Abstract
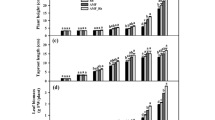
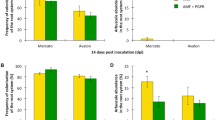
Arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi (AMF), Rhizobia, and plant growth–promoting rhizobacteria (PGPR) are symbiotic partners of legume plants; their symbiotic associations enhance plant growth, development, and nutrient uptake. However, our understanding of their interactions on plant growth and their relationships to root architecture remains limited. A greenhouse experiment was conducted to investigate the individual and combined effects of AMF, Bacillus, and Rhizobium on plant growth and root morphological traits. Triple inoculations significantly promoted plant biomass, stem diameter, and height, and root surface area was significantly enhanced by individual or combined inoculations. The presence of AMF promoted root length and number of root branches while decreasing root volume, mean average diameter, and the root/shoot ratio. The results revealed that AMF and Rhizobium showed a synergistic effect on increasing root surface area but antagonistic effects on root average diameter and root volume. The interaction between Bacillus and AMF altered the negative relationship between specific root length and root diameter. Multipartite symbioses established by AMF, Bacillus, Rhizobium, and Medicago ruthenica had significant negative effects on plant-specific root length, showing the complicated and multifunctional associations of soil microbes and the amplifying roles of soil partner interactions.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Afkhami ME, Almeida BK, Hernandez DJ, Kiesewetter KN, Revillini DP (2020) Tripartite mutualisms as models for understanding plant-microbial interactions. Curr Opin Plant Biol 56:28–36. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.pbi.2020.02.003
Arumugam R, Rajasekaran S, Nagarajan S (2010) Response of arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi and Rhizobium inoculation on growth and chlorophyll content of Vigna unguiculata (L) Walp Var. Pusa 151. J. Environ 14:113–115. https://doi.org/10.4314/JASEM.V14I4.63282
Badri DV, Vivanco JM (2009) Regulation and function of root exudates. Plant Cell Environ 32:666–681. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1365-3040.2009.01926.x
Bauer JT, Kleczewski NM, Bever JD, Bever JD, Clay K, Reynolds HL (2012) Nitrogen-fixing bacteria, arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi, and the productivity and structure of prairie grassland communities. Oecologia 170:1089–1098. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00442-012-2363-3
Berg G, Rybakova D, Grube M, Köberl M (2016) The plant microbiome explored: implications for experimental botany. J Exp Bot 67:995–1002. https://doi.org/10.1093/jxb/erv466
Bourles A, Guentas L, Charvis C, Gensous S, Majorel C, Crossay T, Cavaloc Y, Burtet-Sarramegna V, Jourand P, Amir H (2020) Co-inoculation with a bacterium and arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi improves root colonization, plant mineral nutrition, and plant growth of a Cyperaceae plant in an ultramafic soil. Mycorrhiza 30:121–131. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00572-019-00929-8
Brundrett MC (2002) Coevolution of roots and mycorrhizas of land plants. New Phytol 154:275–304. https://doi.org/10.1046/j.1469-8137.2002.00397.x
Brundrett MC, Tedersoo L (2018) Evolutionary history of mycorrhizal symbioses and global host plant diversity. New Phytol 220:1108–1115. https://doi.org/10.1111/nph.14976
Cao M, Liu R, **ao Z, Hashem A, Allah EFA, Alsayed MF, Harsonowati W, Wu QS (2022) Symbiotic fungi alter the acquisition of phosphorus in Camellia oleifera through regulating root architecture, plant phosphate transporter gene expressions and soil phosphatase activities. J Fungi (Basel) 8:800. https://doi.org/10.3390/jof8080800
Cassán F, Coniglio A, López G, Molina R, Nievas S, de Carlan CLN, Donadio F, Torres D, Rosas S, Pedrosa FO, de Souza E (2020) Everything you must know about Azospirillum and its impact on agriculture and beyond. Biol. Fertil 56:461–479. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00374-020-01463-y
