Abstract
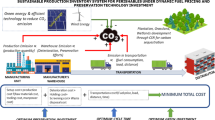
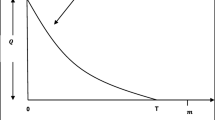
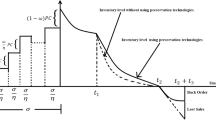
This study presents an inventory model for managing perishable goods, considering preservation technology, permissible payment delay, advertisement and stock-dependent demand, and carbon emission. Proper preservation technology is crucial in extending the lifespan of perishable goods and minimizing waste within the inventory system. The model also takes into account the permissible delay in payment, allowing retailers to navigate financial constraints while maintaining stable operations. Demand for perishable goods is influenced by advertising efforts and stock levels, necessitating a dynamic approach. By incorporating inventory carbon emissions, the framework assists retailers in reducing emissions and optimizing inventory decisions. This approach can help retailers reduce costs, increase profitability, and contribute to sustainability in the retail industry. This research refers to cases and numerical examples, providing management insights and sensitivity analysis to determine the optimal course of action to change the parameters of the model.












Similar content being viewed by others
Data Availability
No data was used for the research described in the article.
References
Abbaspour S, Aghsami A, Jolai F, Yazdani M (2022) An integrated queueing-inventory-routing problem in a green dual-channel supply chain considering pricing and delivery period: a case study of construction material supplier. Journal of Computational Design and Engineering 9(5):1917–1951
Ahmad N, Sangal I, Sharma K, Jaysawal MK, Kumar S, Pal SK, Alam K (2023) A green realistic inventory model with preservation technology for deteriorating items under carbon emission. Materials Today: Proceedings
Ahmed W, Moazzam M, Sarkar B, Rehman SU (2021) Synergic effect of reworking for imperfect quality items with the integration of multi-period delay-in-payment and partial backordering in global supply chains. Engineering 7(2):260–271
Astanti RD, Daryanto Y, Dewa PK (2022) Low-carbon supply chain model under a vendor-managed inventory partnership and carbon cap-and-trade policy. Journal of Open Innovation: Technology, Market, and Complexity 8(1):30
Barron Y (2019) A state-dependent perishability (s, s) inventory model with random batch demands. Ann Oper Res 280:65–98
Cao BB, You TH, Ou CX, Zhu H, Liu CY (2022) Optimizing payment schemes in a decentralized supply chain: a Stackelberg game with quality investment and bank credit. Computers & Industrial Engineering 168
Chaudhary R, Mittal M, Jayaswal MK (2023) A sustainable inventory model for defective items under fuzzy environment. Decision Analytics Journal 7:100207
Chen J, Xu Z, Huang D, Fang C, Wang X, Zhang J (2020) Automotive supply chain networks equilibrium model under uncertain payment delay and objective weights. Computers & Industrial Engineering 150:106866
Das SC, Zidan A, Manna AK, Shaikh AA, Bhunia AK (2020) An application of preservation technology in inventory control system with price dependent demand and partial backlogging. Alex Eng J 59(3):1359–1369
Duary A, Das S, Arif MG, Abualnaja KM, Khan MAA, Zakarya M, Shaikh AA (2022) Advance and delay in payments with the price-discount inventory model for deteriorating items under capacity constraint and partially backlogged shortages. Alex Eng J 61(2):1735–1745
Fadavi N (2022) Subgame perfect Nash equilibrium for dynamic pricing competition with finite planning horizon. ar**v:2208.02842
Feng Y, Liu Y, Chen Y (2022) A robust multi-supplier multi-period inventory model with uncertain market demand and carbon emission constraint. Computers & Industrial Engineering 165:107937
Halim MA, Paul A, Mahmoud M, Alshahrani B, Alazzawi AY, Ismail GM (2021) An overtime production inventory model for deteriorating items with nonlinear price and stock dependent demand. Alex Eng J 60(3):2779–2786
Huang YS, Fang CC, Lin YA (2020) Inventory management in supply chains with consideration of logistics, green investment and different carbon emissions policies. Computers & Industrial Engineering 139:106207
Jauhari WA, Pujawan IN, Suef M (2021) A closed-loop supply chain inventory model with stochastic demand, hybrid production, carbon emissions, and take-back incentives. J Clean Prod 320:128835
Kaushik J (2023) An inventory model with permissible delay in payment and different interest rate charges. Decision Analytics Journal 6:100180
Li R, Liu Y, Teng JT, Tsao YC (2019) Optimal pricing, lot-sizing and backordering decisions when a seller demands an advance-cash-credit payment scheme. Eur J Oper Res 278(1):283–295
Li R, Teng JT (2018) Pricing and lot-sizing decisions for perishable goods when demand depends on selling price, reference price, product freshness, and displayed stocks. Eur J Oper Res 270(3):1099–1108
Lok Y, Supadi S, Wong K (2023) Optimal investment in preservation technology for non-instantaneous deteriorating items under carbon emissions consideration. Computers & Industrial Engineering, page 109446
Ma X, Zhao Y, Luo Q, Bai Q (2022) Preservation technology investment and carbon abatement strategies in a supplier-retailer cold chain based on a differential game. Computers & Industrial Engineering 172:108540
