Abstract
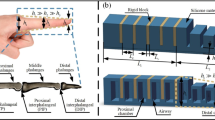
Many robotic systems face substantial challenges when trying to grasp and manipulate objects. Thought of initially as humanoid automata a century ago, this viewpoint is still influential in modern robot design. Many robotic grippers are inspired by the deftness of the human hand. The perceptual, processing, and control issues that conventional grippers have are also experienced by soft-fingered grippers. Precise finger placement, dictated by the shape and attitude of the object, is necessary to accomplish force closure when using soft fingertips to grasp. Soft robotic end-effectors have several advantages, such as a good interface with humans, the capacity to adapt to different environments, a number of degrees of freedom, and the ability to non-destructively grasp items of various shapes. Adding to earlier research that looked at the soft robot in a theoretical way, this study creates an optimized model based on the deformation in terms of bending of the channel cavity under applied pneumatic pressure. A correlation between pneumatic pressure and the pneumatic soft actuator's bending angle has been demonstrated. This research looks at how different design factors affect the bending of a multi-chambered soft actuator that is pneumatically networked. The finite element approach involves fine-tuned (optimised) actuator construction. Using FEM to evaluate aspects affecting actuator mechanical output, the ideal design parameters were discovered using DoE, resulting in a bending angle of ~ 104 degrees at 30 kPa. This study used ANOVA at a 5% significant level to identify which variables most affected the pneumatic actuator's deformation (bending angle). The significant R-square value of 96.42% supports the study's conclusions that the parameters utilised explain an immense percentage of bending angle deviations. Experimental verification of the optimized finite element model findings was conducted. The verification of the actuators' bending angles and output forces reveals that the discrepancy between the two sets of data stayed below 9%. Also, the average grip** success rate attained in the gras** evaluation, which involved four distinct types of items, was almost 97%.


























Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
All data generated or analyzed during this study are included in this article.
Code availability (software application or custom code)
Not Applicable.
References
Alici, G., Canty, T., Mutlu, R., Hu, W.P., Sencadas, V.: Modeling and experimental evaluation of bending behavior of soft pneumatic actuators made of discrete actuation chambers. Soft Robot. 5, 24–35 (2018)
Bader, F., Rahimifard, S.: A methodology for the selection of industrial robots in food handling. Innov. Food Sci. Emerg. Technol. 64, 102379 (2020)
Bhat, A., Yeow, R.C.H.: Utilizing sacrificial molding for embedding motion controlling endostructures in soft pneumatic actuators. In: Proceedings of the IEEE/RSJ International Conference on Intelligent Robots and Systems (IROS), Las Vegas, NV, USA, 24 October 2020–24 January 2020
Brown, E., Rodenberg, N., Amend, J., Mozeika, A., Steltz, E., Zakin, M.R., Lipson, H., Jaeger, H.M.: Universal robotic gripper based on the jamming of granular material. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. 107(44), 18809–18814 (2010)
Cao, Yu., Huang, J., Ding, G., Wang, Y.: Design of nonlinear predictive control for pneumatic muscle actuator based on echo state Gaussian process. IFAC-PapersOnLine 50(1), 1952–1957 (2017)
Chavoshian, M., Taghizadeh, M., Mazare, M.: Hybrid dynamic neural network and PID control of pneumatic artificial muscle using the PSO algorithm. Int. J. Autom. Comput. 17(3), 428–438 (2020)
Dang, H.M., Chi, T.V., Viet, D.N., Hai, N.N., Anh, V.T., Van, B.P.: A method for determining parameters of hyperelastic materials and its application in simulation of pneumatic soft actuator. Int. J. Comput. Mater. Sci. Eng. 10(3), 2150017 (2021)
De Payrebrune, K.M., Oliver, M.O.: On constitutive relations for a rod-based model of a pneu-net bending actuator. Ext. Mech. Lett. 8, 38–46 (2016)
Durakovic, B.: Design of experiments application, concepts, examples: state of the art. Period. Eng. Nat. Sci. 5(3) (2017).
