Abstract
Background
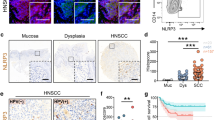
Tumor-associated macrophages (TAMs) play an important role in drug resistance in many tumors, including head and neck squamous cell carcinoma (HNSCC). However, how TAMs interact with HNSCC cells to induce drug resistance, especially under hypoxic conditions, is unclear. In this study, we investigated the mechanism of TAM-induced gefitinib resistance in HNSCC cells and sought for novel therapeutic strategies.
Methods
The effects of hypoxia-treated HNSCC cells on the migration and polarization of macrophages were analyzed. Recombinant cytokine proteins and neutralizing antibodies were used as controls. In addition, we assessed the cytotoxic effects of gefitinib on HNSCC cells treated with M2-type macrophage conditioned medium, and carried out a cytokine antibody array analysis, thereby revealing the key factor CCL15. The relationship between serum CCL15 expression levels and prognosis in HNSCC patients was analyzed. In addition, we performed bioinformatic analyses to pursue the mechanisms of CCL15-induced gefitinib resistance. Finally, metformin was used to evaluate the sensitizing effects of gefitinib treatment on HNSCC cells in vitro and in vivo.
Results
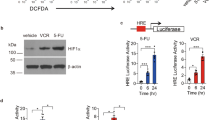
We found that HNSCC cells recruited macrophages by secreting VEGF and polarized the macrophages to the M2 phenotype through IL-6. Conversely, we found that M2-type TAMs promoted HNSCC cell resistance to gefitinib through paracrine CCL15 signaling. The serum CCL15 levels in HNSCC patients showed a significant correlation with patient prognosis. Furthermore, we found that M2-type TAMs could suppress the sensitivity of HNSCC cells to gefitinib through the CCL15-CCR1-NF-κB pathway. In addition, we found that metformin not only inhibited CCL15 expression in M2-type TAMs enhanced by hypoxia, but also suppressed CCR1 surface expression in HNSCC cells. Encouragingly, we found that metformin sensitized HNSCC cells to gefitinib treatment in vitro and in vivo.
Conclusions
Based on our data we conclude that we have identified a novel interaction between M2-type TAMs and HNSCC cells that contributes to gefitinib resistance. We also found that metformin inhibited the cross-talk between macrophages and tumor cells, thereby eliciting therapeutic effects both in vitro and in vivo.






Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- ARG-1:
-
argininase 1
- CCL2/5/15:
-
C-C motif chemokine ligand 2/5/15
- CCR1:
-
C-C motif chemokine receptor 1
- CSF-1:
-
colony stimulating factor 1
- EGFR:
-
epidermal growth factor receptor
- EMT:
-
epithelial-mesenchymal transition
- EOT:
-
eotaxin
- ET-2:
-
endothelin 2
- GSEA:
-
gene set enrichment analysis
- H-CM:
-
hypoxic condition medium
- HE:
-
hematoxylin and eosin
- HIF:
-
hypoxia-inducible factors
- HNSCC:
-
head and neck squamous cell carcinoma
- IL-4/6/10/13:
-
interleukin 4/6/10/13
- KEGG:
-
Kyoto Encyclopedia of Genes and Genomes
- NC:
-
negative control
- N-CM:
-
normoxic condition medium
- NF-κB:
-
nuclear factor kappa-light-chain-enhancer of activated B cells
- OSM:
-
oncostatin M
- PDTC:
-
pyrrolidinedithiocarbamate ammonium
- PMA:
-
phorbol 12-myristate 13-acetate
- SDF-1:
-
stromal cell-derived factor 1
- SEMA3A:
-
semaphorin 3A
- TAMs:
-
Tumor-associated macrophages
- TCGA:
-
the Cancer Genome Atlas
- TEFB:
-
transcription factor EB
- TGF:
-
β: tumor growth factor β
References
M.J. Echarri, A. Lopez-Martin, R. Hitt, Targeted therapy in locally advanced and recurrent/metastatic head and neck squamous cell carcinoma (LA-R/M HNSCC). Cancers 8, 26 (2016)
