Abstract
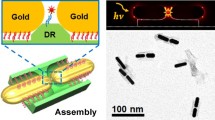
DNA origami have been established as versatile templates to fabricate plasmonic nanostructures in predefined shapes and multiple dimensions. Limited to the size of DNA origami, which are approximate to 100 nm, it is hard to assemble more intricate plasmonic nanostructures in large scale. Herein, we used rectangular DNA origami as the template to anchor two 30-nm gold nanoparticles (AuNPs) which induced dimers nanostructures. Transmission electron microscopy (TEM) images showed the assembly of AuNPs with high yields. Using the linkers to organize the DNA origami templates into nanoribbons, chains of AuNPs were obtained, which was validated by the TEM images. Furthermore, we observed a significant Raman signal enhancement from molecules covalently attached to the AuNP-dimers and AuNP-chains. Our method opens up the prospects of high-ordered plasmonic nanostructures with tailored optical properties.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
F. Peng, Y. Su, Y. Zhong et al., Silicon nanomaterials platform for bioimaging, biosensing, and cancer therapy. Acc. Chem. Res. 47, 612–623 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1021/ar400221g
J. Mcphillips, A. Murphy, M.P. Jonsson et al., High-performance biosensing using arrays of plasmonic nanotubes. ACS Nano 4, 2210–2216 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1021/nn9015828
J. Chao, D. Zhu, Y. Zhang et al., DNA nanotechnology-enabled biosensors. Biosens. Bioelectron. 76, 68–79 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1002/adma.201002767
J. Zhou, Y. Zuo, X. Wan et al., Solution-processed and high-performance organic solar cells using small molecules with a benzodithiophene unit. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 135, 8484–8487 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1021/ja403318y
F. Wang, C. Li, H. Chen et al., Plasmonic harvesting of light energy for Suzuki coupling reactions. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 135, 5588–5601 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1021/ja310501y
Ł. Bujak, T. Ishii, D.K. Sharma et al., Selective turn-on and modulation of resonant energy transfer in single plasmonic hybrid nanostructures. Nanoscale (2017). https://doi.org/10.1039/c6nr08740j
W. Shen, M.F. Bruist, S.D. Goodman et al., A protein-driven DNA device that measures the excess binding energy of proteins that distort DNA. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 43, 4750–4752 (2004). https://doi.org/10.1117/12.2051277
M. Lee, J.U. Kim, K.J. Lee et al., Aluminum nanoarrays for plasmon-enhanced light harvesting. ACS Nano 9, 6206–6213 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1021/acsnano.5b01541
K. Dopf, S. Heunisch, P. Schwab et al., Superresolution optical fluctuation imaging (SOFI) aided nanomanipulation of quantum dots using AFM for novel artificial arrangements of chemically functionalized colloidal quantum dots and plasmonic structures. SPIE Photonics Eur 9, 91260N–912609N (2014). https://doi.org/10.1117/12.2051277
Y. **ong, Z. Liu, C. Sun et al., Two-dimensional imaging by far-field superlens at visible wavelengths. Nano Lett. 7, 3360–3365 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1021/nl0716449
T. Tian, J.-C. Zhang, H.-Z. Lei et al., Synchrotron radiation X-ray fluorescence analysis of Fe, Zn and Cu in mice brain associated with Parkinson’s disease. Nucl. Sci. Tech. 26, 030506 (2015). https://doi.org/10.13538/j.1001-8042/nst.26.030506
N. Fang, H. Lee, C. Sun et al., Sub–diffraction-limited optical imaging with a silver superlens. Science 308, 534–537 (2005). https://doi.org/10.1126/science.1108759
S. Biswas, J. Duan, D. Nepal et al., Plasmonic resonances in self-assembled reduced symmetry gold nanorod structures. Nano Lett. 13, 2220–2225 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1021/nl4007358
J.A. Fan, Y. He, K. Bao et al., DNA-enabled self-assembly of plasmonic nanoclusters. Nano Lett. 11, 4859–4864 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1021/nl203194m
G. Dai, X. Lu, Z. Chen et al., DNA origami-directed, discrete three-dimensional plasmonic tetrahedron nanoarchitectures with tailored optical chirality. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 6, 5388–5392 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1021/am501599f
C. Helgert, E. Pshenay-Severin, M. Falkner et al., Chiral metamaterial composed of three-dimensional plasmonic nanostructures. Nano Lett. 11, 4400–4404 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1021/nl202565e