Giffney, T., **e, M., Yong, A., Wong, A., Mousset, P., McDaid, A., Aw, K.: Soft pneumatic bending actuator with integrated carbon nanotube displacement sensor. Robotics 5(1), 7 (2016)
Hao, Y., Zheyuan, G., Zhexin, X., Shaoya, G., **, Wu.: Voltage-driven nonuniform axisymmetric torsion of a tubular dielectric elastomer actuator reinforced with one family of inextensible fibers. Eur. J. Mech. A/Solids 71, 386–393 (2018)
Hines, L., Kirstin, P., Guo, Z.L., Metin, S.: Soft actuators for small-scale robotics. Adv. Mater. 29(13), 1603483 (2017)
Hu, W., Rahim, M., Weihua, L., Gursel, A.: A structural optimisation method for a soft pneumatic actuator. Robotics 7(2), 24 (2018)
Hwang, Y., Paydar, O.H., Candler, R.N.: Pneumatic microfinger with balloon fins for linear motion using 3D printed molds. Sens. Actuat. A 234, 65–71 (2015)
Ilievski, F., Mazzeo, A.D., Shepherd, R.F., Chen, X., Whitesides, G.M.: Soft robotics for chemists. Angew. Chem. 123(8), 1930–1935 (2011)
Jiang, H., **, C.: Design and simulation analysis of a soft manipulator based on honeycomb pneumatic networks. In: 2016 IEEE International Conference on Robotics and Biomimetics (ROBIO), IEEE, pp. 350–356 (2016)
Jiang, Y., Diansheng, C., Jiacheng, Q., Zhe, L., Ziqi, W., Ying, X.: Soft robotic glove for hand rehabilitation based on a novel fabrication method. In: 2017 IEEE International Conference on Robotics and Biomimetics (ROBIO), pp. 817–822. IEEE (2017)
Jiang, Q., Fengyu, Xu.: Design and motion analysis of adjustable pneumatic soft manipulator for gras** objects. IEEE Access 8, 191920–191929 (2020)
Lalegani, D., Mohammadreza, R.S., Ali, Z., Hamed, Y.N., Mahdi, B.” Soft pneumatic actuators with integrated resistive sensors enabled by multi-material 3D printing. Int. J. Adv. Manufact. Technol., 1–15 (2023)
Lei, J., Ge, Z., Fan, P., Zou, W., Jiang, T., Dong, L.: Design and manufacture of a flexible pneumatic soft gripper. Appl. Sci. 12(13), 6306 (2022)
Li, H., Yao, J., Zhou, P., Chen, X., Yundou, Xu., Zhao, Y.: High-load soft grippers based on bionic winding effect. Soft Rob. 6(2), 276–288 (2019)
Liu, Z., Wang, F., Liu, S., Tian, Y., Zhang, D.: Modeling and analysis of soft pneumatic network bending actuators. IEEE/ASME Trans. Mechatron. 26(4), 2195–2203 (2020)
Ma, K., Jiang, Z., Gao, S., Cao, X., Fengyu, Xu.: Design and analysis of fiber-reinforced soft actuators for wearable hand rehabilitation device. IEEE Robot. Automat. Lett. 7(3), 6115–6122 (2022)
Manti, M., Hassan, T., Passetti, G., D’Elia, N., Laschi, C., Cianchetti, M.: A bioinspired soft robotic gripper for adaptable and effective gras**. Soft Rob. 2(3), 107–116 (2015)
Marechal, L., Balland, P., Lindenroth, L., Petrou, F., Kontovounisios, C., Bello, F.: Toward a common framework and database of materials for soft robotics. Soft Robot. 8, 284–297 (2021a)
Marechal, L., Balland, P., Lindenroth, L., Petrou, F., Kontovounisios, C., Bello, F.: Toward a common framework and database of materials for soft robotics. Soft Rob. 8(3), 284–297 (2021b)
Mosadegh, B., Polygerinos, P., Keplinger, C., Wennstedt, S., Shepherd, R.F., Gupta, U., Shim, J., Bertoldi, K., Walsh, C.J., Whitesides, G.M.: Pneumatic networks for soft robotics that actuate rapidly. Adv. Func. Mater. 24(15), 2163–2170 (2014a)
Mosadegh, B., Polygerinos, P., Keplinger, C., Wennstedt, S., Shepherd, R.F., Gupta, U., Shim, J., Bertoldi, K., Walsh, C.J., Whitesides, G.M.: Pneumatic networks for soft robotics that actuate rapidly. Adv. Funct. Mater. 24, 2163–2170 (2014b)
Paoletti, P., Jones, G.W., Lakshminarayanan, M.: Gras** with a soft glove: Intrinsic impedance control in pneumatic actuators. J. R. Soc. Interface 14(128), 20160867 (2017)
Polygerinos, P., Zheng, W., Johannes, T.B.O., Kevin, C.G., Robert, J.W., Katia, B., Conor, J.W.: Modeling of soft fiber-reinforced bending actuators. IEEE Trans. Robot. 31(3), 778–789 (2015)
Polygerinos, P., Correll, N., Morin, S.A., Mosadegh, B., Onal, C.D., Petersen, K., Cianchetti, M., Tolley, M.T., Shepherd, R.F.: Soft robotics: Review of fluid-driven intrinsically soft devices; manufacturing, sensing, control, and applications in human-robot interaction. Adv. Eng. Mater. 19(12), 1700016 (2017)
Putra, K.B., Tian, X., Plott, J., Shih, A.: Biaxial test and hyperelastic material models of silicone elastomer fabricated by extrusion-based additive manufacturing for wearable biomedical devices. J. Mech. Behav. Biomed. Mater. 107, 103733 (2020)
Shintake, J., Cacucciolo, V., Floreano, D., Shea, H.: Soft robotic grippers. Adv. Mater. 30(29), 1707035 (2018)
Sithiwichankit, C., Chanchareon, R.: Adaptive pincer gras** of soft pneumatic grippers based on object stiffness for modellable and controllable gras** quality. Robotics 11(6), 132 (2022)
