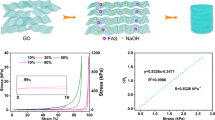
Abstract
Herein, a novel three-dimensional nanocomposite aerogel (rGO/Fe3O4/PANI NAs) with outstanding magnetoresistance and piezoresistance was manufactured by the in-situ polymerized polyaniline nanoarrays (PANI NAs) surrounding magnetic reduced graphene oxide (rGO/Fe3O4) aerogel that was prepared through the combination of hydrothermal method and lyophilization method. This rGO/Fe3O4/PANI NAs nanocomposite aerogel with 60 wt.% loading of PANI NAs well preserved the porous structure and gained a superior mechanical strength (121.04 kPa) compared with that of rGO aerogel, rGO/Fe3O4 aerogel, and rGO/PANI NAs aerogel (43.54, 58.12, and 116.98 kPa, respectively). The rGO/Fe3O4/PANI NAs nanocomposite aerogel could hold its original state with almost 100% recovery ratio after cycling compression tests under 80% of deformation strain at a suitable compression rate of 5 mm min−1. The introduction of PANI NAs into the rGO/Fe3O4 aerogel also brought a satisfactory piezoresistive performance with a large gauge factor up to 2.83 and a superb stability for the electrical signal output (which was decreased only 5.80% after 500 compression cycles) to the rGO/Fe3O4/PANI NAs nanocomposite aerogel. The loading of Fe3O4 and PANI NAs also provided rGO/Fe3O4/PANI NAs nanocomposite aerogel with a negative magnetoresistance value up to − 4.37%. The magnetoresistance was explained via the amelioration of spin transport in the material. The unique negative magnetoresistance and excellent piezoresistance make rGO/Fe3O4/PANI NAs nanocomposite aerogel a promising candidate for the development of advanced electronic devices.
Graphical abstract
A novel three-dimensional nanocomposite aerogel (rGO/Fe3O4/PANI NAs) exhibits amazing negative magnetoresistance and outstanding piezoresistive performance.








Similar content being viewed by others
References
Gu H, Zhang X, Wei H, Huang Y, Wei S, Guo Z (2013) An overview of the magnetoresistance phenomenon in molecular systems. Chem Soc Rev 42:5907–5943
Jiang Y, de Jong EJ, van de Sande V, Gazibegovic S, Badawy G, Bakkers E, Frolov SM (2021) Hysteretic magnetoresistance in nanowire devices due to stray fields induced by micromagnets. Nanotechnology 32: 095001
Choi J, Gani AW, Bechstein DJB, Lee J-R, Utz PJ, Wang SX (2016) Portable, one-step, and rapid GMR biosensor platform with smartphone interface. Biosens Bioelectron 85:1–7
Qin P, Feng Z, Zhou X, Guo H, Wang J, Yan H, Wang X, Chen H, Zhang X, Wu H, Zhu Z, Liu Z (2020) Anomalous Hall effect, robust negative magnetoresistance, and memory devices based on a noncollinear antiferromagnetic metal. ACS Nano 14:6242–6248
Ionete EI, Niculescu AE, Spiridon SI, Monea BF (2021) Magnetoresistance behavior of cryogenic temperature sensors based on single-walled carbon nanotubes. IEEE Sens J 21:2767–2774
Guo J, Li X, Liu H, Young DP, Song G, Song K, Zhu J, Kong J, Guo Z (2021) Tunable magnetoresistance of core-shell structured polyaniline nanocomposites with 0-, 1-, and 2-dimensional nanocarbons. Adv Compos Hybrid Mater 4:51–64
Zhang X, Tong J, Zhu H, Wang Z, Zhou L, Wang S, Miyashita T, Mitsuishi M, Qin G (2017) Room temperature magnetoresistance effects in ferroelectric poly(vinylidene fluoride) spin valves. J Mater Chem C 5:5055–5062
