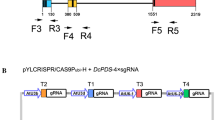
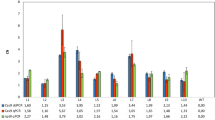
Abstract
Gene editing can modify gene function by inserting or deleting nucleotides in a specific region in a gene, which can alter the desired trait in the plant. In the selection process of gene-editing plants, many populations are created and need to be checked for the edited genes, but traditional gDNA extraction methods are laborious. Here, we used Biocube to extract gDNA and designed a specific primers to identify Cas9 in tomato [marker genes]. Biocubes are directly pressed into plant tissues to absorb and store DNA, and allow for quick and easy gDNA extraction. In this study, using template DNA obtained from tomato (Solanum lycopersicum L.) leaves by the traditional gDNA and the Biocube extraction methods, we confirmed carried DNA and editing in gene-editing plants, and compared the results of the two methods. Template DNA was obtained from cvs. Micro-Tom and M82 by the two extraction methods. Cas9, a gene-specific primer, and rbcl, an internal control, were used in PCR to confirm the presence of carried DNA. To verify the carried DNA, four samples were selected and whole-genome sequencing was performed. High-resolution melting analysis was used to check whether the target gene sequence was edited. Editing was compared using the targeted deep-sequencing results. The results showed no differences between the two gDNA extraction methods. In conclusion, we established a rapid assay for carried DNA and edited sites in gene-editing tomato plants.


Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
The raw data sequences from this study have been submitted to the NCBI Sequence Read Archive (SRA) (http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/sra) under BioProject ID PRJNA692070.
References
Baker M (2012) Gene-editing nucleases. Nat Methods 9:23–26. https://doi.org/10.1038/nmeth.1807
Bibikova M, Beumer K, Trautman JK, Carroll D (2003) Enhancing gene targeting with designed zinc finger nucleases. Science 300(5620):764. https://doi.org/10.1126/science.1079512
Bolger A, Scossa F, Bolger ME et al (2014) The genome of the stress-tolerant wild tomato species Solanum pennellii. Nat Genet 46(9):1034–1038. https://doi.org/10.1038/ng.3046
Chaerani R, Voorrips RE (2006) Tomato early blight (Alternaria solani): the pathogen, genetics, and breeding for resistance. J Gen Plant Pathol 72:335–347. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10327-006-0299-3
Cox MP, Peterson DA, Biggs PJ (2010) SolexaQA: at-a-glance quality assessment of Illumina second-generation sequencing data. BMC Bioinformatics 11:485. https://doi.org/10.1186/1471-2105-11-485
El-Mounadi K, Morales-Floriano ML, Garcia-Ruiz H (2020) Principles, applications, and biosafety of plant genome editing using CRISPR-Cas9. Front Plant Sci 11:56. https://doi.org/10.3389/fpls.2020.00056
Foolad MR (2007) Genome map** and molecular breeding of tomato. Int J Plant Genom 2007:64358. https://doi.org/10.1155/2007/64358
Fulton TM, Van der Hoeven R, Eannetta NT, Tanksley SD (2002) Identification, analysis and utilization of a conserved ortholog set (COS) markers for comparative genomics in higher plants. Plant Cell 14:1457–1467. https://doi.org/10.1105/tpc.010479
Gardner RG, Panthee DR (2010) Grape tomato breeding lines: NC 1 grape, NC 2 grape, and NC 3 grape. HortScience 45:1887–1888. https://doi.org/10.21273/HORTSCI.45.12.1887
Gómez JF, Talle B, Wilson ZA (2015) Anther and pollen development: a conserved developmental pathway. J Integr Plant Biol 57:876–891. https://doi.org/10.1111/jipb.12425
Guo X, Zhang L, Zhu J, Wang A (2017) Christolea crassifolia HARDY gene enhances drought stress tolerance in transgenic tomato plants. Plant Cell Tissue Organ Cult 129:469–481. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11240-017-1192-9
Haft DH, Selengut J, Mongodin EF, Nelson KE (2005) A guild of 45 CRISPR-associated (Cas) protein families and multiple CRISPR/Cas subtypes exist in prokaryotic genomes. PLoS Comput Biol 1(6):e60. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pcbi.0010060