Comas LH, Mueller KE, Taylor LL, Midford PE, Callahan HS, Beerling DJ (2012) Evolutionary patterns and biogeochemical significance of angiosperm root traits. Int J Plant Sci 173:584–595. https://doi.org/10.1086/665823
Cosme M, Wurst S (2013) Interactions between arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi, rhizobacteria, soil phosphorus and plant cytokinin deficiency change the root morphology, yield and quality of tobacco. Soil Biol Biochem 57:436–443. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.soilbio.2012.09.024
Crossay T, Majorel C, Redecker D, Gensous S, Medevielle V, Durrieu G, Cavaloc Y, Amir H (2019) Is a mixture of arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi better for plant growth than single-species inoculants? Mycorrhiza 29:325–339. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00572-019-00898-y
de Sousa SM, de Oliveira CA, Andrade DL, de Carvalho CG, Ribeiro VP, Pastina MM, Marriel IE, de Paula Lana UG, Gomes EA (2020) Tropical Bacillus strains inoculation enhances maize root surface area, dry weight, nutrient uptake and grain yield. J Plant Growth Regul 40:867–877. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00344-020-10146-9
de Souza JEB, Ferreira EPDB (2017) Improving sustainability of common bean production systems by co-inoculating rhizobia and azospirilla. Agric Ecosyst Environ 237:250–257. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.agee.2016.12.040
El-Sawah AM, El-Keblawy A, Ali DFI, Ibrahim HM, El-Sheikh MA, Sharma A, Hamoud YA, Shaghaleh H, Brestic M, Skalicky M, **ong YC, Sheteiwy MS (2021) Arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi and plant growth-promoting rhizobacteria enhance soil key enzymes, plant growth, seed yield, and qualitative attributes of guar. Agriculture-Basel 11. https://doi.org/10.3390/agriculture11030194
Filipini LD, Pilatti FK, Meyer E, Ventura BS, Lourenzi CR, Ventura BS, Lourenzi CR, Lovato PE (2021) Application of Azospirillum on seeds and leaves, associated with Rhizobium inoculation, increases growth and yield of common bean. Arch Microbiol 203:1033–1038. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00203-020-02092-7
Gaju O, Allard V, Martre P, Le Gouis J, Moreau D, Moreau D, Bogard M, Hubbart S, Foulkesa MJ (2014) Nitrogen partitioning and remobilization in relation to leaf senescence, grain yield and grain nitrogen concentration in wheat cultivars. Field Crop Res 155:213–223. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fcr.2013.09.003
Giovannini L, Palla M, Agnolucci M, Avio L, Sbrana C, Turrini A, Giovannetti M (2020) Arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi and associated microbiota as plant biostimulants: research strategies for the selection of the best performing inocula. Agronomy-Basel 10. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy10010106
Goldford JE, Lu N, Bajić D, Estrela S, Tikhonov M, Gorostiaga AS, Segrè D, Mehta P, Sanchez A (2018) Emergent simplicity in microbial community assembly. Science 361:469–474. https://doi.org/10.1126/science.aat1168
Gong T, **n XF (2021) Phyllosphere microbiota: community dynamics and its interaction with plant hosts. J Integr Plant Biol 63:297–304. https://doi.org/10.1111/jipb.13060
Grover M, Bodhankar S, Sharma A, Sharma P, Singh J, Nain L (2021) PGPR mediated alterations in root traits: way toward sustainable crop production. Front Sustain Food Syst 4:618230. https://doi.org/10.3389/fsufs.2020.618230
Guo MW, Zhu L, Li HY, Liu WP, Wu ZN, Wang CH, Liu L, Li ZY, Li J (2022) Mechanism of pod shattering in the forage legume Medicago ruthenica. Plant Physiol Biochem 185:260–267. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.plaphy.2022.06.013
Gutjahr C, Casieri L, Paszkowski U (2009) Glomus intraradices induces changes in root system architecture of rice independently of common symbiosis signaling. New Phytol 182:829–837. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1469-8137.2009.02839.x
