Abstract
Background
Mounting findings have revealed the increasingly appreciated functional importance of Retinoblastoma binding protein (RBBP) family members in tumorigenesis. However, the biological function of RBBP4 in breast cancer, especially in the most malignant and aggressive subtype, i.e., triple-negative breast cancer (TNBC), remains to be elucidated.
Objective
The present study was aimed at elucidating the role of RBBP4 in TNBC pathogenesis.
Methods
The expression of RBBP4 in TNBC tissues and cell lines was examined and its oncogenic-related functions were verified by performing a series of in vitro and in vivo experiments.
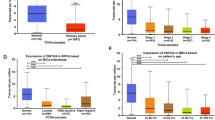
Results
At the cellular and tissue level, a marked increase in the RBBP4 expression was observed. Functionally, RBBP4 knockdown dramatically inhibited the proliferation, invasion, and migration of TNBC cells in vitro. Further, mechanistically, RBBP4 downregulation regulated the inactivation of epithelial-mesenchymal transition (EMT) of TNBC cells. In vivo xenograft model in nude mice also validated these results.
Conclusion
Collectively, our results showed that the inhibition of RBBP4 suppresses the malignant progression of TNBC cells by regulating EMT. Thus, RBBP4 could serve as a novel biomarker and target for TNBC diagnosis and treatment.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Cao X, Li F, Shao J, Lv J, Chang A, Dong W, Zhu F (2021) Circular RNA hsa_circ_0102231 sponges miR-145 to promote non-small cell lung cancer cell proliferation by up-regulating the expression of RBBP4. J Biochem 169:65–73
Gallardo M, Calaf GM (2016) Curcumin inhibits invasive capabilities through epithelial mesenchymal transition in breast cancer cell lines. Int J Oncol 49:1019–1027
Guo Q, Cheng K, Wang X, Li X, Yu Y, Hua Y, Yang Z (2020) Expression of HDAC1 and RBBP4 correlate with clinicopathologic characteristics and prognosis in breast cancer. Int J Clin Exp Pathol 13:563–572
** X, Jiang R, **ang Y, Fan Z, Wu Z, Yang B, Yang L, Wei S, Yang Y (2018) Overexpression of retinoblastoma-binding protein 4 contributes to the radiosensitivity of AGS gastric cancer cells via phosphoinositide3-kinase/protein kinase B pathway suppression. Mol Med Rep 18:1571–1581
Kitange GJ, Mladek AC, Schroeder MA, Pokorny JC, Carlson BL, Zhang Y, Nair AA, Lee JH, Yan H, Decker PA et al (2016) Retinoblastoma binding protein 4 modulates temozolomide sensitivity in glioblastoma by regulating DNA repair proteins. Cell Rep 14:2587–2598
Li D, Song H, Mei H, Fang E, Wang X, Yang F, Li H, Chen Y, Huang K, Zheng L et al (2018) Armadillo repeat containing 12 promotes neuroblastoma progression through interaction with retinoblastoma binding protein 4. Nat Commun 9:2829
Li YD, Lv Z, **e HY, Zheng SS (2019) Retinoblastoma binding protein 4 up-regulation is correlated with hepatic metastasis and poor prognosis in colon cancer patients. Hepatobiliary Pancreat Dis Int 18:446–451
Li YD, Lv Z, Zhu WF (2020) RBBP4 promotes colon cancer malignant progression via regulating Wnt/β-catenin pathway. World J Gastroenterol 26:5328–5342
Li C, Fan Z, Lin X, Cao M, Song F, Song F (2021) Parity and risk of develo** breast cancer according to tumor subtype: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Cancer Epidemiol 75:102050
Lyons TG (2019) Targeted therapies for triple-negative breast cancer. Curr Treat Options Oncol 20:82
Nabeel-Shah S, Garg J, Saettone A, Ashraf K, Lee H, Wahab S, Ahmed N, Fine J, Derynck J, Pu S et al (2021) Functional characterization of RebL1 highlights the evolutionary conservation of oncogenic activities of the RBBP4/7 orthologue in Tetrahymena thermophila. Nucleic Acids Res 49:6196–6212