Mahapatra AS, Mahapatra MS, Sarkar B, Majumder SK (2022) Benefit of preservation technology with promotion and time-dependent deterioration under fuzzy learning. Expert Syst Appl 201:117169
Mahato C, Mahato F, Mahata GC (2023) Bi-level trade credit policy under pricing and preservation technology in inventory models for non-instantaneous deteriorating items under carbon tax policy. Sādhanā 48(3):103
Mallick RK, Patra K, Mondal SK (2023) A new economic order quantity model for deteriorated items under the joint effects of stock dependent demand and inflation. Decision Analytics Journal, page 100288
Marchi B, Zanoni S, Jaber M (2021) Credit-dependent demand in a vendor-buyer model with a two-level delay-in-payments contract under a consignment-stock policy agreement. Appl Math Model 99:585–605
Mashud AHM, Roy D, Daryanto Y, Chakrabortty RK, Tseng ML (2021) A sustainable inventory model with controllable carbon emissions, deterioration and advance payments. J Clean Prod 296:126608
Muthusamy P, Murugesan V, Selvaraj V (2023) Optimal production-inventory decision with shortage for deterioration item and effect of carbon emission policy combination with green technology. Environment, Development and Sustainability, pp 1–66
Palanivel M, Priyan S, Uthayakumar R (2015) An inventory model with finite replenishment, probabilistic deterioration and permissible delay in payments. Journal of Management Analytics 2(3):254–279
Palanivel M, Uthayakumar R (2014) An EPQ model with variable production, probabilistic deterioration and partial backlogging under inflation. Journal of Management Analytics 1(3):200–223
Palanivel M, Uthayakumar R (2015) Finite horizon EOQ model for non-instantaneous deteriorating items with price and advertisement dependent demand and partial backlogging under inflation. Int J Syst Sci 46(10):1762–1773
Palanivel M, Uthayakumar R (2017) Two-warehouse inventory model for non-instantaneous deteriorating items with partial backlogging and permissible delay in payments under inflation. International Journal of Operational Research 28(1):35–69
Palanivel M, Venkadesh M (2024) Impact of inspection error of an economic production quantity model with acceptance sampling, defective items, and rework. Contemporary Mathematics pages 665–684
Pando V, San-José LA, Sicilia J (2020) A new approach to maximize the profit/cost ratio in a stock-dependent demand inventory model. Computers & Operations Research 120:104940
Pando V, San-Jose LA, Sicilia J, Alcaide-Lopez-de Pablo D (2021) Maximization of the return on inventory management expense in a system with price-and stock-dependent demand rate. Computers & Operations Research 127:105134
Priyan S, Mala P, Palanivel M (2022) A cleaner EPQ inventory model involving synchronous and asynchronous rework process with green technology investment. Cleaner Logistics and Supply Chain 4
Rana RS, Kumar D, Prasad K (2023) Sustainable production-inventory system for perishables under dynamic fuel pricing and preservation technology investment. Environ Sci Pollut Res 30(39):90121–90147
Rout C, Paul A, Kumar RS, Chakraborty D, Goswami A (2021) Integrated optimization of inventory, replenishment and vehicle routing for a sustainable supply chain under carbon emission regulations. J Clean Prod 316:128256
San-José LA, Sicilia J, Cárdenas-Barrón LE, González-de-la Rosa M (2024) A sustainable inventory model for deteriorating items with power demand and full backlogging under a carbon emission tax. Int J Prod Econ 268:109098
Sebatjane M (2022) The impact of preservation technology investments on lot-sizing and shipment strategies in a three-echelon food supply chain involving growing and deteriorating items. Operations Research Perspectives 9:100241
Sepehri A, Mishra U, Sarkar B (2021) A sustainable production-inventory model with imperfect quality under preservation technology and quality improvement investment. J Clean Prod 310:127332
Shah NH, Rabari K, Patel E (2021) Dynamic demand and pricing inventory model for non-instantaneous deteriorating items. International Journal of Mathematical, Engineering and Management Sciences 6(2):510
Sharma RSA, Rathore H (2024) An inventory model for deteriorating items with hybrid type demand and return in preservation technology investment. Proceedings of the Indian National Science Academy, pages 1–6
Silva PM, Gonçalves JN, Martins TM, Marques LC, Oliveira M, Reis MI, Araújo L, Correia D, Telhada J, Costa L et al (2022) A hybrid bi-objective optimization approach for joint determination of safety stock and safety time buffers in multi-item single-stage industrial supply chains. Computers & Industrial Engineering 168:108095
Vandana (2023) Partial trade-credit policy under preservation technology: a mathematical analytic approach to inventory models. Proc Natl Acad Sci, India, Sect A 93(2):243–277
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
The authors have contributed equally to this paper.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of Interest
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
M., P., S., V. & M., V. Green Inventory Strategies for Perishable Goods: Integrating Preservation, Carbon Emission, Demand Dynamics, and Payment Latency. Process Integr Optim Sustain (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s41660-024-00426-2
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s41660-024-00426-2