Gutjahr C, Paszkowski U (2013) Multiple control levels of root system remodeling in arbuscular mycorrhizal symbiosis. Front Plant Sci 4:204. https://doi.org/10.3389/fpls.2013.00204
Hack CM, Porta M, Schäufele R, Grimoldi AA (2019) Arbuscular mycorrhiza mediated effects on growth, mineral nutrition and biological nitrogen fixation of Melilotus alba Med. in a subtropical grassland soil. Appl Soil Ecol 134:38–44. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apsoil.2018.10.008
Hartmann A, Rothballer M, Schmid M (2008) Lorenz Hiltner, a pioneer in rhizosphere microbial ecology and soil bacteriology research. Plant Soil 312:7–14. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11104-007-9514-z
Herms CH, Hennessy RC, Bak F, Dresboll DB, Nicolaisen MH (2022) Back to our roots: exploring the role of root morphology as a mediator of beneficial plant-microbe interactions. Environ Microbiol. https://doi.org/10.1111/1462-2920.15926
Iannucci A, Canfora L, Nigro F, De Vita P, Beleggia R (2021) Relationships between root morphology, root exudate compounds and rhizosphere microbial community in durum wheat. Appl Soil Ecol 158:103781. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apsoil.2020.103781
Ide Franzini V, Azcón R, Latanze Mendes F, Aroca R (2010) Interactions between Glomus species and Rhizobium strains affect the nutritional physiology of drought-stressed legume hosts. J Plant Physiol 167:614–619. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jplph.2009.11.010
Jayakumar A, Krishna A, EK NICR (2020) Drought-tolerant and plant growth-promoting endophytic Staphylococcus sp. having synergistic effect with silicate supplementation. Arch Microbiol 202:1899–1906
Jiang Y, Wang W, **e Q, Liu N, Liu L, Wang DP, Zhang XW, Yang CY, Chen XY, Tang DZ, Wang ET (2017) Plants transfer lipids to sustain colonization by mutualistic mycorrhizal and parasitic fungi. Science 356:1172–1175. https://doi.org/10.1126/science.aam9970
Kavadia A, Omirou M, Fasoula DA, Louka F, Ehaliotis C, Ioannidesa IM (2021) Co-inoculations with rhizobia and arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi alters mycorrhizal composition and lead to synergistic growth effects in cowpea that are fungal combination-dependent. Appl Soil Ecol 167. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apsoil.2021.104013
Keymer A, Pimprikar P, Wewer V, Huber C, Brands M, Bucerius SL, Delaux PM, Klingl V, Röpenack-Lahaye EV, Wang TL, Eisenreich W, Dörmann P, Parniske M, Gutjahr C (2017) Lipid transfer from plants to arbuscular mycorrhiza fungi. Elife 6. https://doi.org/10.7554/eLife.29107
Kong DL, Ma CE, Zhang Q, Li L, Chen X, Zeng H, Guo DL (2014) Leading dimensions in absorptive root trait variation across 96 subtropical forest species. New Phytol 203:863–872. https://doi.org/10.1111/nph.12842
Koske RE, Gemma JN (1989) A modified procedure for staining roots to detect VA mycorrhizas. Mycol Res 92. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0953-7562(89)80195-9
Larimer AL, Bever JD, Clay K (2010) The interactive effects of plant microbial symbionts: a review and meta-analysis. Symbiosis (Philadelphia, Pa.) 51:139–148. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13199-010-0083-1
Ma ZQ, Guo DL, Xu XL, Lu MZ, Bardgett RD, Eissenstat DM, McCormack ML, Hedin LO (2018) Evolutionary history resolves global organization of root functional traits. Nature 555:94. https://doi.org/10.1038/nature25783
Maherali H (2014) Is there an association between root architecture and mycorrhizal growth response? New Phytol 204:192–200. https://doi.org/10.1111/nph.12927
Meng L, Srivastava AK, Kucac K, Wu QS (2022) Earthworm (Pheretima guillelmi)-mycorrhizal fungi (Funneliformis mosseae). Appl Soil Ecol 104371. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apsoil.2021.104371
Mommer L, Hinsinger P, Prigent-Combaret C, Visser EJW (2016) Advances in the rhizosphere: stretching the interface of life. Plant Soil 407:1–8. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11104-016-3040-9
Munns DN, Keyser HH (1981) Response of Rhizobium strains to acid and aluminium stress. Soil Biol Biochem 13:115–118. https://doi.org/10.1016/0038-0717(81)90006-7