S. Bhattacharyya, V. Sekar, B. Majumder, D.G. Mehrotra, S. Banerjee, A.K. Bhowmick, N. Alam, G.K. Mandal, J. Biswas, P.K. Majumder, N. Murmu, CDKN2A-p53 mediated antitumor effect of Lupeol in head and neck cancer. Cell Oncol 40, 145–155 (2017)
C. Lo Nigro, N. Denaro, A. Merlotti, M. Merlano, Head and neck cancer: Improving outcomes with a multidisciplinary approach. Cancer Manag Res 9, 363–371 (2017)
S. Roy, M. Kar, S. Roy, A. Saha, S. Padhi, B. Banerjee, Role of beta-catenin in cisplatin resistance, relapse and prognosis of head and neck squamous cell carcinoma. Cell Oncol 41, 185–200 (2018)
O. Casanovas, D.J. Hicklin, G. Bergers, D. Hanahan, Drug resistance by evasion of antiangiogenic targeting of VEGF signaling in late-stage pancreatic islet tumors. Cancer Cell 8, 299–309 (2005)
F. Shojaei, N. Ferrara, Role of the microenvironment in tumor growth and in refractoriness/resistance to anti-angiogenic therapies. Drug Resist Updat 11, 219–230 (2008)
L.B. Rivera, G. Bergers, CANCER. Tumor angiogenesis, from foe to friend. Science 349, 694–695 (2015)
S.O. Lim, C.W. Li, W. **a, H.H. Lee, S.S. Chang, J. Shen, J.L. Hsu, D. Raftery, D. Djukovic, H. Gu, W.C. Chang, H.L. Wang, M.L. Chen, L. Huo, C.H. Chen, Y. Wu, A. Sahin, S.M. Hanash, G.N. Hortobagyi, M.C. Hung, EGFR signaling enhances aerobic glycolysis in triple-negative breast Cancer cells to promote tumor growth and immune escape. Cancer Res 76, 1284–1296 (2016)
C. Pozzi, A. Cuomo, I. Spadoni, E. Magni, A. Silvola, A. Conte, S. Sigismund, P.S. Ravenda, T. Bonaldi, M.G. Zampino, C. Cancelliere, P.P. Di Fiore, A. Bardelli, G. Penna, M. Rescigno, The EGFR-specific antibody cetuximab combined with chemotherapy triggers immunogenic cell death. Nat Med 22, 624–631 (2016)
S.N. Kazaz, I. Oztop, Treatment after first-generation epidermal growth factor receptor tyrosine kinase inhibitor resistance in non-small-cell lung Cancer. Turk Thorac J 18, 66–71 (2017)
O. Tetsu, M.J. Hangauer, J. Phuchareon, D.W. Eisele, F. McCormick, Drug resistance to EGFR inhibitors in lung Cancer. Chemotherapy 61, 223–235 (2016)
J.B. Cooper, E.E. Cohen, Mechanisms of resistance to EGFR inhibitors in head and neck cancer. Head Neck 31, 1086–1094 (2009)
S. Ma, S. Pradeep, W. Hu, D. Zhang, R. Coleman, A. Sood, The role of tumor microenvironment in resistance to anti-angiogenic therapy. F1000Res 7, 326 (2018)
M.C. Ocana, B. Martinez-Poveda, A.R. Quesada, M.A. Medina, Metabolism within the tumor microenvironment and its implication on cancer progression: An ongoing therapeutic target. Med Res Rev 39, 70-113 (2019)
S. Han, W. Xu, Z. Wang, X. Qi, Y. Wang, Y. Ni, H. Shen, Q. Hu, W. Han, Crosstalk between the HIF-1 and Toll-like receptor/nuclear factor-kappaB pathways in the oral squamous cell carcinoma microenvironment. Oncotarget 7, 37773–37789 (2016)
X. Qi, W. Xu, J. **e, Y. Wang, S. Han, Z. Wei, Y. Ni, Y. Dong, W. Han, Metformin sensitizes the response of oral squamous cell carcinoma to cisplatin treatment through inhibition of NF-kappaB/HIF-1alpha signal axis. Sci Rep 6, 35788 (2016)
X. Yin, Z. Wei, C. Song, C. Tang, W. Xu, Y. Wang, J. **e, Z. Lin, W. Han, Metformin sensitizes hypoxia-induced gefitinib treatment resistance of HNSCC via cell cycle regulation and EMT reversal. Cancer Manag Res 10, 5785–5798 (2018)
A.C. Johansson, A. Ansell, F. Jerhammar, M.B. Lindh, R. Grenman, E. Munck-Wikland, A. Ostman, K. Roberg, Cancer-associated fibroblasts induce matrix metalloproteinase-mediated cetuximab resistance in head and neck squamous cell carcinoma cells. Mol Cancer Res 10, 1158–1168 (2012)