A. Dhawan, Y. Du, D. Batchelor et al., Hybrid top-down and bottom-up fabrication approach for wafer-scale plasmonic nanoplatforms. Small 7, 727–731 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1002/smll.201002186
B. Wei, M. Dai, P. Yin, Complex shapes self-assembled from single-stranded DNA tiles. Nature 485, 623–626 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1038/nature11075
P.W. Rothemund, Folding DNA to create nanoscale shapes and patterns. Nature 440, 297–302 (2006). https://doi.org/10.1038/nature04586
E.S. Andersen, M. Dong, M.M. Nielsen et al., Self-assembly of a nanoscale DNA box with a controllable lid. Nature 459, 73–76 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1038/nature07971
H. Dietz, S.M. Douglas, W.M. Shih, Folding DNA into twisted and curved nanoscale shapes. Science 325, 725–730 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1126/science.1174251
H. Zhang, J. Chao, D. Pan et al., DNA origami-based shape IDs for single-molecule nanomechanical genoty**. Nat. Commun. 8, 14738 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1038/ncomms14738
A. Kuzyk, R. Schreiber, Z. Fan et al., DNA-based self-assembly of chiral plasmonic nanostructures with tailored optical response. Nature 483, 311–314 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1038/nature10889
H. Gu, J. Chao, S.-J. **ao et al., A proximity-based programmable DNA nanoscale assembly line. Nature 465, 202–205 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1038/nature09026
M.J. Urban, C. Zhou, X. Duan et al., Optically resolving the dynamic walking of a plasmonic walker couple. Nano Lett. 15, 8392–8396 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.nanolett.5b04270
X. Lan, Z. Chen, G. Dai et al., Bifacial DNA origami-directed discrete, three-dimensional, anisotropic plasmonic nanoarchitectures with tailored optical chirality. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 135, 11441–11444 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1021/ja404354c
P. KüHler, E.-M. Roller, R. Schreiber et al., Plasmonic DNA-origami nanoantennas for surface-enhanced Raman spectroscopy. Nano Lett. 14, 2914–2919 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1021/nl5009635
V.V. Thacker, L.O. Herrmann, D.O. Sigle et al., DNA origami based assembly of gold nanoparticle dimers for surface-enhanced Raman scattering. Nat. Commun. 5, 3448–3453 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1038/ncomms4448
B. Liu, C. Song, D. Zhu et al., DNA-origami-based assembly of anisotropic plasmonic gold nanostructures. Small 13, 1603991–1603999 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1002/smll.201603991
X. Lan, X. Lu, C. Shen et al., Au nanorod helical superstructures with designed chirality. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 137, 457–462 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1021/ja511333q
C. Zhou, X. Duan, N. Liu, A plasmonic nanorod that walks on DNA origami. Nat. Commun. 6, 9102 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1038/ncomms9102
S. Pal, Z. Deng, H. Wang et al., DNA directed self-assembly of anisotropic plasmonic nanostructures. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 133, 17606–17609 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1021/ja207898r
M. Pilo-Pais, A. Watson, S. Demers et al., Surface-enhanced Raman scattering plasmonic enhancement using DNA origami-based complex metallic nanostructures. Nano Lett. 14, 2099–2104 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1021/nl5003069
Z. Chen, X. Lan, Y.-C. Chiu et al., Strong chiroptical activities in gold nanorod dimers assembled using DNA origami templates. Acs Photonics 2, 392–397 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1021/ph500434f
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Additional information
This work was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 21475064), the Natural Science Foundation of Jiangsu Province (No. BK20151504), Program for Changjiang Scholars and Innovative Research Team in University (No. IRT_15R37), Sci-Tech Support Plan of Jiangsu Province (No. BE2014719), the Priority Academic Program Development of Jiangsu Higher Education Institutions (No. PAPD, YX03001), the Mega-projects of Science and Technology Research (No. AWS13C007) and NUPTSF (No. 214175).
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhao, MZ., Wang, X., **ng, YK. et al. DNA origami-templated assembly of plasmonic nanostructures with enhanced Raman scattering. NUCL SCI TECH 29, 6 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s41365-017-0347-z
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s41365-017-0347-z