Abstract
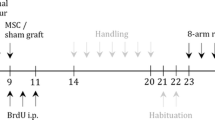
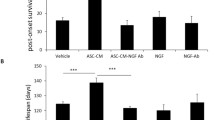
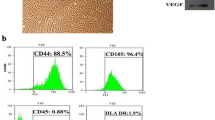
Mesenchymal stem cells (MSCs) secrete neurotrophic factors, and have been reported to improve functional outcomes in animal models of neurodegenerative diseases such as cerebral ischemia, stroke, spinal cord lesions, and Parkinson’s disease. Previously, we found that adipose tissue-derived mesenchymal stem cells (ASCs) cultured at high cell density (HD-ASCs) expressed interferon-beta (IFN-β). Here we demonstrate that ASCs expressing IFN-β also express brain-derived neurotrophic factor (BDNF). Growth rates of neuroblastoma cells (SK-N-BE(2)C) were increased when co-cultured with HD-ASCs or treated with concentrated medium obtained from HD-ASCs (HD-ASC-CM). The HD-ASC-CM induced AKT phosphorylation in SK-N-BE(2)C cells, and AKT inhibition by Ly294002 reduced cell viability of SK-N-BE(2)C cells. Additionally, a protective effect on SK-N-BE(2)C cells exposed to 6-hydroxydopamine (6-OHDA) was observed in the HD-ASC-CM or brain-derived neurotrophic factor (BDNF) treated cells. The protective effect of the HD-ASC-CM was neutralized by anti-BDNF antibody. In the 6-OHDA-induced Parkinson’s disease rat model, ASCs reduced amphetamine-induced rotations and a greater number of tyrosine hydroxylase (TH)-positive cells were observed in the HD-ASCs-injected group compared with sham controls and the low density cultured ASC-injected group. Moreover, the expression of BDNF, nerve growth factor (NGF), TH, and proliferating cell nuclear antigen (PCNA) in ipsilateral midbrain tissues including substantia nigra pars compacta (SNc) was increased by transplantation of HD-ASCs. These data indicate that HD-ASCs may induce neuroprotective effects through BDNF expression and subsequent increase of proliferation in neuronal cells both in vitro and in vivo.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ambjorn M, Ejlerskov P, Liu Y, Lees M, Jaattela M, Issazadeh-Navikas S (2013) IFNB1/interferon-beta-induced autophagy in MCF-7 breast cancer cells counteracts its proapoptotic function. Autophagy 9:287–302
Azoulay D, Mausner-Fainberg K, Urshansky N, Fahoum F, Karni A (2009) Interferon-beta therapy up-regulates BDNF secretion from PBMCs of MS patients through a CD40-dependent mechanism. J Neuroimmunol 211:114–119
Biernacki K, Antel JP, Blain M, Narayanan S, Arnold DL, Prat A (2005) Interferon beta promotes nerve growth factor secretion early in the course of multiple sclerosis. Arch Neurol 62:563–568
Borden EC, Sen GC, Uze G, Silverman RH, Ransohoff RM, Foster GR, Stark GR (2007) Interferons at age 50: past, current and future impact on biomedicine. Nat Rev Drug Discov 6:975–990
Bouchez G, Sensebe L, Vourc’h P, Garreau G, Bodard S, Rico A, Guilloteau D, Charbord P, Besnard JC, Chalon S (2008) Partial recovery of dopaminergic pathway after graft of adult mesenchymal stem cells in a rat model of Parkinson’s disease. Neurochem Int 52:1332–1342
Campagnoli C, Roberts IA, Kumar S, Bennett PR, Bellantuono I, Fisk NM (2001) Identification of mesenchymal stem/progenitor cells in human first-trimester fetal blood, liver, and bone marrow. Blood 98:2396–2402
Chen X, Katakowski M, Li Y, Lu D, Wang L, Zhang L, Chen J, Xu Y, Gautam S, Mahmood A, Chopp M (2002) Human bone marrow stromal cell cultures conditioned by traumatic brain tissue extracts: growth factor production. J Neurosci Res 69:687–691