A. Mantovani, P. Allavena, The interaction of anticancer therapies with tumor-associated macrophages. J Exp Med 212, 435–445 (2015)
L.M. Nusblat, M.J. Carroll, C.M. Roth, Crosstalk between M2 macrophages and glioma stem cells. Cell Oncol 40, 471–482 (2017)
N. Eiro, L. Gonzalez, A. Martinez-Ordonez, B. Fernandez-Garcia, L.O. Gonzalez, S. Cid, F. Dominguez, R. Perez-Fernandez, F.J. Vizoso, Cancer-associated fibroblasts affect breast cancer cell gene expression, invasion and angiogenesis. Cell Oncol 41, 369–378 (2018)
P. Nilendu, S.C. Sarode, D. Jahagirdar, I. Tandon, S. Patil, G.S. Sarode, J.K. Pal, N.K. Sharma, Mutual concessions and compromises between stromal cells and cancer cells: driving tumor development and drug resistance. Cell Oncol 41, 353–367 (2018)
S. Stieb, A. Eleftheriou, G. Warnock, M. Guckenberger, O. Riesterer, Longitudinal PET imaging of tumor hypoxia during the course of radiotherapy. Eur J Nucl Med Mol Imaging 45, 2201–2217 (2018)
K. Harada, T. Ferdous, T. Harada, Y. Ueyama, Metformin in combination with 5-fluorouracil suppresses tumor growth by inhibiting the Warburg effect in human oral squamous cell carcinoma. Int J Oncol 49, 276–284 (2016)
C. Murdoch, A. Giannoudis, C.E. Lewis, Mechanisms regulating the recruitment of macrophages into hypoxic areas of tumors and other ischemic tissues. Blood 104, 2224–2234 (2004)
C. Tripathi, B.N. Tewari, R.K. Kanchan, K.S. Baghel, N. Nautiyal, R. Shrivastava, H. Kaur, M.L. Bhatt, S. Bhadauria, Macrophages are recruited to hypoxic tumor areas and acquire a pro-angiogenic M2-polarized phenotype via hypoxic cancer cell derived cytokines Oncostatin M and Eotaxin. Oncotarget 5, 5350–5368 (2014)
Y. Deng, Y. Yang, B. Yao, L. Ma, Q. Wu, Z. Yang, L. Zhang, B. Liu, Paracrine signaling by VEGF-C promotes non-small cell lung cancer cell metastasis via recruitment of tumor-associated macrophages. Exp Cell Res 364, 208–216 (2018)
T. Chanmee, P. Ontong, K. Konno, N. Itano, Tumor-associated macrophages as major players in the tumor microenvironment. Cancers 6, 1670–1690 (2014)
Z. Zhou, Y. Peng, X. Wu, S. Meng, W. Yu, J. Zhao, H. Zhang, J. Wang, W. Li, CCL18 secreted from M2 macrophages promotes migration and invasion via the PI3K/Akt pathway in gallbladder cancer. Cell Oncol 42, 81–92 (2019)
L. Ding, G. Liang, Z. Yao, J. Zhang, R. Liu, H. Chen, Y. Zhou, H. Wu, B. Yang, Q. He, Metformin prevents cancer metastasis by inhibiting M2-like polarization of tumor associated macrophages. Oncotarget 6, 36441–36455 (2015)
M.J. Schonenberger, W.J. Kovacs, Hypoxia signaling pathways: modulators of oxygen-related organelles. Front Cell Dev Biol 3(42) (2015)
K.L. Talks, H. Turley, K.C. Gatter, P.H. Maxwell, C.W. Pugh, P.J. Ratcliffe, A.L. Harris, The expression and distribution of the hypoxia-inducible factors HIF-1alpha and HIF-2alpha in normal human tissues, cancers, and tumor-associated macrophages. Am J Pathol 157, 411–421 (2000)
Y. Li, J. Wu, P. Zhang, CCL15/CCR1 axis is involved in hepatocellular carcinoma cells migration and invasion. Tumour Biol 37, 4501–4507 (2016)
L.Z. Liu, Z. Zhang, B.H. Zheng, Y. Shi, M. Duan, L.J. Ma, Z.C. Wang, L.Q. Dong, P.P. Dong, J.Y. Shi, S. Zhang, Z.B. Ding, A.W. Ke, Y. Cao, X.M. Zhang, R. **, J. Zhou, J. Fan, X.Y. Wang, Q. Gao, CCL15 recruits suppressive monocytes to facilitate immune escape and disease progression in hepatocellular carcinoma. Hepatology 69, 143-159 (2019)
J.D. Qin, Z.H. Cao, X.F. Li, X.L. Kang, Y. Xue, Y.L. Li, D. Zhang, X.Y. Liu, Y.Z. Xue, Effect of ammonium pyrrolidine dithiocarbamate (PDTC) on NF-kappaB activation and CYP2E1 content of rats with immunological liver injury. Pharm Biol 52, 1460–1466 (2014)