Guo J, Chen Z, Abdul W, Kong J, Khan MA, Young DP, Zhu J, Guo Z (2021) Tunable positive magnetoresistance of magnetic polyaniline nanocomposites. Adv Compos Hybrid Mater 4:534–542
Cai J, Wang W, Pan D, Young DP, Gu H, Guo Z (2020) Electrical transport in polyaniline-barium ferrite nanocomposites with negative giant magnetoresistance. J Phys Chem C 124:22646–22655
Guo J, Li X, Chen Z, Zhu J, Mai X, Wei R, Sun K, Liu H, Chen Y, Naik N, Guo Z (2022) Magnetic NiFe2O4/polypyrrole nanocomposites with enhanced electromagnetic wave absorption. J Mater Sci Technol 108:64–72
Gu H, Zhang H, Lin J, Shao Q, Young DP, Sun L, Shen TD, Guo Z (2018) Large negative giant magnetoresistance at room temperature and electrical transport in cobalt ferrite-polyaniline nanocomposites. Polymer 143:324–330
Wu H, Zhong Y, Tang Y, Huang Y, Liu G, Sun W, **e P, Pan D, Liu C, Guo Z (2021) Precise regulation of weakly negative permittivity in CaCu3Ti4O12 metacomposites by synergistic effects of carbon nanotubes and grapheme. Adv Compos Hybrid Mater: https://doi.org/10.1007/s42114-021-00378-y
Gu H, Xu X, Cai J, Wei S, Wei H, Liu H, Young DP, Shao Q, Wu S, Ding T, Guo Z (2019) Controllable organic magnetoresistance in polyaniline coated poly(p-phenylene-2,6-benzobisoxazole) short fibers. Chem Commun 55:10068–10071
Jeon J, Lee DH, Kim YS, Chung HJ, Jhang SH, Kwon Y, Lee S, Park BH (2020) Large temperature-independent magnetoresistance without gating operation in monolayer graphene. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces 12:53134–53140
Li X, Sagar RUR, Zhong L, Liu Y, Hui D, Zhang M (2019) Nonsaturating negative magnetoresistance in laser-induced graphene. Mater Lett 248:43–47
Shi W, Han G, Chang Y, Song H, Hou W, Chen Q (2020) Using stretchable PPy@PVA composites as a high-sensitivity strain sensor to monitor minute motion. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces 12:45373–45382
Kim H-J, Thukral A, Yu C (2018) Highly sensitive and very stretchable strain sensor based on a rubbery semiconductor. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces 10:5000–5006
Chao M, Wang Y, Ma D, Wu X, Zhang W, Zhang L, Wan P (2020) Wearable MXene nanocomposites-based strain sensor with tile-like stacked hierarchical microstructure for broad-range ultrasensitive sensing. Nano Energy 78: 105187
Gu H, Zhang H, Ma C, Sun H, Liu C, Dai K, Zhang J, Wei R, Ding T, Guo Z (2019) Smart strain sensing organic–inorganic hybrid hydrogels with nano barium ferrite as the cross-linker. J Mater Chem C 7:2353–2360
Cao M, Su J, Fan S, Qiu H, Su D, Li L (2021) Wearable piezoresistive pressure sensors based on 3D graphene. Chem Eng J 406: 126777
Zhong Y, Tan X, Shi T, Huang Y, Cheng S, Chen C, Liao G, Tang Z (2018) Tunable wrinkled graphene foams for highly reliable piezoresistive sensor. Sens Actuators A: Phys 281:141–149
Wei H, Li A, Kong D, Li Z, Cui D, Li T, Dong B, Guo Z (2021) Polypyrrole/reduced graphene aerogel film for wearable piezoresisitic sensors with high sensing performances. Adv Compos Hybrid Mater 4:86–95
Gao F, Gu HB, Wang HW, Wang XF, **ang B, Guo ZH (2015) Magnetic amine-functionalized polyacrylic acid-nanomagnetite for hexavalent chromium removal from polluted water. RSC Adv 5:60208–60219
