Abstract
Purpose
The objective of this study was to develop a liquid-filled hard capsule (LFHC) formulation of choline alfoscerate (CA) by screening with empty capsules and excipients, and to assess its in vitro/in vivo activity by comparing with those of a commercially available soft gelatin capsule or tablet. CA is a common acetylcholine precursor in the brain, which has been used for the treatment of memory loss and cognitive malfunction. CA is highly hygroscopic, and deformation or leakage occurs when a commercial soft gelatin capsule or tablet is stored at high humidity.
Methods
LFHCs composed of hypromellose or gelatin were evaluated, and a compatibility study between excipients with a formulation including CA was conducted. CA and the selected excipient were encapsulated using a liquid-filling machine and sealed with a sealing machine. CA-loaded LFHCs were tested using an in vitro release study, stability test, and in vivo pharmacokinetic (PK) study with commercial soft gelatin capsules.
Results
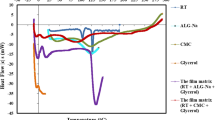
CA was more stable in LFHCs with hypromellose capsules than LFHCs with gelatin capsules, and concentrated glycerin was a suitable excipient as a diluent in liquid formulation. The optimized formulation of LFHCs released CA (> 95%) within 30 min in distilled water. The stability of LFHCs with hypromellose capsules was also confirmed under long-term and accelerated conditions for 6 months. In harsh conditions, LFHCs with hypromellose capsules showed better physical stability than commercial soft gelatin capsules or tablets. In an in vivo PK study, the area under the plasma drug concentration–time curve (AUC0→t) of LFHCs with hypromellose capsules and soft gelatin capsules was 2.26 ± 0.89 and 2.22 ± 0.87 µg⋅h/mL, respectively; the maximum plasma concentration (Cmax) was 0.46 ± 0.16 and 0.047 ± 0.15 µg/mL, respectively; and the time to maximum peak concentration was 1.67 and 1.67 h, respectively. In addition, the calculated 90% confidence intervals of the geometric mean ratio of LFHCs to Gliatilin® for Cmax and AUC0→t were 0.978 (0.901, 1.063) and 1.053 (0.933, 1.190), respectively, and satisfied the bioequivalence acceptance criteria of 80.00–125.00%.
Conclusion
CA-loaded LFHCs with hypromellose capsules were more stable than other dosage forms, thereby making it an alternative formulation for the treatment of memory loss and cognitive malfunction.






Similar content being viewed by others
Data Availability
All data are available on request to the corresponding author.
References
Bowtle WJ (2007) Materials, process, and manufacturing considerations for lipid-based hard-capsule formats. Oral lipid-based formulations. CRC Press, Boca Raton, pp 101–128
Catanesi M, d’Angelo M, Antonosante A, Castelli V, Alfonsetti M, Benedetti E, Desideri G, Ferri C, Cimini A (2020) Neuroprotective potential of choline alfoscerate against β-amyloid injury: Involvement of neurotrophic signals. Cell Biol Int 44(8):1734–1744. https://doi.org/10.1002/cbin.11369
Chang RK, Raghavan KS, Hussain MA (1998) A study on gelatin capsule brittleness: moisture tranfer between the capsule shell and its content. J Pharm Sci 87:556–558. https://doi.org/10.1021/js9704238
Choi SU, Cho SW (2013) Formulation of liquid choline alphoscerate as a solid dosage form. J Korea Acad-Ind Cooperation Soc 14:6324–6329. https://doi.org/10.5762/KAIS.2013.14.12.6324
Cole ET, Scott RA, Cade D, Connor AL, Wilding IR (2004) In vitro and in vivo pharmacoscintigraphic evaluation of ibuprofen hypromellose and gelatin capsules. Pharm Res 21:793–798. https://doi.org/10.1023/B:PHAM.0000026430.73789.e6
Cole ET, Cadé D, Benameur H (2008) Challenges and opportunities in the encapsulation of liquid and semi-solid formulations into capsules for oral administration. Adv Drug Deliv Rev 60:747–756. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.addr.2007.09.009
Damian F, Harati M, Schwartzenhauer J, Van Cauwenberghe O, Wettig SD (2021) Challenges of dissolution methods development for soft gelatin capsules. Pharmaceutics 13(2):214. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics13020214
Gatti G, Barzaghi N, Acuto G, Abbiati G, Fossati T, Perucca E (1992) A comparative study of free plasma choline levels following intramuscular administration of L-α-glycerylphosphorylcholine and citicoline in normal volunteer. Int J Clin Pharmacol Ther Toxicol 30(9):331–335
Gyllenstrand AB (2007) Medication management and patient compliance in old age. Karolinska Institutet, Solna
Kang HA, Kim SM, Kang SR, Kang MS, Lee SN et al (2010) Bioequivalence of Cholicerin soft capsule to Gliatilin soft capsule (choline Alphoscerate 400 Mg). J Pharm Investig 40:109–115. https://doi.org/10.4333/KPS.2010.40.2.109
Kathpalia H, Sharma K, Doshi G (2014) Recent trends in hard gelatin capsule delivery system. J Adv Pharm Res Apr-Jun 4:165–177
Ku MS, Li W, Dulin W, Donahue F, Cade D, Benameur H, Hutchison K (2010) Performance qualification of a new Hypromellose capsule: Part 1. Comparative evaluation of physical, mechanical and processability quality attributes of VCaps® Plus, Quali-V® and gelatin capsules. Int J Pharm 386(1–2):30–41. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijpharm.2009.10.050
Lu X, Shah P (2017) Dissolution of gelatin capsules: Evidence and confirmation of crosslinking. Dissolut Technol 24:6–21. https://doi.org/10.14227/DT240317P6
Min MH, Park JH, Hur JH, Shin HC, Cho Y et al (2019) Formulation and bioequivalence studies of choline alfoscerate tablet comparing with soft gelatin capsule in healthy male volunteers. Drug Des Dev Ther 13:1049. https://doi.org/10.2147/DDDT.S193424
Ministry of Food, Drug, and Safety, Korean Pharmacopeia XII (2019)
Richardson M, Stegemann S (2007) Capsule filling. Tablets Capsules 5:12–18
Traini E, Bramanti V, Amenta F (2013) Choline alphoscerate (alpha-glyceryl-phosphoryl-choline) an old choline-containing phospholipid with a still interesting profile as cognition enhancing agent. Curr Alzheimer Res 10:1070–1079
Yu HJ, Kim YL, Kim MJ, Park JM, Park SY et al (2022) The Effect of choline alphoscerate on non spatial memory and neuronal differentiation in a rat model of dual stress. Brain Res 1786:147900. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.brainres.2022.147900
Zhaoyu L, Vance DE (2008) Phosphatidylcholine and choline homeostasis. J Lipid Res 49:1187–1194. https://doi.org/10.1194/jlr.R700019-JLR200
Funding
This study was supported by GENUONE sciences (Seoul, Korea).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
All authors (S.‑W. Woo, S.‑J. Hwang, and C.‑W. Cho) declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Research involving human and animal rights
This article contains studies with human subjects performed by any of the authors. The human study protocol was approved by the institutional review board of Dong-A University Hospital (No. DAUHIRB-17–121), and followed the principles of the Declaration of Helsinki.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Woo, Sw., Hwang, SJ. & Cho, CW. Liquid-filled hard capsule formulation of choline alfoscerate: preparation and in vitro/in vivo evaluation. J. Pharm. Investig. 53, 517–526 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s40005-023-00618-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s40005-023-00618-x