Hamayun M, Khan SA, Khan MA, Khan AL, Kang S-M, Kim S-K, Joo G-J, Lee I-J (2009) Gibberellin production by pure cultures of a new strain of Aspergillus fumigatus. World J Microbiol Biotechnol 25(10):1785–1792. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11274-009-0078-3
Hong SB, Kwak HR, Kim MK, Seo JK, Shin JS, Han JH, Kim JS, Choi HS (2015) Simple and rapid detection for rice stripe virus using RT-PCR and Porous Ceramic Cubes. Res Plant Dis 21(4):321–325. https://doi.org/10.5423/RPD.2015.21.4.321
Jeong HJ, Kang JH, Zhao MA, Kwon JK, Choi HS, Bae JH, Lee HA, Joung YH, Choi D, Kang BC (2014) Tomato male sterile 1035 is essential for pollen development and meiosis in anthers. J Exp Bot 65(22):6693–6709. https://doi.org/10.1093/jxb/eru389
Kahlau S, Aspinall S, Gray JC, Bock R (2006) Sequence of the tomato chloroplast DNA and evolutionary comparison of solanaceous plastid genomes. J Mol Evol 63(2):194–207. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00239-005-0254-5
Khan SA, Hamayun M, Kim H-Y, Yoon H-J, Lee I-J, Kim J-G (2009) Gibberellin production and plant growth promotion by a newly isolated strain of Gliomastix murorum. World J Microbiol Biotechnol 25(5):829–833. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11274-009-9981-x
Kim YG, Cha J, Chandrasegaran S (1996) Hybrid restriction enzymes: zinc finger fusions to Fok I cleavage domain. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 93(3):1156–1160. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.93.3.1156
Kim TE, Lee SW, Shin JS, Kim HJ (2016a) Optimization of storage temperature and period about Solanaceae DNA extracted with porous ceramic matters (Bio cube). Korean J Hortic Sci Technol 34(S2):122
Kim TE, Sung SY, Kim HJ (2016b) A potential use of porous ceramic matters for simple preparation of DNA in Tomatoes. Korean J Hortic Sci Technol 5(S1):112
Kim HJ, Lee SW, Sun SJ, Shin JS (2017a) Optimization of storage temperature and period of radish and cabbage DNA extracted with porous ceramic matter (Bio-cube). Korean J Hortic Sci Technol 35(S1):105
Kim HJ, Sun SJ, Lee SW, Shin JS (2017b) A potential use of porous ceramic matters for simple preparation of DNA in Water Melon. Korean J Hortic Sci Technol 35(S1):105–106
Kim DH, Jung YJ, Kim JH, Kim HK, Nam KH, Lee HJ, Kim MK, Nou IS, Kang KK (2019) Development of male-sterile elite lines using marker-assisted backcrossing (MABC) in tomato. Hortic Sci Technol 37:744–755. https://doi.org/10.7235/HORT.20190074
Kimura S, Sinha N (2008) Tomato (Solanum lycopersicum): a model fruit-bearing crop. CSH Protoc. 2008:pdp-emo105. https://doi.org/10.1101/pdb.emo105
Li H, Durbin R (2009) Fast and accurate short read alignment with Burrows–Wheeler transform. Bioinformatics 25:1754–1760. https://doi.org/10.1093/bioinformatics/btp324
Li J-F, Norville JE, Aach J, McCormack M, Zhang D, Bush J, Church GM, Sheen J (2013) Multiplex and homologous recombination–mediated genome editing in Arabidopsis and Nicotiana benthamiana using guide RNA and Cas9. Nat Biotechnol 31(8):688–691. https://doi.org/10.1038/nbt.2654
Lin Q, Zong Y, Xue C, Wang S, ** S, Zhu Z, Gao C (2020) Prime genome editing in rice and wheat. Nat Biotechnol 38(5):582–585. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41587-020-0455-x
Liu W, ** of targeted mutations. Mol Plant 8(9):1431–1433. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.molp.2015.05.009
Ma X, Zhang X, Liu H, Li Z (2020) Highly efficient DNA-free plant genome editing using virally delivered CRISPR–Cas9. Nat Plants 6(7):773–779. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41477-020-0704-5
Mardis ER (2008) Next-generation DNA sequencing methods. Annu Rev Genom Hum Genet 9:387–402. https://doi.org/10.1146/annurev.genom.9.081307.164359
Martin M (2011) Cutadapt removes adapter sequences from high-throughput sequencing reads. Embnet J 17:10–12. https://doi.org/10.14806/ej.17.1.200
Mulepati S, Héroux A, Bailey S (2014) Crystal structure of a CRISPR RNA–guided surveillance complex bound to a ssDNA target. Science 345(6203):1479–1484. https://doi.org/10.1126/science.1256996