Wang YQ, **e WH, Liu H, Gu HB (2020) Hyperelastic magnetic reduced graphene oxide three-dimensional framework with superb oil and organic solvent adsorption capability. Adv Compos Hybrid Mater 3:473–484
Guo J, Bao H, Zhang Y, Shen X, Kim J-K, Ma J, Shao L (2021) Unravelling intercalation-regulated nanoconfinement for durably ultrafast sieving graphene oxide membranes. J Memb Sci 619: 118791
Chen Y, Wang Y, Su T, Chen J, Zhang C, Lai X, Jiang D, Wu Z, Sun C, Li B, Guo Z (2019) Self-healing polymer composites based on hydrogen bond reinforced with graphene oxide. ES Mater Manuf 4:31–37
Li R, Yang Y, Wu D, Li K, Qin Y, Tao Y, Kong Y (2019) Covalent functionalization of reduced graphene oxide aerogels with polyaniline for high performance supercapacitors. Chem Commun 55:1738–1741
Mondal S, Rana U, Malik S (2017) Reduced graphene oxide/Fe3O4/polyaniline nanostructures as electrode materials for an all-solid-state hybrid supercapacitor. J Phys Chem C 121:7573–7583
Li S, Yang C, Sarwar S, Nautiyal A, Zhang P, Du H, Liu N, Yin J, Deng K, Zhang X (2019) Facile synthesis of nanostructured polyaniline in ionic liquids for high solubility and enhanced electrochemical properties. Adv Compos Hybrid Mater 2:279–288
Gu H, Gao C, Zhou X, Du A, Naik N, Guo Z (2021) Nanocellulose nanocomposite aerogel towards efficient oil and organic solvent adsorption. Adv Compos Hybrid Mater 4:459–468
Qi G, Liu Y, Chen L, **e P, Pan D, Shi Z, Quan B, Zhong Y, Liu C, Fan R, Guo Z (2021) Lightweight Fe3C@Fe/C nanocomposites derived from wasted cornstalks with high-efficiency microwave absorption and ultrathin thickness. Adv Compos Hybrid Mater 4:1226–1238
Wu X, Tang L, Zheng S, Huang Y, Yang J, Liu Z, Yang W, Yang M (2018) Hierarchical unidirectional graphene aerogel/polyaniline composite for high performance supercapacitors. J Power Sources 397:189–195
Gu H, Lou H, Tian J, Liu S, Tang Y (2016) Reproducible magnetic carbon nanocomposites derived from polystyrene with superior tetrabromobisphenol A adsorption performance. J Mater Chem A 4:10174–10185
Kakade PM, Kachere AR, Mandlik NT, Rondiya SR, Jadkar SR, Bhosale SV (2021) Graphene oxide assisted synthesis of magnesium oxide nanorods. ES Mater Manuf 12:63–71
Mezgebe MM, Yan Z, Wei G, Gong S, Zhang F, Guang S, Xu H (2017) 3D graphene-Fe3O4-polyaniline, a novel ternary composite for supercapacitor electrodes with improved electrochemical properties. Mater Today Energy 5:164–172
Wang H, Shi P, Rui M, Zhu A, Liu R, Zhang C (2020) The green synthesis rGO/Fe3O4/PANI nanocomposites for enhanced electromagnetic waves absorption. Prog Org Coat 139: 105476
Yao F, **e W, Yang M, Zhang H, Gu H, Du A, Naik N, Young DP, Lin J, Guo Z (2021) Interfacial polymerized copolymers of aniline and phenylenediamine with tunable magnetoresistance and negative permittivity. Mater Today Phys 21: 100502
Hu Q, Zhou J, Qiu B, Wang Q, Song G, Guo Z (2021) Synergistically improved methane production from anaerobic wastewater treatment by iron/polyaniline composite. Adv Compos Hybrid Mater 4:265–273
Ingle RV, Shaikh SF, Pankaj KÂ, Bhujbal Pankaj KÂ, Pathan HM, Tabhane VA (2020) Polyaniline doped with protonic acids: optical and morphological studies. ES Mater Manuf 8:54–59
Wang Y, Gao X, Fu Y, Wu X, Wang Q, Zhang W, Luo C (2019) Enhanced microwave absorption performances of polyaniline/graphene aerogel by covalent bonding. Compos B: Eng 169:221–228
