Abstract
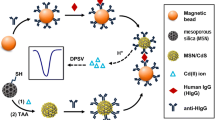
Interferon-γ is a kind of protein with a wide range of biological activities, which can regulate the immune function of the body, and can be used as an important marker to detect and treat bovine tuberculosis diseases. Here, a picogram-level bovine interferon-γ (BoIFN-γ) electrochemical impedance immunosensor was constructed for the first time using mesoporous silica nanospheres (MSNs) to immobilize specific monoclonal BoIFN-γ antibodies. The MSNs and BoIFN-γ immunosensors were characterized using scanning electron microscopy, transmission electron microscope, nitrogen adsorption experiment, X-ray photoelectron spectra, and contact angle measurements. MSNs possess a substantial specific surface area and significant hydrophilicity, and can immobilize many antibody molecules, thereby improving detection sensitivity. The immunosensor has a linear detection range from 0.001 to 10.0 ng/mL with an exceptionally low detection limit of 0.62 pg/mL. Compared to the traditional BoIFN-γ analysis method, BoIFN-γ immunosensor presents superiorities in sensitivity, wide linear range as well as short processing time. More importantly, the BoIFN-γ sensor exhibits high selectivity, reliable repeatability as well as stability, providing a promising application prospect for the early diagnosis of Mycobacterium bovis infection.






Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
The data supporting the finding reported herein are available on reasonable request from the corresponding author.
References
Reyes LV, Luk AD, Tyring SK, Hellman JM, Lefkowitz SS. Properties of bovine interferons. Experientia. 1984;40:1410–1.
Douglas PC, Kate M, Alf L, Michael AC, Dirk A, Steven G, David C, Paul EB. Cloning, sequence, and expression of bovine interleukin 2. Proc Nati Acad Sci. 1986;83:3223–7.
Suryaprakash RS, Belden EL. Bovine Interleukin 2: production and characterization. Vet Immunol Immunopathol. 1988;18:165–72.
Guo Y, An D, Liu Y, Bao J, Luo X, Cheng X, Wang Y, Gao M, Wang J. Characterization and signaling pathway analysis of interferon-kappa in bovine. Dev Comp Immunol. 2017;67:213–20.
Jiang B, Wang J, Liu W, Cheng J, Xu J, Cao M, Li Y. Comparative transcriptome analysis of MDBK cells reveals that BoIFN-gamma augmented host immune responses to bovine herpesvirus 1 infection. Front Microbiol. 2022;13: 973278.
Sinclair JA, Dawson KL, Buddle BM. The effectiveness of parallel gamma-interferon testing in New Zealand’s bovine tuberculosis eradication programme. Pre Vet Med. 2016;127(1):94–9.
Burlakovskiy M, Saveleva N, Rumyantsev AM, Yemelyanov VV, Padkina MV, Lutova L. The structure of T-DNA insertions in transgenic tobacco plants producing bovine Interferon-Gamma. Appl Sci. 2022;12(2):761.
Buzdugan SN, Chambers MA, Delahay RJ, Drewe JA. Quantitative interferon-gamma responses predict future disease progression in badgers naturally infected with Mycobacterium bovis. Epidemiol Infect. 2017;145(15):3204–13.
Yang ZJ, Jian ZQ, Chen X, Li J, Qin PY, Zhao J, Jiao XA, Hu XY. Electrochemical impedance immunosensor for sub-picogram level detection of bovine interferon gamma based on cylinder-shaped TiO2 nano-rods. Biosens Bioelectron. 2015;63:190–5.
Gao XT, Guo XY, Li M, Hong J, Lin WD, Fang LC, Jiang YT, Zhu HF, Zhang ZF, Ding JB, **n T. Interleukin 8 and pentaxin (C-Reactive Protein) as potential new biomarkers of bovine tuberculosis. J Clin Microbiol. 2019;57(10):e00274-e319.
Peters SO, Hussain T, Adenaike AS, Hazzard J, Morenikeji OB, De Donato M, Paul S, Babar M, Yakubu A, Imumorin IG. Evolutionary pattern of interferon alpha genes in bovidae and genetic diversity of IFNAA in the Bovine Genome. Front Immunol. 2020;11: 580412.
Hazem FMA, Tyler CT, Bishoy W, Mitchell VP, Adel MT. Transcriptional profiling of early and late phases of bovine tuberculosis. Infect Immun. 2022;90(2):e00313-e321.
Lisle GW, Green RS, Buddle BM. Factors affecting the gamma interferon test in the detection of bovine tubeculosis in cattle. J Vet Diagn Invest. 2017;29(2):198–202.
Guo YL, Song ZF, Li CF, Yu YY, Dai H, Luo XX, Wang YJ, Wang JW, Gao MC. A novel type-I interferon family, bovine interferon-Chi, is involved inpositive-feedback regulation of interferon production. Front Immunol. 2020;11: 528854.
