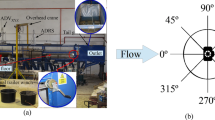
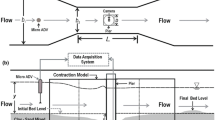
Abstract
A few investigations on clear water local scour around vertical bridge piers on clay-sand mixed (cohesive sediment) beds are found in the literature. However, no research has been reported on local scour around inclined bridge piers for clay-sand mixed cohesive beds. This research work was carried out to investigate the impact of dual inclined bridge piers (convergent-vertical piers) on maximum scour depth installed in flow direction on four beds containing different clay contents from 20–80% with sand. Three different pier shapes of different cross sections were tested (circular, rectangular & diamond) in each case. The effect of inclination (0°, 5°, 10°, 15°, 20°) with the vertical on the same beds was analyzed and discussed. The results revealed a considerable reduction in maximum scour depth with inclined bridge piers in comparison with vertical bridge piers. The least scour depth was observed around 10° inclination for rectangular and circular shaped sections and 5° for diamond bridge pier. On average 53.25%, 57.25%, and 72% reduction in scour depth was observed for inclined rectangular, diamond, and circular bridge piers respectively as compared to the vertical bridge piers. The circular bridge pier proved the most effective inclined pier, exhibiting the least scour depth among the three pier shapes. Furthermore, no equation was found in the literature to predict the maximum scour depth around inclined bridge piers on clay-sand mixed beds, so three non-linear regression-based equations for three different upstream collinear piers as a function of clay content percentage and inclination were predicted which reasonably described the experimental data.












Similar content being viewed by others
References
Aksoy AO, Bombar G, Arkis T, Guney MS (2017) Study of the time-dependent clear water scour around circular bridge piers. J Hydrol Hydromech 65(1):26–34
Ali SM, Khan AN, Rahman S, Reinhorn AMJES (2011) A survey of damages to bridges in Pakistan after the major earthquake of 8 October 2005. Earthquake Spectra 27(4):947–970
Al-Shukur A-HK, Obeid ZH (2016) Experimental study of bridge pier shape to minimize local scour. Int J Civil Eng Technol 7(1):162–171
Ansari SA, Kothyari UC, Ranga Raju KG (2002) Influence of cohesion on scour around bridge piers. J Hydraul Res 40(6):717–729
Baranwal A, Das BS, Setia BJERE (2023) A Comparative Study of Scour around Various Shaped Bridge Pier. Eng Res Express 5(1):015052
Bozkuş Z, Özalp MC, Dinçer AE (2018) Effect of pier inclination angle on local scour depth around bridge pier groups. Arab J Sci Eng 43(10):5413–5421
Bozkus Z, Çeşme M (2010) Reduction of scouring depth by using inclined piers. Can J Civ Eng 37(12):1621–1630
Briaud JL, Ting FC, Chen HC, Gudavalli R, Perugu S, Wei G (1999) SRICOS: prediction of scour rate in cohesive soils at bridge piers. J Geotech Geoenviron Eng 125(4):237–246
Briaud J-L, Chen H-C, Li Y, Nurtjahyo P (2004) SRICOS-EFA method for complex piers in fine-grained soils. J. Geotech. Geoenviron. Eng. 130(11):1180–1191
Çeşme M (2005) Experimental investigation of local scour around inclined dual bridge piers (Master’s thesis, Middle East Technical University)
Chaudhuri S, Debnath K (2013) Observations on initiation of pier scour and equilibrium scour hole profiles in cohesive sediments. ISH J Hydraulic Eng 19(1):27–37
Chaudhuri S, Pandey M, Debnath K, Oliveto G (2022) A comparative study on equilibrium scour volume around circular cylinders in clay–sand mixed cohesive beds, at near-threshold velocity of sand–an experimental approach. Water Supply 22(8):6777–6791
Chiew YM, Melville BW (1987) Local scour around bridge piers. J Hydraul Res 25(1):15–26
Debnath K, Chaudhuri S (2010) Laboratory experiments on local scour around cylinder for clay and clay–sand mixed beds. Eng Geol 111(1–4):51–61
Debnath K, Chaudhuri S (2011) Effect of suspended sediment concentration on local scour around the cylinder for clay–sand mixed sediment beds. Eng Geol. 117(3–4):236–245
Debnath K, Chaudhuri S (2012) Local scour around non-circular piers in clay–sand mixed cohesive sediment beds. Eng Geol 151:1–14
Debnath K, Nikora V, Aberle J, Westrich B, Muste M (2007a) Erosion of cohesive sediments: resuspension, bed load, and erosion patterns from field experiments. J Hydraul Eng ASCE 133(5):508–520
Debnath K, Nikora V, Elliott A (2007b) Stream bank erosion: in situ flume tests. J Irrig Drain Eng, ASCE 133(3):256–264
Debnath K, Chaudhuri S, Manik MK (2014) Local scour around abutment in clay/sand-mixed cohesive sediment bed. ISH J Hydraul Eng 20(1):46–64
Farooq R, Ghumman ARJW (2019) Impact assessment of pier shape and modifications on scouring around bridge pier. Water 11(9):1761
Hassan ZF, Karim IR, Al-Shukur AJCEJ (2020) Effect of Interaction between Bridge Piers on Local Scouring in Cohesive Soils. Civil Eng J 6(4):659–669
Hong JH, Goyal MK, Chiew YM, Chua LH (2012) Predicting time-dependent pier scour depth with support vector regression. J. of Hydrology 468 469:241–248
Iftikhar A, Sarwar K, Aslam MF (2021) Study of clear water local scour phenomenon around bridge pier groups. Hydrol Water Res 13
Jafari-Asl J, Ben Seghier MEA, Ohadi S, Dong Y, Plevris VJM (2021) A Comparative Study on the Efficiency of Reliability Methods for the Probabilistic Analysis of Local Scour at a Bridge Pier in Clay-Sand-Mixed Sediments. Modelling 2(1):63–77