He S, Jiang X, Li S, Ran F, Long J, Shao L (2020) Intermediate thermal manipulation of polymers of intrinsic microporous (PIMs) membranes for gas separations. AIChE J 66: e16543
Luo J, Zhong W, Zou Y, **ong C, Yang W (2016) Preparation of morphology-controllable polyaniline and polyaniline/graphene hydrogels for high performance binder-free supercapacitor electrodes. J Power Sources 319:73–81
Wang X, Zeng X, Cao D (2018) Biomass-derived nitrogen-doped porous carbons (NPC) and NPC/polyaniline composites as high performance supercapacitor materials. Eng Sci 1:55–63
Xu X, Fu Q, Gu H, Guo Y, Zhou H, Zhang J, Pan D, Wu S, Dong M, Guo Z (2020) Polyaniline crystalline nanostructures dependent negative permittivity metamaterials. Polymer 188: 122129
Huang J, Liu X, Yang Z, Wu X, Wang J, Yang S (2019) Extremely elastic and conductive N-doped graphene sponge for monitoring human motions. Nanoscale 11:1159–1168
Mi H-Y, **g X, Politowicz AL, Chen E, Huang H-X, Turng L-S (2018) Highly compressible ultra-light anisotropic cellulose/graphene aerogel fabricated by bidirectional freeze drying for selective oil absorption. Carbon 132:199–209
Li C, Ding M, Zhang B, Qiao X, Liu C-Y (2018) Graphene aerogels that withstand extreme compressive stress and strain. Nanoscale 10:18291–18299
Zhang H, Liu N, Shi Y, Liu W, Yue Y, Wang S, Ma Y, Wen L, Li L, Long F, Zou Z, Gao Y (2016) Piezoresistive sensor with high elasticity based on 3d hybrid network of sponge@CNTs@Ag NPs. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces 8:22374–22381
Liu H, Dong M, Huang W, Gao J, Dai K, Guo J, Zheng G, Liu C, Shen C, Guo Z (2017) Lightweight conductive graphene/thermoplastic polyurethane foams with ultrahigh compressibility for piezoresistive sensing. J Mater Chem C 5:73–83
Wu X, Han Y, Zhang X, Zhou Z, Lu C (2016) Large-area compliant, low-cost, and versatile pressure-sensing platform based on microcrack-designed carbon black@polyurethane sponge for human–machine interfacing. Adv Funct Mater 26:6246–6256
Zhao S, Gao Y, Zhang G, Deng L, Li J, Sun R, Wong C-P (2015) Covalently bonded nitrogen-doped carbon-nanotube-supported Ag hybrid sponges: synthesis, structure manipulation, and its application for flexible conductors and strain-gauge sensors. Carbon 86:225–234
Zhai Y, Yu Y, Zhou K, Yun Z, Huang W, Liu H, **a Q, Dai K, Zheng G, Liu C, Shen C (2020) Flexible and wearable carbon black/thermoplastic polyurethane foam with a pinnate-veined aligned porous structure for multifunctional piezoresistive sensors. Chem Eng J 382: 122985
Bae GY, Pak SW, Kim D, Lee G, Kim DH, Chung Y, Cho K (2016) Linearly and highly pressure-sensitive electronic skin based on a bioinspired hierarchical structural array. Adv Mater 28:5300–5306
Sutar RA, Kumari L, Murugendrappa MV (2020) Three-dimensional variable range hop** and thermally activated conduction mechanism of polypyrrole/zinc cobalt oxide nanocomposites. J Phys Chem C 124:21772–21781
Rai RC, Hinz J, McKenna D, Pawlak J, DeMarco M (2019) Magnetic and electrical transport properties of YbFe2O4. Phys Rev B 100:7
Gu H, Guo J, Wei H, Guo S, Liu J, Huang Y, Khan MA, Wang X, Young DP, Wei S, Guo Z (2015) Strengthened magnetoresistive epoxy nanocomposite papers derived from synergistic nanomagnetite-carbon nanofiber nanohybrids. Adv Mater 27:6277–6282