Stano, G., Arleo, L., Percoco, G.: Additive manufacturing for soft robotics: design and fabrication of airtight, monolithic bending PneuNets with embedded air connectors. Micromachines 11(5), 485 (2020)
Sun, Z.-S., Guo, Z.-H., Tang, W.: Design of wearable hand rehabilitation glove with soft hoop-reinforced pneumatic actuator. J. Central South Univ. 26(1), 106–119 (2019)
Tai, K., El-Sayed, A.-R., Shahriari, M., Biglarbegian, M., Mahmud, S.: State of the art robotic grippers and applications. Robotics 5(2), 11 (2016)
Tho, T.P., Nguyen, T.T.: Design and development of the sorting system based on robot. In: 2015 15th International Conference on Control, Automation and Systems (ICCAS), IEEE, pp. 1639–1644 (2015)
Wakimoto, S., Suzumori, K., Ogura, K.: Miniature pneumatic curling rubber actuator generating bidirectional motion with one air-supply tube. Adv. Robot. 25(9–10), 1311–1330 (2011)
Wang, Z., Hirai, S.: Soft gripper dynamics using a line-segment model with an optimization-based parameter identification method. IEEE Robot. Autom. Lett. 2(2), 624–631 (2017)
Wang, X., Wu, P., Feng, Q., Wang, G.: Design and test of tomatoes harvesting robot. J. Agric. Mech. Res. 38(4), 94–98 (2016a)
Wang, Z., Panagiotis, P., Johannes, T.B.O., Kevin, C.G., Katia, B., Conor, J.W.: Interaction forces of soft fiber reinforced bending actuators. IEEE/ASME Trans. Mech. 22(2), 717–727 (2016b)
Wang, S., Yuan L., Yue S., **aobin L., Ning S., Xuebo Z., Ningbo Y.: A localization and navigation method with ORB-SLAM for indoor service mobile robots. In: 2016 IEEE international conference on real-time computing and robotics (RCAR). IEEE, pp. 443–447 (2016c)
Wang, J., Fei, Y., Pang, Wu.: Design, modeling, and testing of a soft pneumatic glove with segmented pneunets bending actuators. IEEE/ASME Trans. Mechatron. 24(3), 990–1001 (2019)
Wang, X., Kang, H., Zhou, H., Au, W., Wang, M.Y., Chen, C.: Development and evaluation of a robust soft robotic gripper for apple harvesting. Comput. Electron. Agric. 204, 107552 (2023)
Xavier, M.S., Fleming, A.J., Yong, Y.K.: Finite element modeling of soft fluidic actuators: overview and recent developments. Adv. Intell. Syst. 3(2), 2000187 (2021)
Yang, F., Ruan, Qi., Man, Y., **e, Z., Yue, H., Li, B., Liu, R.: Design and optimize of a novel segmented soft pneumatic actuator. IEEE Access 8, 122304–122313 (2020)
Yarali, E., Noroozi, R., Moallemi, A., Taheri, A., Baghani, M.: Develo** an analytical solution for a thermally tunable soft actuator under finite bending. Mech. Based Des. Struct. Mach. 50(5), 1793–1807 (2022)
Yeoh, O.H.: Some forms of the strain energy function for rubber. Rubber Chem. Technol. 66(5), 754–771 (1993)
Yu, M., Liu, W., Zhao, J., Hou, Y., Hong, X., Zhang, H.: Modeling and analysis of a composite structure-based soft pneumatic actuators for soft-robotic gripper. Sensors 22(13), 4851 (2022)
Zhou, J., Chen, S., Wang, Z.: A soft-robotic gripper with enhanced object adaptation and gras** reliability. IEEE Robot. Automat. Lett. 2(4), 2287–2293 (2017)
Zolfagharian, A., Lakhi, M., Ranjbar, S., Sayah Irani, M., Nafea, M., Bodaghi, M.: 4D printing parameters optimisation for bi-stable soft robotic gripper design. J. Braz. Soc. Mech. Sci. Eng. 45(4), 224 (2023)
Acknowledgements
The authors thank the Robotics lab of Department of Mechanical Engineering, SRM Institute of Science and Technology, Kattankulathur, Chennai, Tamil Nādu, India, for providing Robot facilities and necessary support.
Funding
It is certified on behalf of corresponding author (Prabhu Sethuramalingam) that present research is not funded by any external agency.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
All authors contributed to the study conception and design of soft gripper. Taguchi L9 orthogonal FEA analysis were performed by [Mr. Dhruba Jyoti Sut] and Taguchi Optimization were performed by [Prof. Prabhu Sethuramalingam]. The first draft of the manuscript was written and verified by [Mr. Dhruba Jyoti Sut and Prof. Prabhu Sethuramalingam]. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
Ethical approval
Not applicable.
Consent to participate
Not applicable.
Consent to publish
Not applicable.
Replication of results
No results are presented.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Sut, D.J., Sethuramalingam, P. Design optimisation and an experimental assessment of soft actuator for robotic gras**. Int J Intell Robot Appl (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s41315-024-00355-w
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s41315-024-00355-w