Nadeem SM, Ahmad M, Zahir ZA, Javaid A, Ashra M (2014) The role of mycorrhizae and plant growth promoting rhizobacteria (PGPR) in improving crop productivity under stressful environments. Biotechnol Adv 32:429–448. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biotechadv.2013.12.005
Nadeem SM, Zahir ZA, Naveed M, Asghar HN, Arshad M (2010) Rhizobacteria capable of producing ACC-deaminase may mitigate salt stress in wheat. Soil Sci Soc Am J 74:533–542. https://doi.org/10.2136/sssaj2008.0240
Neumann U, Kosier B, Jahnke J, Priefer UB, Al-Halbouni D (2011) Soil factors exhibit greater influence than bacterial inoculation on alfalfa growth and nitrogen fixation. FEMS Microbiol Ecol 77:590–599. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1574-6941.2011.01139.x
Olanrewaju OS, Glick BR, Babalola OO (2017) Mechanisms of action of plant growth promoting bacteria. World J Microbiol Biotechnol 33:197. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11274-017-2364-9
Ostonen I, Püttsepp Ü, Biel C, Alberton O, Bakker MR, Lõhmus K, Majdi H, Metcalfe D, Olsthoorn AFM, Pronk A, Vanguelova E, Weih M, Brunner I (2007) Specific root length as an indicator of environmental change. Plant Biosystems 141:426–442. https://doi.org/10.1080/11263500701626069
Pan J, Huang C, Peng F, Zhang WJ, Luo J, Ma SX, Xue X (2020) Effect of arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi (AMF) and plant growth-promoting bacteria (PGPR) inoculations on Elaeagnus angustifolia L. in saline soil. Appl Sci 10:945. https://doi.org/10.3390/app10030945
Primieri S, Santos JCP, Antunes PM (2021) Nodule-associated bacteria alter the mutualism between arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi and N-2 fixing bacteria. Soil Biol Biochem 154. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.soilbio.2021.108149
Routray S, Kumari S, Borah B, Shelat H, Solanki JP, Khanna V (2021) A review on rhizobia and PGPRs interactions in legumes. Pharma Innov J 7:1448–1457
Schwartz A, Ortiz I, Maymon M, Herbold CW, Fujishige NA, Vijanderan JA, Villella W, Hanamoto K, Diener A, Sanders ER, DeMason DA, Hirsch AM (2013) Bacillus simplex—a little known PGPB with anti-fungal activity—alters pea legume root architecture and nodule morphology when coinoculated with Rhizobium leguminosarum bv. viciae. Agronomy (Basel) 3:595–620. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy3040595
Seago JJ, Fernando DD (2013) Anatomical aspects of angiosperm root evolution. Ann Bot 112:223–238. https://doi.org/10.1093/aob/mcs266
Smith S, Read D (2008) Mycorrhizal symbiosis. UK: Academic Press, London
Smith SE, Read DJ (2010) Mycorrhizal symbiosis. UK: Academic Press, London
Spitzer CM, Lindahl B, Wardle DA, Sundqvist MK, Gundale MJ, Fanin N, Kardol P (2021) Root trait–microbial relationships across tundra plant species. New Phytol 229:1508–1520. https://doi.org/10.1111/nph.16982
Tavasolee A, Nasser A, Gholamreza S, Mardi M (2011) Interactive effects of arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi and rhizobial strains on chickpea growth and nutrient content in plant. Afr J Biomed Res 10:7585–7591. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-1-4020-5765-6_26
Vacheron J, Desbrosses G, Bouffaud ML, Touraine B, Moënne-Loccoz Y, Muller D, Legendre L, Wisniewski-Dyé F, Prigent-Combaret C (2013) Plant growth-promoting rhizobacteria and root system functioning. Front Plant Sci 4:356. https://doi.org/10.3389/fpls.2013.00356
van der Heijden MG, Bardgett RD, van Straalen NM (2008) The unseen majority: soil microbes as drivers of plant diversity and productivity in terrestrial ecosystems. Ecol Lett 11:296–310. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1461-0248.2007.01139.x
Vejan P, Abdullah R, Khadiran T, Ismail S, Nasrulhaq BA (2016) Role of plant growth promoting rhizobacteria in agricultural sustainability-a review. Molecules 21. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules21050573
Veresoglou SD, Menexes G (2010) Impact of inoculation with Azospirillum spp. on growth properties and seed yield of wheat: a meta-analysis of studies in the ISI Web of Science from 1981 to 2008. Plant Soil 337:469–480. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11104-010-0543-7
