Abstract
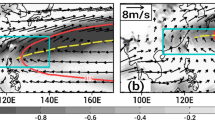
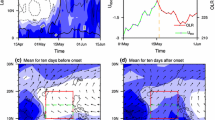
This study investigates characteristics of the convective quasi-biweekly oscillation (QBWO) over the South China Sea (SCS) and western North Pacific (WNP) in spring, and the interannual variation of its intensity. Convective QBWO over the WNP and SCS shows both similarities and differences. Convective QBWO over the WNP originates mainly from southeast of the Philippine Sea and propagates northwestward. In contrast, convective QBWO over the SCS can be traced mainly to east of the Philippines and features a westward propagation. Such a westward or northwestward propagation is probably related to n = 1 equatorial Rossby waves. During the evolution of convective QBWO over the WNP and SCS, the vertical motion and specific humidity exhibit a barotropic structure and the vertical relative vorticity shows a baroclinic structure in the troposphere. The dominant mode of interannual variation of convective QBWO intensity over the SCS-WNP region in spring is homogeneous. Its positive phase indicates enhanced convective QBWO intensity accompanied by local enhanced QBWO intensity of vertical motion throughout the troposphere as well as local enhanced (weakened) QBWO intensity of kinetic energy, vertical relative vorticity, and wind in the lower (upper) troposphere. The positive phase usually results from local increases of the background moisture and anomalous vertical shear of easterlies. The latter contributes to the relationship between the dominant mode and QBWO intensities of kinetic energy, vertical relative vorticity, and wind. Finally, a connection between the dominant mode and the sea surface temperature anomalies in the tropical Pacific Ocean is demonstrated.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Adler, R. F., G. J. Huffman, A. Chang, et al., 2003: The version-2 global precipitation climatology project (GPCP) monthly precipitation analysis (1979-present). J. Hydrometeorol., 4, 1147–1167, doi:10.1175/1525-7541(2003)004<1147:TVGPCP>2.0.CO;2.
Chatterjee, P., and B. N. Goswami, 2004: Structure, genesis and scale selection of the tropical quasi-biweekly mode. Quart. J. Roy. Meteor. Soc., 130, 1171–1194, doi: 10.1256/qj.03.133.
Chen, G. H., and C. H. Sui, 2010: Characteristics and origin of quasi-biweekly oscillation over the western North Pacific during boreal summer. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos., 115, D14113, doi: 10.1029/2009jd013389.
Chen, G. H., and X. Wang, 2017: Effect of the westward-propagating zonal wind anomaly on the initial development of quasi-biweekly oscillation over the South China Sea during early summer. Atmos. Ocean. Sci. Lett., 10, 89–95, doi: 10.1080/16742834.2017.1243002.
Chen, J. P., Z. P. Wen, R. G. Wu, et al., 2015: Influences of northward propagating 25-90-day and quasi-biweekly oscillations on eastern China summer rainfall. Climate Dyn., 45, 105–124, doi: 10.1007/s00382-014-2334-y.
Chen, T. C., and J. M. Chen, 1995: An observational study of the South China Sea monsoon during the 1979 summer: Onset and life cycle. Mon. Wea. Rev., 123, 2295–2318, doi: 10.1175/1520-0493(1995)123<2295:AOSOTS>2.0.CO;2.
Chen, X., J. Ling, and C. Y. Li, 2016: Evolution of the Madden-Julian oscillation in two types of El Niño. J. Climate, 29, 1919–1934, doi: 10.1175/JCLI-D-15-0486.1.
Dee, D. P., S. M. Uppala, A. J. Simmons, et al., 2011: The ERA-Interim reanalysis: Configuration and performance of the data assimilation system. Quart. J. Roy. Meteor. Soc., 137, 553–597, doi: 10.1002/qj.828.
Duchon, C. E., 1979: Lanczos filtering in one and two dimensions. J. Appl. Meteor, 18, 1016–1022, doi: 10.1175/1520-0450(1979)018<1016:LFIOAT>2.0.CO;2.
Fukutomi, Y., and T. Yasunari, 1999: 10-25 day intraseasonal variations of convection and circulation over East Asia and western North Pacific during early summer. J. Meteor. Soc. Japan, 77, 753–769, doi: 10.2151/jmsj1965.77.3_753.
