Abstract
Background
Fasting proinsulin/fasting insulin, proinsulin/insulin, vitamin D3, and waistline are each associated with the risk of diabetes. The aim of this study was to explore the effects of fasting proinsulin/fasting insulin, proinsulin/insulin, vitamin D3, and waistline on diabetes prediction in the Chinese Han population.
Methods
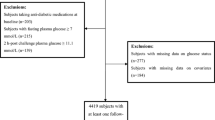
Our study consisted of 490 subjects with glucose metabolism dysfunction (GMD) and 770 healthy subjects. Spearman’s correlation analysis was used to assess the relationship of clinical characteristics with prediabetes. Receiver operation characteristic (ROC) curve analysis was used to identify the diagnostics value in diagnosing prediabetes.
Results
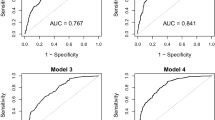
Our study indicated that fasting proinsulin/fasting insulin, vitamin D3, and waistline were positively associated with prediabetes. Fasting proinsulin/fasting insulin (OR = 1.73, p = 0.002), vitamin D3 (OR = 1.02, p < 0.001), and waistline (OR = 1.04, p < 0.001) were significantly related to an increased risk of prediabetes. Stratified analyses results showed that fasting proinsulin/fasting insulin (odds ratio [OR] = 2.51, p = 0.001), vitamin D3 (OR = 1.02, p = 0.043), and waistline (OR = 1.03, p = 0.006) had a strong association with prediabetes in men, while only vitamin D3 (OR = 1.03, p < 0.001) and waistline (OR = 1.05, p < 0.001) were strongly related to prediabetes risk in women. ROC curve analysis results revealed that the area under the curve (0.936, p < 0.001) and sensitivity (100%) in combination of the fasting proinsulin/fasting insulin, proinsulin/true insulin, vitamin D3, and waistline provided a better diagnostic value of than either parameter alone.
Conclusion
The fasting proinsulin/fasting insulin, vitamin D3, and waistline showed a strong association with an increased risk of prediabetes. The combination of fasting proinsulin/ fasting insulin, proinsulin/true insulin, vitamin D3, and waistline provides a helpful diagnostic indicator for diagnosing prediabetes in the Chinese Han population.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Sims EK, Mirmira RG, Evans-Molina C. The role of beta-cell dysfunction in early type 1 diabetes. Curr Opin Endocrinol Diabetes Obes. 2020;27(4):215–24.
Kahn LG, Philippat C, Nakayama SF, Slama R, Trasande L. Endocrine-disrupting chemicals: implications for human health. Lancet Diabetes Endocrinol. 2020;8(8):703–18.
Fagherazzi G, Ravaud P. Digital diabetes: perspectives for diabetes prevention, management and research. Diabetes Metab. 2019;45(4):322–9.
Zheng Y, Ley SH, Hu FB. Global aetiology and epidemiology of type 2 diabetes mellitus and its complications. Nat Rev Endocrinol. 2018;14(2):88–98.
Wang L, Gao P, Zhang M, Huang Z, Zhang D, Deng Q, Li Y, Zhao Z, Qin X, ** D. Prevalence and ethnic pattern of diabetes and prediabetes in China in 2013. JAMA. 2017;317(24):2515–23.
Li T, Quan H, Zhang H, Lin L, Lin L, Ou Q, Chen K. Subgroup analysis of proinsulin and insulin levels reveals novel correlations to metabolic indicators of type 2 diabetes. Aging. 2020;12(11):10715–35.
Hanley AJ, D’Agostino R, Wagenknecht LE, Saad MF, Savage PJ, Bergman R, Haffner SM. Increased proinsulin levels and decreased acute insulin response independently predict the incidence of type 2 diabetes in the insulin resistance atherosclerosis study. Diabetes. 2002;51(4):1263–70.
Kolokas K, Koufakis T, Avramidis I, Gerou S, Chatzidimitriou M, Kazakos K, Kotsa K. Fasting insulin levels correlate with the frequency of hypoglycemic events in people with type 2 diabetes on treatment with sulfonylureas: a pilot study. Indian journal of pharmacology. 2020;52(1):44–8.
Then C, Gar C, Thorand B, Huth C, Then H, Meisinger C, Heier M, Peters A, Koenig W, Rathmann W et al. Proinsulin to insulin ratio is associated with incident type 2 diabetes but not with vascular complications in the KORA F4/FF4 study. BMJ Open Diabetes Res Care. 2020;8(1):1–9.
Yoshino H, Kawakami K, Yoshino G, Hirose T. Age-related changes of proinsulin processing in diabetic and non-diabetic Japanese individuals. Geriatr Gerontol Int. 2018;18(7):1046–50.
El Shabrawy AM, Elbana KA, Abdelsalam NM. Proinsulin/insulin ratio as a predictor of insulin resistance and B-cell dysfunction in obese Egyptians ((insulin resistance & B-cell dysfunction in obese Egyptians)). Diabetes Metab Syndr. 2019;13(3):2094–6.
Lu Y, Zheng Y, Wang N, Chen Y, Li Q, Han B, Chen Y, Cheng J, Zhai H, **a F. The relationship between vitamin D and type 2 diabetes is intriguing: glimpses from the spect-China study. Ann Nutr Metab. 2017;71(3–4):195–202.
Carrara D, Bruno RM, Bacca A, Taddei S, Duranti E, Ghiadoni L, Bernini G. Cholecalciferol treatment downregulates renin–angiotensin system and improves endothelial function in essential hypertensive patients with hypovitaminosid D. J Hypertens. 2016;34(11):2199–205.