Okafor CC, Grooms DL, Bolin SR, Averill JJ, Kaneene JB. Evaluation of the Interferon-γ assay on blood collected at exsanguination of cattle under field conditions for surveillance of bovine tuberculosis. Transbound Emerg Dis. 2014;61(6):e68–75.
Baca-estrada ME, Godson DL, Hughes HPA, Donkersgped JV, Kessel AV, Hraland R, Shuster DE, Da-ley M, Babiuk LA. Effect of recombinant bovine interleukin-l beta on Viral/Bacterial Pneumonia in Cattle. J Interferon Cytokine Res. 1995;15:431–9.
Rothel J, Jones S, Corner L, Cox J, Wood P. A sandwich enzyme immunoassay for bovine interferon-gamma and its use for the detection of tuberculosis in cattle. Aust Vet J. 1990;67:134–7.
Al-Mouqatea S, Alkhamis M, Akbar B, Ali A, Al-Aqeel H, Bin-Heji A, Razzaque M, Alvarez J, Perez A. Bayesian estimation of ELISA and gamma interferon test accuracy for the detection of bovine tuberculosis in caudal fold test-negative dairy cattle in Kuwait. J Vet Diagn Invest. 2018;30(3):468–70.
Gil Rosa B, Akingbade OE, Guo X, Gonzalez-Macia L, Crone MA, Cameron LP, Freemont P, Choy KL, Guder F, Yeatman E, Sharp DJ, Li B. Multiplexed immunosensors for point-of-care diagnostic applications. Biosens Bioelectron. 2022;203: 114050.
Li ZH, Hu XT, Shi JY, Zou XB, Huang XW, Zhou XC, Tahir HE, Holmes M, Povey M. Bacteria counting method based on polyaniline/bacteria thin film. Biosens Bioelectron. 2016;81:75–9.
Hales JE, Matmon G, Dalby PA, Ward JM, Aeppli G. Virus lasers for biological detection. Nat Commun. 2019;10(1):3594.
Jani IV, Peter TF. Nucleic acid point-of-care testing to improve diagnostic preparedness. Clin Infect Dis. 2022;75(4):723–8.
Terry RL, Meyran D, Ziegler DS, Haber M, Ekert PG, Trapani JA, Neeson PJ. Immune profiling of pediatric solid tumors. J Clin Investig. 2020;130(7):3391–402.
Shi F, Xu JM, Hu ZF, Ren CL, Xue YD, Zhang YC, Li J, Wang CY, Yang ZJ. Bird nest-like zinc oxide nanostructures for sensitive electrochemical glucose biosensor. Chin Chem Lett. 2021;32(10):3185–8.
Cho KG, Lee JI, Lee S, Hong K, Kang MS, Lee KH. Light-emitting devices based on electrochemiluminescence gels. Adv Funct Mater. 2020;30(33):1907936.
Zhang H, Kang WK, Wang Y, Wang XZ, Lu LH. An enzymatic reaction modulated fluorescence-on omethoate biosensor based on Fe3O4@GO and copper nanoparticles. J Anal Test. 2022;6:3–11.
Li RY, Liu Q, ** Y, Li BX. Fluorescent enzyme-linked immunoassay strategy based on enzyme-triggered in-situ synthesis of fluorescent copper nanoclusters. Sens Actuators B Chem. 2019;281:28–33.
Eltzov E, Marks RS. Colorimetric stack pad immunoassay for bacterial identification. Biosens Bioelectron. 2017;87:572–8.
Hsu W, Shih YT, Lee MS, Huang HY, Wu WN. Bead number effect in a magnetic-beads-based digital microfluidic immunoassay. Biosensors. 2022;12(5):340.
Mou L, Jiang X. Materials for microfluidic immunoassays: a review. Adv Healthc Mater. 2017;6(15):1601403.
Peng YP, He YW, Shen YF, Liang AM, Zhang XB, Liu YJ, Lin JH, Wang JP, Li YB, Fu YC. Fluorescence nanobiosensor for simultaneous detection of multiple veterinary drugs in chicken samples. J Anal Test. 2022;6:77–88.
Shoute LCT, Abdelrasoul GN, Ma YH, Duarte PA, Edwards C, Zhou R, Zeng J, Feng YW, Charlton CL, Kanji JN, Babiuk S, Chen J. Label-free impedimetric immunosensor for point-of-care detection of COVID-19 antibodies. Microsyst Nanoeng. 2023. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41378-022-00460-5.
Paimard G, Shahlaei M, Moradipour P, Akbari H, Jafari M, Arkan E. An impedimetric immunosensor modified with electrospun core-shell nanofibers for determination of the carcinoma embryonic antigen. Sens Actuators B Chem. 2020;311: 127928.
Chinnadayyala SR, Park J, Abbasi MA, Cho S. Label-free electrochemical impedimetric immunosensor for sensitive detection of IgM rheumatoid factor in human serum. Biosens Bioelectron. 2019;143: 111642.