Gushchina, D., and B. Dewitte, 2012: Intraseasonal tropical atmospheric variability associated with the two flavors of El Niño. Mon. Wea. Rev., 140, 3669–3681, doi: 10.1175/MWR-D-11-00267.1.
Hsu, P. C., T. H. Lee, C. H. Tsou, et al., 2017: Role of scale interactions in the abrupt change of tropical cyclone in autumn over the western North Pacific. Climate Dyn., 49, 3175–3192, doi: 10.1007/s00382-016-3504-x.
Jia, X. L., and S. Yang, 2013: Impact of the quasi-biweekly oscillation over the western North Pacific on East Asian subtropical monsoon during early summer. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos., 118, 4421–4434, doi: 10.1002/jgrd.50422.
Kikuchi, K., and B. Wang, 2009: Global perspective of the quasi-biweekly oscillation. J. Climate, 22, 1340–1359, doi: 10.1175/2008JCLI2368.1.
Li, C. H., T. Li, A. L. Lin, et al., 2015: Relationship between summer rainfall anomalies and sub-seasonal oscillations in South China. Climate Dyn., 44, 423–439, doi: 10.1007/s00382-014-2172-y.
Li, R. C. Y., and W. Zhou, 2013: Modulation of western North Pacific tropical cyclone activity by the ISO. Part I: Genesis and intensity. J. Climate, 26, 2904–2918, doi: 10.1175/JCLI-D-12-00210.1.
Li, T., and B. Wang, 2005: A review on the western North Pacific monsoon: Synoptic-to-interannual variabilities. Terrestrial, Atmospheric and Oceanic Sciences, 16, 285–314, doi: 10.3319/TAO.2005.16.2.285(A).
Liebmann, B., and C. A. Smith, 1996: Description of a complete (interpolated) outgoing longwave radiation dataset. Bull. Amer. Meteor. Soc., 77, 1275–1277, doi: 10.1175/1520-0477-77.6.1274.
Lin, A. L., and T. Li, 2008: Energy spectrum characteristics of boreal summer intraseasonal oscillations: Climatology and variations during the ENSO develo** and decaying phases. J. Climate, 21, 6304–6320, doi: 10.1175/2008JCLI2331.1.
Mao, J. Y., and J. C. L. Chan, 2005: Intraseasonal variability of the South China Sea summer monsoon. J. Climate, 18, 2388–2402, doi: 10.1175/JCLI3395.1.
North, G. R., T. L. Bell, R. F. Cahalan, et al., 1982: Sampling errors in the estimation of empirical orthogonal functions. Mon. Wea. Rev., 110, 699–706, doi: 10.1175/1520-0493(1982)110<0699:SEITEO>2.0.CO;2.
Ren, X. J., X. Q. Yang, and X. G. Sun, 2013: Zonal oscillation of western Pacific subtropical high and subseasonal SST variations during Yangtze persistent heavy rainfall events. J. Climate, 26, 8929–8946, doi: 10.1175/JCLI-D-12-00861.1.
Smith, T. M., R. W. Reynolds, T. C. Peterson, et al, 2008: Improvements to NOAA’s historical merged land-ocean surface temperature analysis (1880-2006). J. Climate, 21, 2283–2296, doi: 10.1175/2007JCLI2100.1.
Teng, H. Y., and B. Wang, 2003: Interannual variations of the boreal summer intraseasonal oscillation in the Asian-Pacific region. J. Climate, 16, 3572–3584, doi: 10.1175/1520-0442 (2003)016<3572:IVOTBS>2.0.CO;2.
Waliser, D. E., N. E. Graham, and C. Gautier, 1993: Comparison of the highly reflective cloud and outgoing longwave radiation datasets for use in estimating tropical deep convection. J. Climate, 6, 331–353, doi: 10.1175/1520-0442(1993)006<0331:cothrc>2.0.co;2.
Wang, B., and X. S. **e, 1996: Low-frequency equatorial waves in vertically sheared zonal flow. Part I: Stable waves. J. At-mos. Sci., 53, 449–467, doi: 10.1175/1520-0469(1996)053<0449:LFEWIV>2.0.CO;2.
Wang, B., R. G. Wu, and X. H. Fu, 2000: Pacific-East Asian tele-connection: How does ENSO affect East Asian climate? J. Climate, 13, 1517–1536, doi: 10.1175/1520-0442(2000)013<1517:PEATHE>2.0.CO;2.