Nagini S (2017) Breast cancer: current molecular therapeutic targets and new players. Anticancer Agents Med Chem 17:152–163
Nath A, Mitra S, Mistry T, Pal R, Nasare VD (2021) Molecular targets and therapeutics in chemoresistance of triple-negative breast cancer. Med Oncol 39:14
Oliveira SHP, Brito VGB, Frasnelli SCT, Ribeiro BDS, Ferreira MN, Queiroz DP, Beltan CT, Lara VS, Santos CF (2019) Aliskiren attenuates the inflammatory response and wound healing process in diabetic mice with periodontal disease. Front Pharmacol 10:708
Qiao N, Wang S, Hu L (2015) Retinoblastoma-binding protein 2 induces epithelial-mesenchymal transition in esophageal squamous cancer cells. Biotechnol Lett 37:2365–2370
Ramadoss S, Chen X, Wang CY (2012) Histone demethylase KDM6B promotes epithelial-mesenchymal transition. J Biol Chem 287:44508–44517
Reddy TP, Rosato RR, Li X, Moulder S, Piwnica-Worms H, Chang JC (2020) A comprehensive overview of metaplastic breast cancer: clinical features and molecular aberrations. Breast Cancer Res 22:121
Saleh T, Jankowski W, Sriram G, Rossi P, Shah S, Lee KB, Cruz LA, Rodriguez AJ, Birge RB, Kalodimos CG (2016) Cyclophilin A promotes cell migration via the Abl-Crk signaling pathway. Nat Chem Biol 12:117–123
Shrivastava S, Jeengar MK, Thummuri D, Koval A, Katanaev VL, Marepally S, Naidu VGM (2017) Cardamonin, a chalcone, inhibits human triple negative breast cancer cell invasiveness by downregulation of Wnt/β-catenin signaling cascades and reversal of epithelial-mesenchymal transition. BioFactors 43:152–169
Sun A, Li F, Liu Z, Jiang Y, Zhang J, Wu J, Shi Y (2018) Structural and biochemical insights into human zinc finger protein AEBP2 reveals interactions with RBBP4. Protein Cell 9:738–742
Tsujii A, Miyamoto Y, Moriyama T, Tsuchiya Y, Obuse C, Mizuguchi K, Oka M, Yoneda Y (2015) Retinoblastoma-binding protein 4-regulated classical nuclear transport is involved in cellular senescence. J Biol Chem 290:29375–29388
Wang Z, Li Z, Wu Q, Li C, Li J, Zhang Y, Wang C, Sun S, Sun S (2020) DNER promotes epithelial-mesenchymal transition and prevents chemosensitivity through the Wnt/β-catenin pathway in breast cancer. Cell Death Dis 11:642
Yan Z, Zhang K, Ji M, Xu H, Chen X (2021) A dual PI3K/HDAC inhibitor downregulates oncogenic pathways in hematologic tumors in vitro and in vivo. Front Pharmacol 12:741697
Zhou D, Kannappan V, Chen X, Li J, Leng X, Zhang J, Xuan S (2015) RBP2 induces stem-like cancer cells by promoting EMT and is a prognostic marker for renal cell carcinoma. Exp Mol Med 48:e238
Zhou H, Li G, Wang Y, Jiang R, Li Y, Wang H, Wang F, Ma H, Cao L (2021) Microbial metabolite sodium butyrate attenuates cartilage degradation by restoring impaired autophagy and autophagic flux in osteoarthritis development. Front Pharmacol 12:659597
Funding
The Project was supported by the Hunan Provincial Natural Science Foundation of China (2021JJ80015).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
All authors have read and approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
Zitong Zheng, Xu Yao, and Yi Liu declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zheng, Z., Yao, X. & Liu, Y. RBBP4 plays a vital role in the malignant progression of triple-negative breast cancer by regulating epithelial-mesenchymal transition. Genes Genom 44, 1301–1309 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13258-022-01262-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13258-022-01262-9