Walker V, Couillerot O, Von FA, Bellvert F, Jansa J, Maurhofer M, Bally R, Moënne-Loccoz Y, Comte G (2012) Variation of secondary metabolite levels in maize seedling roots induced by inoculation with Azospirillum, Pseudomonas and Glomus consortium under field conditions. Plant Soil 356:151–163. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11104-011-0960-2
Wang XL, Wang GQ, Hao MD (2015) Modeling of the Bacillus subtilis bacterial biofilm growing on an agar substrate. Comput Math Method Me 2015:581829. https://doi.org/10.1155/2015/581829
Wang TZ, Ren LF, Li C, Zhang D, Zhang XX, Zhou G, Gao D, Chen RJ, Chen YH, Wang ZL, Shi FL, Farmer AD, Li YS, Zhou MY, Young ND, Zhang WH (2021a) The genome of a wild Medicago species provides insights into the tolerant mechanisms of legume forage to environmental stress. BMC Biol 19:96. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12915-021-01033-0
Wang Y, Wang JC, Guo DD, Zhang HB, Che YH, Li YY, Tian B, Wang ZH, Sun GY, Zhang HH (2021b) Physiological and comparative transcriptome analysis of leaf response and physiological adaption to saline alkali stress across pH values in alfalfa (Medicago sativa). Plant Physiol Biochem 167:140–152. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.plaphy.2021.07.040
Wei XT, Shi YN, Qin FW, Zhou HK, Shao XQ (2021) Effects of experimental warming, precipitation increase and their interaction on AM fungal community in an alpine grassland of the Qinghai-Tibetan Plateau. Eur J Soil Biol 102. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ejsobi.2020.103272
**e MM, Zou YN, Wu QS, Zhang ZZ (2020) Single or dual inoculation of arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi and rhizobia regulates plant growth and nitrogen acquisition in white clover. Plant Soil Environ 66:287–294. https://doi.org/10.17221/234/2020-PSE
**e JX, Liang BC, Li ZR, Ji ZK, Ou WY, Liu H, Wang HC, Kazhuocairang HZQ (2021a) Characteristics of complete chloroplast genome of a high-quality forage on Qinghai-Tibet Plateau, Medicago archiducis-nicolai Sirj. (Fabaceae: Trifolieae). Mitochondrial DNA B Resour 6:217–219. https://doi.org/10.1080/23802359.2020.1861558
**e LL, Bi YL, Ma SP, Shang JX, Hu QC, Christie P (2021b) Combined inoculation with dark septate endophytes and arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi: synergistic or competitive growth effects on maize? BMC Plant Biol 21:498. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12870-021-03267-0
Acknowledgements
We appreciate the reviewers for their practical comments that improved the quality of this manuscript. We also thank **aoting Wei and Fengyan Jiang for their help in sampling.
Funding
This study was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant numbers 31971746 and 32171685) and the Second Batch of Forestry and Grassland Ecological Protection and Restoration Funds in 2020: Biodiversity Conservation Project in Qinghai Area of Qilian Mountain National Park (QHTX-2021-009).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Lu Yu: drafting of the article, analysis and interpretation of the data, and conception and design. Hui Zhang: conception and design, and analysis and interpretation of the data. Wantong Zhang and Bing Han: provision of the study materials or patients. Huakun Zhou, **nming Lu, and Yanfang Deng: administrative, technical, or logistic support. **nqing Shao and Kesi Liu: critical revision of the article for important intellectual content, and final approval of the article
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of Interest
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Yu, L., Zhang, H., Zhang, W. et al. Arbuscular Mycorrhizal Fungi Alter the Interaction Effects Between Bacillus and Rhizobium on Root Morphological Traits of Medicago ruthenica L.. J Soil Sci Plant Nutr 23, 2868–2877 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s42729-023-01242-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s42729-023-01242-2