T. Kitamura, T. Fujishita, P. Loetscher, L. Revesz, H. Hashida, S. Kizaka-Kondoh, M. Aoki, M.M. Taketo, Inactivation of chemokine (C-C motif) receptor 1 (CCR1) suppresses colon cancer liver metastasis by blocking accumulation of immature myeloid cells in a mouse model. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 107, 13063–13068 (2010)
A. Laitala, J.T. Erler, Hypoxic signalling in tumour stroma. Front Oncol 8, 189 (2018)
B. Barleon, S. Sozzani, D. Zhou, H.A. Weich, A. Mantovani, D. Marme, Migration of human monocytes in response to vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) is mediated via the VEGF receptor flt-1. Blood 87, 3336–3343 (1996)
L. Chen, S. Wang, Y. Wang, W. Zhang, K. Ma, C. Hu, H. Zhu, S. Liang, M. Liu, N. Xu, IL-6 influences the polarization of macrophages and the formation and growth of colorectal tumor. Oncotarget 9, 17443–17454 (2018)
A. Pardigol, U. Forssmann, H.D. Zucht, P. Loetscher, P. Schulz-Knappe, M. Baggiolini, W.G. Forssmann, H.J. Magert, HCC-2, a human chemokine: gene structure, expression pattern, and biological activity. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 95, 6308–6313 (1998)
Y. Li, H.P. Yu, P. Zhang, CCL15 overexpression predicts poor prognosis for hepatocellular carcinoma. Hepatol Int 10, 488–492 (2016)
N.J. Beasley, R. Leek, M. Alam, H. Turley, G.J. Cox, K. Gatter, P. Millard, S. Fuggle, A.L. Harris, Hypoxia-inducible factors HIF-1alpha and HIF-2alpha in head and neck cancer: relationship to tumor biology and treatment outcome in surgically resected patients. Cancer Res 62, 2493–2497 (2002)
X.S. Deng, S. Wang, A. Deng, B. Liu, S.M. Edgerton, S.E. Lind, R. Wahdan-Alaswad, A.D. Thor, Metformin targets Stat3 to inhibit cell growth and induce apoptosis in triple-negative breast cancers. Cell Cycle 11, 367–376 (2012)
L. Li, R. Han, H. **ao, C. Lin, Y. Wang, H. Liu, K. Li, H. Chen, F. Sun, Z. Yang, J. Jiang, Y. He, Metformin sensitizes EGFR-TKI-resistant human lung cancer cells in vitro and in vivo through inhibition of IL-6 signaling and EMT reversal. Clin Cancer Res 20, 2714–2726 (2014)
S. Eikawa, M. Nishida, S. Mizukami, C. Yamazaki, E. Nakayama, H. Udono, Immune-mediated antitumor effect by type 2 diabetes drug, metformin. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 112, 1809–1814 (2015)
Acknowledgments
This study was supported by the Jiangsu Natural Science Fund for Excellent Young Scholars [BK20160051], Natural Science Foundation of Jiangsu Province [BK20180136], Natural Science Foundation of Jiangsu Province [BK20180138], Key Research and Development Program of Jiangsu Province [BE2017741] and Nan**g Municipal Science and Technology Commission [201715039].
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Ethics statement
All experiments were approved by the Ethics Review Board of the Nan**g Stomatological Hospital (approval number: 2017-NKL012). All animal experiments and experimental protocols used were in accordance with the animal care and use committee of the medical school of Nan**g University.
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Electronic supplementary material
ESM 1
(DOCX 2097 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Yin, X., Han, S., Song, C. et al. Metformin enhances gefitinib efficacy by interfering with interactions between tumor-associated macrophages and head and neck squamous cell carcinoma cells. Cell Oncol. 42, 459–475 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13402-019-00446-y
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13402-019-00446-y