Yamamoto E, Jørgensen TN. Immunological effects of vitamin D and their relations to autoimmunity. J Autoimmun. 2019;100:7–16.
Aludwan M, Kobyliak N, Abenavoli L, Kyriienko D, Fagoonee S, Pellicano R, Komisarenko I. Vitamin D3 deficiency is associated with more severe insulin resistance and metformin use in patients with type 2 diabetes. Minerva Endocrinol. 2020;45(3):172–80.
Song Q, Sergeev IN. Calcium and vitamin D in obesity. Nutr Res Rev. 2012;25(1):130–41.
Chandler PD, Wang L, Zhang X, Sesso HD, Moorthy MV, Obi O, Lewis J, Prince RL, Danik JS, Manson JE. Effect of vitamin D supplementation alone or with calcium on adiposity measures: a systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials. Nutr Rev. 2015;73(9):577–93.
Zheng JS, Luan J, Sofianopoulou E, Sharp SJ. The association between circulating 25-hydroxyvitamin D metabolites and type 2 diabetes in European populations: a meta-analysis and Mendelian randomisation analysis. 2020;17(10):1–21.
Klahold E, Penna-Martinez M, Bruns F, Seidl C, Wicker S, Badenhoop K. Vitamin D in type 2 diabetes: genetic susceptibility and the response to supplementation. Hormone and metabolic research = Hormon- und Stoffwechselforschung = Hormones et metabolisme 2020; 52(7):492–499.
Ahmed LHM, Butler AE. Vitamin D(3) metabolite ratio as an indicator of vitamin D status and its association with diabetes complications. 2020;20(1):161–9.
Ling C, Rönn T. Epigenetics in human obesity and type 2 diabetes. Cell Metab. 2019;29(5):1028–44.
Cui R, Qi Z, Zhou L, Li Z, Li Q, Zhang J. Evaluation of serum lipid profile, body mass index, and waistline in Chinese patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus. Clin Interv Aging. 2016;11:445.
Han TS, Al-Gindan YY, Govan L, Hankey CR, Lean MEJ. Associations of BMI, waist circumference, body fat, and skeletal muscle with type 2 diabetes in adults. Acta Diabetol. 2019;56(8):947–54.
Li L, Wang J, ** Z, Li Y, Wang C, Shi Y, Zhou W, Zhang L. Interaction analysis of gene variants of TCF7L2 and body mass index and waist circumference on type 2 diabetes. Clinical nutrition (Edinburgh, Scotland). 2020;39(1):192–7.
Kuai M, Li Y, Sun X, Ma Z, Lin C, **g Y, Lu Y, Chen Q, Wu X, Kong X. A novel formula Sang-Tong-Jian improves glycometabolism and ameliorates insulin resistance by activating PI3K/AKT pathway in type 2 diabetic KKAy mice. Biomed Pharmacother. 2016;84:1585–94.
Rodbard HW, Rodbard D. Biosynthetic Human Insulin and Insulin Analogs. Am J Ther. 2020;27(1):e42–51.
Garbossa SG, Folli F. Vitamin D, sub-inflammation and insulin resistance. A window on a potential role for the interaction between bone and glucose metabolism. Rev Endoc Metab Disord. 2017;18(2):243–58.
Wieder-Huszla S, Jurczak A, Szkup M, Barczak K, Dołęgowska B, Schneider-Matyka D, Owsianowska J, Grochans E. Relationships between vitamin D3 and metabolic syndrome. 2019; 16(2):175–187.
Fagundes GE, Macan TP, Rohr P, Damiani AP, Da Rocha FR, Pereira M, Longaretti LM, Vilela TC, Ceretta LB, Mendes C, et al. Vitamin D3 as adjuvant in the treatment of type 2 diabetes mellitus: modulation of genomic and biochemical instability. Mutagenesis. 2019;34(2):135–45.
Guglielmi V, Sbraccia P. Obesity phenotypes: depot-differences in adipose tissue and their clinical implications. Eating and weight Disorders-Studies on anorexia, bulimia and obesity. 2018;23(1):3–14.
Liu X, Xu J. Body mass index and waistline are predictors of survival for hepatocellular carcinoma after hepatectomy. Med Sci Monit. 2015;21:2203.
Ren Y, Liu Y, Sun X, Wang B, Zhao Y, Luo X, Wang C, Li L, Zhang L, Zhou J et al. Cohort study to determine the waist circumference cutoffs for predicting type 2 diabetes mellitus in rural China. 2018;34(6):1–13.
Awasthi A, Rao CR, Hegde DS, Rao NK. Association between type 2 diabetes mellitus and anthropometric measurements - a case control study in South India. J Prev Med Hyg. 2017;58(1):E56-e62.
Acknowledgments
We sincerely thank all participants in this study.
Funding
This study was supported by the National Key Research and Development Program of China (2016YFC1305000, 2016YFC1305001, and 2018YFC1315603), the National Natural Science Foundation of China (81820108007), and Hainan Provincial Key Research and Development Project (ZDYF2018130).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflicts of interest.
Ethical approval
Before the start of the study, all individuals provided written informed consents in compliance with the World Medical Association ethics policy. The study protocol was approved by the Ethics Committee of the Hainan Provincial People’s Hospital.
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Quan, H., Fang, T., Lin, L. et al. Effects of fasting proinsulin/fasting insulin, proinsulin/insulin, vitamin D3, and waistline on diabetes prediction among the Chinese Han population. Int J Diabetes Dev Ctries 42, 218–226 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13410-021-00983-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13410-021-00983-z