Khalid M, Muzzammil M, Alam JJA (2018) Reliability analysis of local scour at bridge pier in clay-sand mixed sediments. Aquademia 2(1):01
Khan RA, Kumar M, Ahmed M, Rafi MM, Lodi SH. (2015) Earthquake damage assessment of bridges in Karachi. NED Univ J Res 12(3)
Kothyari UC (2008) Bridge scour status and research challenges. ISH J Hydraulic Eng 14(1):1–27
Link O, Klischies K, Montalva G, Dey S (2013) Effects of bed compaction on scour at piers in sand-clay mixtures. J Hydraul Eng 139(9):1013–1019
Mahmood S, A-u-H Khan, Mayo SM (2016) Exploring underlying causes and assessing damages of 2010 flash flood in the upper zone of Panjkora River. Nat Hazards 83:1213–1227
Melville BW (1997) Pier and abutment scour integrated approach. J Hydraul Eng 123(2):125–136
Melville BW, Chiew Y-M (1999) Time scale for local scour at bridge piers. J Hydraul Eng 125(1):59–65
Misuriya G, Eldho T, Mazumder B (2023) (2023) Estimation of the local scour around the cylindrical pier over the gravel bed for a low coarseness ratio. IntJ River Basin Manag. https://doi.org/10.1080/15715124.2023.2187400
Molinas A and Hosni MM (1999) Effects of gradation and cohesion on bridge scour Volume 4: Experimental study of scour around circular piers in cohesive soils. Retrieved from
Muzzammil M, Alama J, Danish MJAP (2015) Scour Prediction at Bridge Piers in Cohesive Bed Using Gene Expression Programming. Aquatic Procedia 4:789–796
Omara H, Abdeelaal G, Nadaoka K, Tawfik A (2020) Develo** empirical formulas for assessing the scour of vertical and inclined piers. Mar Georesources Geotechnol 38(2):133–143
Pasha MM, Mahmood AH, and Shams S (2016) An analysis of scouring effects on various shaped bridge piers. Brunei Darussalam J Technol Commer 29–42
Raudkivi AJ (1986) Functional trends of scour at bridge piers. J Hydraul Eng 112(1):1–13
Richardson EV, and Davis SR (1995) Evaluating scour at bridges (No. HEC 18). United States. Federal highway administration Office of technology applications
Shah AA, Ajiang C, Khan NA, Alotaibi BA, Tariq MAURJW (2022) Flood Risk Perception and Its attributes among rural households under develo** country conditions: the case of Pakistan. Water 14(6):992
Shen HW, Schneider VR, Karaki S (1969) Local scour around bridge piers. J. Hydr. Div. 95(6):1919–1940
Sheppard DM, Miller WJJOHE Jr (2006) Live-bed local pier scour exp. J Hydraul Eng 132(7):635–642
Ting FC, Briaud J-L, Chen H, Gudavalli R, Perugu S, Wei G (2001) Flume tests for scour in clay at circular piers. J Hydraul Eng 127(11):969–978
Vaghefi M, Ghodsian M, Salimi SJS (2016) The effect of circular bridge piers with different inclination angles toward downstream on scour. Sadhana 41:75–86
Wardhana K, Hadipriono FC (2003) Analysis of recent bridge failures in the United States. J. Perform. Constr. Facil 17(3):144–150
YYi R, Zhou R (2015) Reason and risk of bridge collapse in recent 15 years. Transp Sci Technol 5: 61–4 (In Chinese)
Funding
The authors declare that no funds, grants, or other support were received during the preparation of this manuscript.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
The research, as indicated by its title, presents a novel contribution to the field. The co-author (Engr. Qadeer Ahmad) defended the proposal title, securing approval for its continuation as an innovative study. The author (Usman Ghani), a seasoned PhD supervisor, provided invaluable expertise, offering guidance and technical support in material selection and the preparation of pier shapes according to literature specifications. During the experimental phase, the author played a pivotal role in establishing optimal conditions in the hydraulics laboratory of the Civil Engineering Department at the University of Engineering and Technology Taxila, Pakistan. The author meticulously inspected each experiment both before commencement and upon completion, ensuring clarity and addressing any issues promptly. Experiment initiation was contingent upon the author's inspection, and any discrepancies encountered during experimentation were swiftly resolved. The co-author undertook data analysis and statistical procedures, subsequently engaging in discussions with the author to address any discrepancies observed. The manuscript's composition, including the integration of graphs and tables, adhered to submission guidelines under the author's guidance. The author demonstrated a dedicated commitment to addressing feedback from esteemed reviewers, with the co-author diligently implementing revisions as suggested. After thorough review and modification, the manuscript was resubmitted with the author's approval. Overall, I express gratitude for the author's unwavering dedication and support throughout this endeavor.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors have no conflicts of interest to declare. All co-authors have seen and agree with the contents of the manuscript and there is no financial interest to report. We certify that the submission is original work and is not under review at any other publication.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Ahmad, Q., Ghani, U. Experimental Investigation of Local Scour Around Inclined Bridge Piers on Clay-Sand Mixed Cohesive Sediment Bed in Clear-Water Conditions. Iran J Sci Technol Trans Civ Eng (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s40996-024-01529-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s40996-024-01529-z