Murray MG, Thompson WF (1980) Rapid isolation of high molecular weight plant DNA. Nucleic Acids Res 8:4321–4326. https://doi.org/10.1093/nar/8.19.4321
Panthee DR, Gardner RG (2013) ‘Mountain Vineyard’ hybrid grape tomato and its parents: NC 4 grape and NC 5 grape tomato breeding lines. HortScience 48:1189–1191. https://doi.org/10.21273/HORTSCI.48.9.1189
PTY, Technelysium. Ltd. (2018) Chromas Lite Software. https://chromas.software.informer.com/download/. Accessed 14 Jan 2013
Rozen S, Skaletsky H (2000) Primer3 on the WWW for general users and for biologist programmers. Methods Mol Biol 132:365–386. https://doi.org/10.1385/1-59259-192-2:365
Sanger F, Coulson AR (1975) A rapid method for determining sequences in DNA by primed synthesis with DNA polymerase. J Mol Biol 94(3):441–448. https://doi.org/10.1016/0022-2836(75)90213-2
Sanger F, Nicklen S, Coulson AR (1977) DNA sequencing with chain-terminating. Proc Natl Acad Sci 74:5463–5467. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.74.12.5463
Scott JW, Harbaugh BK (1989) Micro-Tom: a miniature dwarf tomato. Agricultural Experiment Station Institute of Food and Agricultural Sciences University of Florida, Gainesville. Circular S-370:1–6
Stella S, Montoya G (2016) The genome editing revolution: a CRISPR-Cas TALE off-target story. Bioessays Suppl 1:S4–S13. https://doi.org/10.1002/bies.201670903
Sun H-J, Uchii S, Watanabe S, Ezura H (2006) A highly efficient transformation protocol for Micro-Tom, a model cultivar for tomato functional genomics. Plant Cell Physiol 47(3):426–431. https://doi.org/10.1093/pcp/pci251
Thomas HR, Percival SM, Yoder BK, Parant JM (2014) High-throughput genome editing and phenoty** facilitated by high resolution melting curve analysis. PLoS ONE 9(12):e114632. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0114632
Tiwari M, Kumar Trivedi P, Pandey A (2021) Emerging tools and paradigm shift of gene editing in cereals, fruits, and horticultural crops for enhancing nutritional value and food security. Food Energy Secur 10(1):e258
Tomato Genome Consortium (2012) The tomato genome sequence provides insights into fleshy fruit evolution. Nature 485(7400):635–641. https://doi.org/10.1038/nature11119
Wattoo JI, Saleem Z, Shahzad MS, Arif A, Hameed A, Saleem A (2016) DNA barcoding: amplification and sequence analysis of rbcl and matK genome regions in three divergent plant species. Adv Life Sci 4:03–07
Wittwer CT, Reed GH, Gundry CN, Vandersteen JG, Pryor RJ (2003) High-resolution genoty** by amplicon melting analysis using LCGreen. Clin Chem 49(6):853–860. https://doi.org/10.1373/49.6.853
Zhang D, Zhang Z, Unver T, Zhang B (2021) CRISPR/Cas: a powerful tool for gene function study and crop improvement. J Adv Res 29:207–221. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jare.2020.10.003
Acknowledgements
This research was conducted with the support of the Cooperative Research Program for Agriculture Science and Technology Development (Project No.: PJ01579903), Rural Development Administration, Republic of Korea.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Conceptualization and supervision: JHO; in silico analysis: SHB, HWJ, JHO; assisting in sample preparation and DNA extraction: EHK, SMK; all experiments: SHB, EHK, SMK, HWJ, JHO; data analysis, interpretation: SHB, JSS, JHO; manuscript editing, and review: SHB, JHO; project administration and funding acquisition: JHO. All authors read the article and approved the manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Human and animal rights
This article does not contain any studies with human participants or animals performed by any of the authors.
Additional information
Communicated by Seon-In Yeom.
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Bae, SH., Oh, JH., Kim, E.H. et al. Establishment of a rapid assay for sequencing of carried DNA and edited sites in gene-editing tomato plants. Hortic. Environ. Biotechnol. 63, 515–521 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13580-022-00427-5
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13580-022-00427-5