Hui GH, Ji P, Mi SS, Deng SP. Electrochemical impedance spectrum frequency optimization of bitter taste cell-based sensors. Biosens Bioelectron. 2013;47:164–70.
Liu YJ, Jiang D, Wang SY, Cai GZ, Xue L, Li YB, Liao M, Lin JH. A microfluidic biosensor for rapid detection of Salmonella typhimurium based on magnetic separation, enzymatic catalysis and electrochemical impedance analysis. Chin Chem Lett. 2022;33(6):3156–60.
Mahmoud AM, Tang T, Harrison DJ, Lee WE, Jemere AB. A regenerating self-assembled gold nanoparticle-containing electrochemical impedance sensor. Biosens Bioelectron. 2014;56:328–33.
Bai LW, Shi YF, Zhang X, Liu XB, Wu F, Liu C, Jia JF, Lu WB. A two-dimensional NiMoO4 nanowire electrode for the sensitive determination of hydroquinone in four types of actual water samples. J Anal Test. 2022;6:382–92.
Bernardos A, Piacenza E, Sancenon F, Hamidi M, Maleki A, Turner RJ, Martinez-Manez R. Mesoporous silica-based materials with bactericidal properties. Small. 2019;15(24): e1900669.
Muramoto N, Sugiyama T, Matsuno T, Wada H, Kuroda K, Shimojima A. Preparation of periodic mesoporous organosilica with large mesopores using silica colloidal crystals as templates. Nanoscale. 2020;12(41):21155–64.
Ijaz A, Yagci MB, Ow-Yang CW, Demirel AL, Mikó A. Formation of mesoporous silica particles with hier-archical morphology. Micropor Mesopor Mater. 2020;303:1102040.
Li J, Li XH, Huang Y, Zhong YH, Lan QC, Wu XY, Hu RX, Zhang GS, Hu XY, Yang ZJ. Biofunctionalized mesoporous silica nanospheres for the ultrasensitive chemiluminescence immunoassay of tumor markers. N J Chem. 2018;42:11264.
Deng SX, Cui CX, Liu L, Duan LY, Wang JC, Zhang YP, Qu LB. A facile and controllable one-pot synthesis approach to amino-functionalized hollow silica nanoparticles with accessible ordered mesoporous shells. Chin Chem Lett. 2021;32(3):1177–80.
Toru O, Katsuya K, Masahiro T. Immobilization of antibodies on mesoporous silica materials and their binding abilities to antigens. JCS-Japan. 2011;119:238–45.
Facio DS, Luna M, Mosquera MJ. Facile preparation of mesoporous silica monoliths by an inverse micelle mechanism. Micropor Mesopor Mater. 2017;245(15):166–76.
Bilo M, Lee YJ, FrÖba M. Millimeter-sized micellar-templated silica beads and phenylene-bridged mesoporous organosilica beads. Micropor Mesopor Mater. 2019;284:327–35.
Shi F, Li JY, **ao JX, Ma XX, Xue YD, Li J, Shen M, Yang ZJ. Urchin-like PtNPs@Bi2S3: synthesis and application in electrochemical biosensor. Analyst. 2022;147:430–5.
Ding S, Mosher C, Lee XY, Das SR, Cargill AA, Tang X, Chen B, McLamore ES, Gomes C, Hostetter JM, Claussen JC. Rapid and label-free detection of interferon gamma via an electrochemical aptasensor comprising a ternary surface monolayer on a Gold interdigitated electrode array. ACS Sens. 2017;2(2):210–7.
Gumbo R, Sylvester TT, Goosen WJ, Buss PE, Klerk LM, Schalkwyk OL, MxCall A, Warren RM, Helden PD, Miller MA, Kerr T. Adaptation and diagnostic potential of a commercial cat interferon gamma re-lease assay for the detection of mycobacterium bovis infection in african lions (Panthera leo). Pathogens. 2022;11(7):765.
Josephine C, Wynand JG, Peter EB, Paul DH, Robin W, Sven DC, Michele AM. A commercial ELISA for detection of interferon gamma in white rhinoceros. J Vet Diagn Invest. 2019;31(4):531–6.
Crulhas BP, Hadley D, Liu Y, Shin DS, Stybayeva G, Imanbekova M, Hill AE, Pedrosa V, Revzin A. An electrochemical aptasensor for detection of bovine interferon gamma. Anal Methods. 2017;9(31):4527–32.
Acknowledgements
This research was funded by by National Key Research and Development Program of China (2021YFD1800403), National Natural Science Foundation of China (21475116, 21575125 and 81302016), Natural Science Foundation of Jiangsu Province (BK20221370, BK20221281), Key University Natural Science Foundation of Jiangsu Province (20KJA150004), the Project for Science and Technology of Yangzhou (YZ2022074, YZ2020076), Cross-cooperation project of Subei Peoples' Hospital of Jiangsu Province (SBJC220009), the Postgraduate Research & Practice Innovation Program of Jiangsu Province (KYCX21_3203).