Abstract
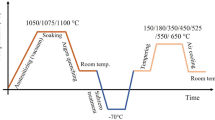
55Cr17Mo1VN high nitrogen martensitic stainless steel is usually applied to the high-quality mold, which is largely produced by the pressurized electro slag remelting process. The microstructure evolution of quenching and tempering heat treatment were investigated and an optimal heat treatment process to achieve excellent mechanical properties was found out. The main precipitates in the steel included carbon-rich type M23C6 and nitrogen-rich type M2N. With increasing austenitizing temperature, the equivalent diameter of the precipitates got fined, and retained austenite content increased significantly when the austenitizing temperature exceeded 1020 °C. The fracture mode gradually changed from brittle fracture to ductile fracture with increasing tempering temperature from 200 to 550 °C. The experimental steel tempered at 350 °C achieved a good combination of hardness (60.6 HRC) and strength (2299.2 MPa) to meet service requirements. Flake M23C6 precipitated along martensite lath boundaries and the secondary hardening phenomenon occurred when the tempering temperature was 450 °C. Due to the high nitrogen content, M2N precipitated from the inside of laths and matrix when tempered at 550 °C.









Similar content being viewed by others
References
R.S.E. Schneider, R.A. Mesquita, Int. Heat Treat. Surf. Eng. 5 (2011) 94–100.
R. Schneider, J. Perko, G. Reithofer, Mater. Manuf. Process. 24 (2009) 903–908.
W.J. Tong, W.M. Li, X.M. Zang, P. Wang, H.B. Li, D.J. Li, J. Iron Steel Res. Int. 28 (2021) 19–28.
S.J. Li, G.G. Cheng, Y. Huang, W.X. Dai, Z.Q. Miao, J. Iron Steel Res. Int. 27 (2020) 380–391.
Q.T. Zhu, J. Li, C.B. Shi, W.T. Yu, Int. J. Miner. Metall. Mater. 22 (2015) 1149–1156.
H.C. Zhu, Z.H. Jiang, H.B. Li, J.H. Zhu, H. Feng, S.C. Zhang, B.B. Zhang, P.B. Wang, G.H. Liu, Steel Res. Int. 88 (2017) 1600509.
A. Bénéteau, P. Weisbecker, G. Geandier, E. Aeby-Gautier, B. Appolaire, Mater. Sci. Eng. A 391 (2005) 63–70.
Y.S. Choi, J.G. Kim, Y.S. Park, J.Y. Park, Mater. Lett. 61 (2007) 244–247.
W.J. Kaluba, T. Kaluba, R. Taillard, Scripta Mater. 41 (1999) 1289–1293.
A. Rajasekhar, G. Madhusudhan Reddy, T. Mohandas, V.S.R. Murti, Mater. Des. 30 (2009) 1612–1624.
Y.R. Liu, D. Ye, Q.L. Yong, J. Su, K.Y. Zhao, W. Jiang, J. Iron Steel Res. Int. 18 (2011) No. 11, 60–66.
S. Yuan, X.C. Wu, Mater. Mech. Eng. 35 (2011) 61–64.
X.S. Yu, C. Wu, R.X. Shi, Y.S. Yuan, Adv. Manuf. (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s40436-021-00352-3.
L. Yao, W. Shi, in: Society of Automotive Engineers of China (SAE-China) (Eds.), Proceedings of SAE-China Congress 2016, Springer, Shanghai, China, 2017, pp. 313–325.
C.Y. Wang, J. Shi, W.Q. Cao, H. Dong, Mater. Sci. Eng. A 527 (2010) 3442–3449.
S. Li, Y. **e, X. Wu, Cryogenics 50 (2010) 89–92.
X.P. Ma, L.J. Wang, B. Qin, C.M. Liu, S.V. Subramanian, Mater. Des. 34 (2012) 74–81.
H. Semba, F. Abe, Energy Mater. 1 (2013) 238–244.
G.X. Qiu, D.P. Zhan, L. Cao, H.S. Zhang, J. Iron Steel Res. Int. 28 (2021) 1168–1179.
M.E. Mehtedi, P. Ricci, L. Drudi, S.E. Mohtadi, M. Cabibbo, S. Spigarelli, Mater. Des. 33 (2012) 136–144.
D. Das, A.K. Dutta, K.K. Ray, Mater. Sci. Eng. A 527 (2010) 2182–2193.
J.W. Park, H.C. Lee, S. Lee, Metall. Mater. Trans. A 30 (1999) 399–409.
C.K. Kim, J.I. Park, S. Lee, Y.C. Kim, N.J. Kim, J.S. Yang, Metall. Mater. Trans. A 36 (2005) 87–97.
T. Tsuchiyama, K. Inoue, K. Hyodo, D. Akama, N. Nakada, S. Takaki, T. Koyano, ISIJ Int. 59 (2019) 161–168.
A.N. Isfahany, H. Saghafian, G. Borhani, J. Alloy. Compd. 509 (2011) 3931–3936.
G.R. Ebrahimi, H. Keshmiri, A. Momeni, Ironmak. Steelmak. 38 (2011) 123–128.
G. Krauss, Mater. Sci. Eng. A 273–275 (1999) 40–57.
D.M. Lal, S. Renganarayanan, A. Kalanidhi, Cryogenics 41 (2001) 149–155.
V.G. Gavriljuk, W. Theisen, V.V. Sirosh, E.V. Polshin, A. Kortmann, G.S. Mogilny, Y.N. Petrov, Y.V. Tarusin, Acta Mater. 61 (2013) 1705–1715.
C. Pandey, N. Saini, M.M. Mahapatra, P. Kumar, Eng. Failure Anal. 71 (2017) 131–147.
H. Nakagawa, T. Miyazaki, J. Mater. Sci. 34 (1999) 3901–3908.
K. Chen, Z. Jiang, F. Liu, H. Li, C. Kang, W. Zhang, A. Wang, Metall. Mater. Trans. A 51 (2020) 3565–3575.
Y. Han, H. Li, H. Feng, Y. Tian, Z. Jiang, T. He, Mater. Sci. Eng. A 814 (2021) 141235.
Y. Han, H. Li, H. Feng, K. Li, Y. Tian, Z. Jiang, J. Mater. Sci. Technol. 65 (2021) 210–215.
X.P. Ma, L.J. Wang, B. Qin, C.M. Liu, S.V. Subramanian, Adv. Mater. Res. 311–313 (2011) 910–915.
J. Dai, H. Feng, H.B. Li, Z.H. Jiang, H. Li, S.C. Zhang, P. Zhou, T. Zhang, Corros. Sci. 174 (2020) 108792.
H. Feng, H.B. Li, W.C. Jiao, Z.H. Jiang, M.H. Cai, H.C. Zhu, Z.G. Chen, Metall. Mater. Trans. A 50 (2019) 4987–4999.
Acknowledgements
This research was sponsored by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant Nos. U1960203, U1908223, and 51774074), Talent Project of Revitalizing Liaoning (Grant No. XLYC1902046), State Key Laboratory of Metal Material for Marine Equipment and Application (Grant No. HG-SKL (2019) 13) and the "Innovation & Entrepreneurship Talents” Introduction Plan of Jiangsu Province in 2018.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kang, Cp., Liu, Fb., Zheng, Hb. et al. Microstructure evolution and mechanical properties of PESR 55Cr17Mo1VN plastic die steel during quenching and tempering treatment. J. Iron Steel Res. Int. 28, 1625–1633 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s42243-021-00689-w
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s42243-021-00689-w