Wang, L., T. Li, L. Chen, et al, 2018: Modulation of the MJO intensity over the equatorial western Pacific by two types of El Nino. Climate Dyn., 51, 687–700, doi: 10.1007/s00382-017-3949-6.
Wen, M., and R. H. Zhang, 2008: Quasi-biweekly oscillation of the convection around Sumatra and low-level tropical circulation in boreal spring. Mon. Wea. Rev., 136, 189–205, doi: 10.1175/2007MWR1991.1.
Wen, M., T. Li, R. H. Zhang, et al., 2010: Structure and origin of the quasi-biweekly oscillation over the tropical Indian Ocean in boreal spring. J. Atmos. Sci., 67, 1965–1982, doi: 10.1175/2009JAS3105.1.
Wu, B., T. J. Zhou, and T. Li, 2017: Atmospheric dynamic and thermodynamic processes driving the western North Pacific anomalous anticyclone during El Niño. Part II: Formation processes. J. Climate, 30, 9637–9650, doi: 10.1175/JCLI-D-16-0495.1.
Wu, R. G., 2018: Feedback of 10-20-day intraseasonal oscillations on seasonal mean SST in the tropical western North Pacific during boreal spring through fall. Climate Dyn., 51, 4169–4184, doi: 10.1007/s00382-016-3362-6.
Wu, R. G., and X. Cao, 2017: Relationship of boreal summer 10-20-day and 30-60-day intraseasonal oscillation intensity over the tropical western North Pacific to tropical Indo-Pacific SST. Climate Dyn., 48, 3529–3546, doi: 10.1007/s00382-016-3282-5.
Wu, R. G., and L. Song, 2018: Spatiotemporal change of intraseasonal oscillation intensity over the tropical Indo-Pacific Ocean associated with El Niño and La Niña events. Climate Dyn., 50, 1221–1242, doi: 10.1007/s00382-017-3675-0.
**e, X. S., and B. Wang, 1996: Low-frequency equatorial waves in vertically sheared zonal flow. Part II: Unstable waves. J. Atmos. Sci., 53, 3589–3605, doi: 10.1175/1520-0469(1996)053<3589:LFEWIV>2.0.CO;2.
Xu, Z. Q., T. Li, and K. Fan, 2017: The weakened intensity of the atmospheric quasi-biweekly oscillation over the western North Pacific during late summer around the late 1990s. J. Climate, 30, 9807–9826, doi: 10.1175/JCLI-D-16-0759.1.
Yang, J., B. Wang, and B. Wang, 2008: Anticorrelated intensity change of the quasi-biweekly and 30-50-day oscillations over the South China Sea. Geophys. Res. Lett., 35, L16702, doi: 10.1029/2008GL034449.
Yuan, Y., and S. Yang, 2012: Impacts of different types of El Nino on the East Asian climate: Focus on ENSO cycles. J. Climate, 25, 7702–7722, doi: 10.1175/JCLI-D-11-00576.1.
Yuan, Y., C. Y. Li, and J. Ling, 2015: Different MJO activities between EP El Nino and CP El Nino. Scientia Sinica Terrae, 45, 318–334, doi: 10.1360/zd-2015-45-3-318. (in Chinese)
Zhang, R. H., A. Sumi, and M. Kimoto, 1996: Impact of El Niño on the East Asian monsoon: A diagnostic study of the ’86/87 and ’91/92 events. J. Meteor. Soc. Japan, 74, 49–62, doi: 10.2151/jmsjl965.74.1_49.
Zhou, W., and J. C. L. Chan, 2005: Intraseasonal oscillations and the South China Sea summer monsoon onset. Int. J. Climatol., 25, 1585–1609, doi: 10.1002/joc.1209.
Zveryaev, I. I., 2002: Interdecadal changes in the zonal wind and the intensity of intraseasonal oscillations during boreal summer Asian monsoon. Tellus A, 54, 288–298, doi: 10.1034/j.1600-0870.2002.00235.X.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Supported by the China Meteorological Administration Special Public Welfare Research Fund (GYHY201506001) and National Natural Science Foundation of China (41421004, 41730964, and 41325018).
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Xu, Z., Fan, K. & Wang, H. Springtime Convective Quasi-Biweekly Oscillation and Interannual Variation of Its Intensity over the South China Sea and Western North Pacific. J Meteorol Res 33, 323–335 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13351-019-8167-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13351-019-8167-1