Kim W, Kawaguchi K, Koshizaki N, Sohma M, Matsumoto T (2003) Fabrication and magnetoresistance of tunnel junctions using half-metallic Fe3O4. J Appl Phys 93:8032–8034
Gupta S, Narayan J (2019) Non-equilibrium processing of ferromagnetic heavily reduced graphene oxide. Carbon 153:663–673
Qiu B, Guo J, Wang Y, Wei X, Wang Q, Sun D, Khan MA, Young DP, O’Connor R, Huang X, Zhang X, Weeks BL, Wei S, Guo Z (2015) Dielectric properties and magnetoresistance behavior of polyaniline coated carbon fabrics. J Mater Chem C 3:3989–3998
Banerjee D, Kar AK (2018) Influence of polaron do** and concentration dependent FRET on luminescence of PAni–PMMA blends for application in PLEDs. Phys Chem Chem Phys 20:23055–23071
Weng Z, Gillin WP, Kreouzis T (2020) Fitting the magnetoresponses of the OLED using polaron pair model to obtain spin-pair dynamics and local hyperfine fields. Sci Rep 10:16806
Yuan P, Qiao X, Yan D, Ma D (2018) Magnetic field effects on the quenching of triplet excitons in exciplex-based organic light emitting diodes. J Mater Chem C 6:5721–5726
Gu H, Guo J, He Q, Jiang Y, Huang Y, Haldolaarachige N, Luo Z, Young DP, Wei S, Guo Z (2014) Magnetoresistive polyaniline/multi-walled carbon nanotube nanocomposites with negative permittivity. Nanoscale 6:181–189
Li T, Xu Y, Zhang Z, Liang Z, Odunmbaku O, Huang X, Boi FS, Zhang S, Liu Y, Wen J, Yu T (2020) Self-assembly prepared millimeter length ferromagnetic carbon nanotubes with spin nontrivial electronic transport properties. ACS Appl Electron Mater 2:491–498
Chen W, Lu H-Z, Zilberberg O (2019) Weak localization and antilocalization in nodal-line semimetals: dimensionality and topological effects. Phys Rev Lett 122: 196603
Bhaumik M, Mahule TS, Srinivasu VV, Maity A (2019) Investigation of the electrical charge transport mechanism and magnetoresistance response in chloride-doped polyaniline-Fe composite nanofibers. J Phys D: Appl Phys 52: 345304
Jiang Y, Liu M, Yan X, Ono T, Feng L, Cai J, Zhang D (2018) Electrical breakdown-induced tunable piezoresistivity in graphene/polyimide nanocomposites for flexible force sensor applications. Adv Mater Technol 3:1800113
Wu C, Huang X, Wu X, Qian R, Jiang P (2013) Mechanically flexible and multifunctional polymer-based graphene foams for elastic conductors and oil-water separators. Adv Mater 25:5658–5662
Funding
The authors are grateful for the support and funding from the Foundation of the National Key Research and Development Program of China (2017YFA0204600), Shanghai Rising-Star Program (No. 19QA1409400), and Fundamental Research Funds for the Central Universities. This work is supported by Shanghai Science and Technology Commission (19DZ2271500). The authors also thank Bei**g Zhongkebaice Technology Service Co., Ltd for the HRTEM measurements.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
**e, W., Yao, F., Gu, H. et al. Magnetoresistive and piezoresistive polyaniline nanoarrays in-situ polymerized surrounding magnetic graphene aerogel. Adv Compos Hybrid Mater 5, 1003–1016 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s42114-021-00413-y
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s42114-021-00413-y