De Ugarte DA, Morizono K, Elbarbary A, Alfonso Z, Zuk PA, Zhu M, Dragoo JL, Ashjian P, Thomas B, Benhaim P, Chen I, Fraser J, Hedrick MH (2003) Comparison of multi-lineage cells from human adipose tissue and bone marrow. Cells Tissues Organs 174:101–109
Dormady SP, Bashayan O, Dougherty R, Zhang XM, Basch RS (2001) Immortalized multipotential mesenchymal cells and the hematopoietic microenvironment. J Hematother Stem Cell Res 10:125–140
Geeta R, Ramnath RL, Rao HS, Chandra V (2008) One year survival and significant reversal of motor deficits in parkinsonian rats transplanted with hESC derived dopaminergic neurons. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 373:258–264
Hedlund E, Pruszak J, Lardaro T, Ludwig W, Vinuela A, Kim KS, Isacson O (2008) Embryonic stem cell-derived Pitx3-enhanced green fluorescent protein midbrain dopamine neurons survive enrichment by fluorescence-activated cell sorting and function in an animal model of Parkinson’s disease. Stem Cells 26:1526–1536
Hornykiewicz O (1973) Parkinson’s disease: from brain homogenate to treatment. Fed Proc 32:183–190
Huang H, **ao T, He L, Ji H, Liu XY (2012) Interferon-beta-armed oncolytic adenovirus induces both apoptosis and necroptosis in cancer cells. Acta Biochim Biophys Sin 44:737–745
Ibanez CF (1994) Structure-function relationships in the neurotrophin family. J Neurobiol 25:1349–1361
Isacson O (2003) The production and use of cells as therapeutic agents in neurodegenerative diseases. Lancet Neurol 2:417–424
Jiang Y, Jahagirdar BN, Reinhardt RL, Schwartz RE, Keene CD, Ortiz-Gonzalez XR, Reyes M, Lenvik T, Lund T, Blackstad M, Du J, Aldrich S, Lisberg A, Low WC, Largaespada DA, Verfaillie CM (2002) Pluripotency of mesenchymal stem cells derived from adult marrow. Nature 418:41–49
** S, Kawanokuchi J, Mizuno T, Wang J, Sonobe Y, Takeuchi H, Suzumura A (2007) Interferon-beta is neuroprotective against the toxicity induced by activated microglia. Brain Res 1179:140–146
Lee HS, Huang GT, Chiang H, Chiou LL, Chen MH, Hsieh CH, Jiang CC (2003) Multipotential mesenchymal stem cells from femoral bone marrow near the site of osteonecrosis. Stem Cells 21:190–199
Levy YS, Bahat-Stroomza M, Barzilay R, Burshtein A, Bulvik S, Barhum Y, Panet H, Melamed E, Offen D (2008) Regenerative effect of neural-induced human mesenchymal stromal cells in rat models of Parkinson’s disease. Cytotherapy 10:340–352
Munoz JR, Stoutenger BR, Robinson AP, Spees JL, Prockop DJ (2005) Human stem/progenitor cells from bone marrow promote neurogenesis of endogenous neural stem cells in the hippocampus of mice. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 102:18171–18176
Muraoka K, Shingo T, Yasuhara T, Kameda M, Yuen WJ, Uozumi T, Matsui T, Miyoshi Y, Date I (2008) Comparison of the therapeutic potential of adult and embryonic neural precursor cells in a rat model of Parkinson disease. J Neurosurg 108:149–159
Murrell W, Wetzig A, Donnellan M, Feron F, Burne T, Meedeniya A, Kesby J, Bianco J, Perry C, Silburn P, Mackay-Sim A (2008) Olfactory mucosa is a potential source for autologous stem cell therapy for Parkinson’s disease. Stem Cells 26:2183–2192
Nomura T, Honmou O, Harada K, Houkin K, Hamada H, Kocsis JD (2005) I.V. infusion of brain-derived neurotrophic factor gene-modified human mesenchymal stem cells protects against injury in a cerebral ischemia model in adult rat. Neuroscience 136:161–169
