J., Wu, B., Zhou, J., Heng, B. C., Zou, X. H., Ouyang, H., & Liu, H. (2017). Exosomes from embryonic mesenchymal stem cells alleviate osteoarthritis through balancing synthesis and degradation of cartilage extracellular matrix. Stem Cell Research and Therapy., 8, 1–3.
Nurul, A. A., Azlan, M., Ahmad Mohd Zain, M. R., Sebastian, A. A., Fan, Y. Z., & Fauzi, M. B. (2021). Mesenchymal stem cells: Current concepts in the management of inflammation in osteoarthritis. Biomedicines., 9(7), 785.
Tofiño-Vian, M., Guillén, M. I., Perez del Caz, M. D., Castejón, M. A., & Alcaraz, M. J. (2017). Extracellular vesicles from adipose-derived mesenchymal stem cells downregulate senescence features in osteoarthritic osteoblasts. Oxidative Medicine and Cellular Longevity. https://doi.org/10.1155/2017/7197598
Tofiño-Vian, M., Guillén, M. I., Pérez del Caz, M. D., Silvestre, A., & Alcaraz, M. J. (2018). Microvesicles from human adipose tissue-derived mesenchymal stem cells as a new protective strategy in osteoarthritic chondrocytes. Cellular Physiology and Biochemistry., 47(1), 11–25.
Wu, J., Kuang, L., Chen, C., Yang, J., Zeng, W. N., Li, T., Chen, H., Huang, S., Fu, Z., Li, J., & Liu, R. (2019). miR-100-5p-abundant exosomes derived from infrapatellar fat pad MSCs protect articular cartilage and ameliorate gait abnormalities via inhibition of mTOR in osteoarthritis. Biomaterials, 1(206), 87–100.
Filardo, G., Previtali, D., Napoli, F., Candrian, C., Zaffagnini, S., & Grassi, A. (2021). PRP injections for the treatment of knee osteoarthritis: a meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials. Cartilage., 13(1), 364S-S375.
Otahal, A., Kramer, K., Kuten-Pella, O., Weiss, R., Stotter, C., Lacza, Z., Weber, V., Nehrer, S., & De Luna, A. (2020). Characterization and chondroprotective effects of extracellular vesicles from plasma-and serum-based autologous blood-derived products for osteoarthritis therapy. Frontiers in Bioengineering and Biotechnology., 25(8), 584050.
Liu, X., Wang, L., Ma, C., Wang, G., Zhang, Y., & Sun, S. (2019). Exosomes derived from platelet-rich plasma present a novel potential in alleviating knee osteoarthritis by promoting proliferation and inhibiting apoptosis of chondrocyte via Wnt/β-catenin signaling pathway. Journal of Orthopaedic Surgery and Research., 14, 1–6.
Ahmed, S. M., & Mstafa, R. J. (2022). Identifying severity grading of knee osteoarthritis from x-ray images using an efficient mixture of deep learning and machine learning models. Diagnostics., 12(12), 2939.
Ingenito, F., Roscigno, G., Affinito, A., Nuzzo, S., Scognamiglio, I., Quintavalle, C., & Condorelli, G. (2019). The role of exo-miRNAs in cancer: A focus on therapeutic and diagnostic applications. International Journal of Molecular Sciences., 20(19), 4687.
Zhao, Y., & Xu, J. (2018). Synovial fluid-derived exosomal lncRNA PCGEM1 as biomarker for the different stages of osteoarthritis. International Orthopaedics., 42, 2865–2872.
Miao, C., & Zhou, W. (2021). The research progress of exosomes in osteoarthritis, with particular emphasis on the mediating roles of miRNAs and lncRNAs. Frontiers in Pharmacology., 21(12), 685623.
Gao, K., Zhu, W., Li, H., Ma, D., Liu, W., Yu, W., Wang, L., Cao, Y., & Jiang, Y. (2020). Association between cytokines and exosomes in synovial fluid of individuals with knee osteoarthritis. Modern Rheumatology., 30(4), 758–764.
Acknowledgements
None.
Funding
This study was funded by the Fundamental Research Grant Scheme (FRGS/1/2021/SKK0/USM/03/7) from Ministry of Higher Education (MOHE), Malaysia.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Nazmul Huda Syed and Asma Abdullah Nurul conceived and designed the study. Syed Nazmul Huda performed the literature search and acquired the data. Syed Nazmul Huda and Iffath Misbah wrote the initial manuscript. Maryam Azlan, Muhammad Rajaei, and Asma Abdullah Nurul critically reviewed the manuscript for important intellectual content and approved for submission.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The author(s) declared no potential conflicts of interest with respect to research, authorship, and/or publication of this article.
Ethical Standard Statement
This article does not contain any studies with human or animal subjects performed by the any of the authors.
Informed consent
For this type of study informed consent is not required.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Syed, N.H., Misbah, I., Azlan, M. et al. Exosomes in Osteoarthritis: A Review on Their Isolation Techniques and Therapeutic Potential. JOIO 58, 866–875 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s43465-024-01175-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s43465-024-01175-7