O’Keeffe FE, Scott SA, Tyers P, O’Keeffe GW, Dalley JW, Zufferey R, Caldwell MA (2008) Induction of A9 dopaminergic neurons from neural stem cells improves motor function in an animal model of Parkinson’s disease. Brain 131:630–641
Pakkenberg B, Moller A, Gundersen HJ, Mouritzen Dam A, Pakkenberg H (1991) The absolute number of nerve cells in substantia nigra in normal subjects and in patients with Parkinson’s disease estimated with an unbiased stereological method. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry 54:30–33
Park HJ, Lee PH, Bang OY, Lee G, Ahn YH (2008) Mesenchymal stem cells therapy exerts neuroprotection in a progressive animal model of Parkinson’s disease. J Neurochem 107:141–151
Pestka S (2007) The interferons: 50 years after their discovery, there is much more to learn. J Biol Chem 282:20047–20051
Ryu H, Oh JE, Rhee KJ, Baik SK, Kim J, Kang SJ, Sohn JH, Choi E, Shin HC, Kim YM, Kim HS, Bae KS, Eom YW (2014) Adipose tissue-derived mesenchymal stem cells cultured at high density express IFN-beta and suppress the growth of MCF-7 human breast cancer cells. Cancer Lett 352:220–227
Sadan O, Bahat-Stromza M, Barhum Y, Levy YS, Pisnevsky A, Peretz H, Ilan AB, Bulvik S, Shemesh N, Krepel D, Cohen Y, Melamed E, Offen D (2009) Protective effects of neurotrophic factor-secreting cells in a 6-OHDA rat model of Parkinson disease. Stem Cells Dev 18:1179–1190
Schabitz WR, Sommer C, Zoder W, Kiessling M, Schwaninger M, Schwab S (2000) Intravenous brain-derived neurotrophic factor reduces infarct size and counterregulates Bax and Bcl-2 expression after temporary focal cerebral ischemia. Stroke 31:2212–2217
Sensebe L, Deschaseaux M, Li J, Herve P, Charbord P (1997) The broad spectrum of cytokine gene expression by myoid cells from the human marrow microenvironment. Stem Cells 15:133–143
Theofilopoulos AN, Baccala R, Beutler B, Kono DH (2005) Type I interferons (alpha/beta) in immunity and autoimmunity. Annu Rev Immunol 23:307–336
Wernig M, Zhao JP, Pruszak J, Hedlund E, Fu D, Soldner F, Broccoli V, Constantine-Paton M, Isacson O, Jaenisch R (2008) Neurons derived from reprogrammed fibroblasts functionally integrate into the fetal brain and improve symptoms of rats with Parkinson’s disease. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 105:5856–5861
Zafranskaya M, Oschmann P, Engel R, Weishaupt A, van Noort JM, Jomaa H, Eberl M (2007) Interferon-beta therapy reduces CD4 + and CD8 + T-cell reactivity in multiple sclerosis. Immunology 121:29–39
Acknowledgments
This research was supported by Basic Science Research Program through the National Research Foundation of Korea (NRF) funded by the Ministry of Education (NRF-2012R1A1A2004981).
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Joon Beom Park and ** Suk Lee have contributed equally to this work.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Park, J.B., Lee, J.S., Cho, B.P. et al. Adipose tissue-derived mesenchymal stem cells cultured at high cell density express brain-derived neurotrophic factor and exert neuroprotective effects in a 6-hydroxydopamine rat model of Parkinson’s disease. Genes Genom 37, 213–221 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13258-014-0239-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13258-014-0239-0