Abstract
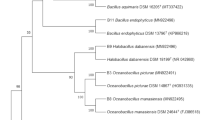
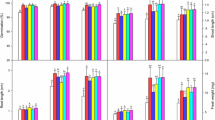
Halotolerant phosphate-solubilizing microorganisms (PSMs) capable of producing plant-growth-promoting traits were grown on salt medium containing Ca3(PO4)2 or egg yolk. The number of colonies on plates with Ca3(PO4)2 was higher than that on plates with egg yolk. Further, a total of 42 PSM isolates were purified. The majority were Bacillus spp., while one Providencia rettgeri strain was confirmed, for the first time, as a PSM. All PSMs had a phosphate-solubilizing index (PSI) between 1.1 and 2.58 and a strong capacity for dissolving calcium phosphate between 2.25 and 442 mg·L−1. In contrast, these PSMs were less effective when dissolving aluminum phosphate, ferric phosphate and lecithin. Isolates were also tested for growth-promoting substances. The results showed that all isolates were able to secrete indole-3-acetic acid in amounts ranging from 2.7 to 31.8 mg·L−1 and exopolysaccharide within the range 74.3 and 225.7 mg·L−1. Only 12 siderophore-producing strains with siderophore units of 1.9–42.1% were detected. Among them, ten isolates with solubilization rates greater than 200 mg·L−1 and relatively high NaCl tolerance (1.5 M) were classified as candidate PSMs. Eight different organic acids with different contents were detected in the culture filtrates, and propionic and oxalic acids have been proposed as the main mechanisms for solubilization. The ten isolates have the potential for use as bioinoculants to protect plants in saline environments.




Similar content being viewed by others
Change history
08 January 2019
In the original article the acknowledgement section was incorrectly published
References
Ahemad M, Kibret M (2012) Mechanisms and applications of plant growth promoting rhizobacteria: current perspective. J King Univ 26:1–20. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jksus.2013.05.001
Azziz G, Bajsa N, Haghjou T, Taulé C, Valverde Á, Igual JM (2012) Abundance, diversity and prospecting of culturable phosphate solubilizing bacteria on soils under crop-pasture rotations in a no-tillage regime in uruguay. Appl Soil Ecol 61:320–326. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apsoil.2011.10.004
Bahadur I, Maurya BR, Meena VS, Saha M, Kumar A, Aeron A (2016) Mineral release dynamics of tricalcium phosphate and waste muscovite by mineral-solubilizing rhizobacteria isolated from indo-gangetic plain of India. Geomicrobiol J 34:454–466. https://doi.org/10.1080/01490451.2016.1219431
Baig KS, Arshad M, Zahir ZA, Cheema MA (2010) Comparative efficacy of qualitative and quantitative methods for rock phosphate solubilization with phosphate solubilizing rhizobacteria. Soil Environ 29:82–86
Barroso CB, Nahas E (2005) The status of soil phosphate fractions and the ability of fungi to dissolve hardly soluble phosphates. Appl Soil Ecol 29:73–83. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apsoil.2004.09.005
Behera BC, Singdevsachan SK, Mishra RR, Dutta SK, Thatoi HN (2014) Diversity, mechanism and biotechnology of phosphate solubilising microorganism in mangrove—a review. Biocatal Agric Biotechnol 3:97–110. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bcab.2013.09.008
Chung H, Park M, Madhaiyan M, Seshadri S, Song J, Cho H, Sa T (2005) Isolation and characterization of phosphate solubilizing bacteria from the rhizosphere of crop plants of Korea. Soil Biol Biochem 37:1970–1974. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.soilbio.2005.02.025
Delvasto P, Valverde A, Ballester A, Igual JM, Munoz JA, Gonzalez F, Blazquez ML, Garcia C (2006) Characterization of brushite as a re-crystallization product formed during bacterial solubilization of hydroxyapatite in batch cultures. Soil Biol Biochem 38:2645–2654. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.soilbio.2006.03.020
Glickmann E, Dessaux Y (1995) A critical-examination of the specificity of the salkowski reagent for indolic compounds produced by phytopathogenic bacteria. Appl Environ Microbiol 61:793–796
Han HS, Lee KD (2005) Physiological responses of soybean—inoculation of Bradyrhizobium japonicum with PGPR in saline soil conditions. Res J Agric Biol Sci 1:216–221
Jackson ML (1973) Soil chemical analysis. Prentice Hall of India Pvt. Ltd., New Delhi
Joshi P, Bhatt AB (2011) Diversity and function of plant growth promoting rhizobacteria associated with wheat rhizosphere in north himalayan region. Int J Environ Sci 1:1135–1143
Liu W, Hou J, Wang Q, Ding L, Luo Y (2014) Isolation and characterization of plant growth-promoting rhizobacteria and their effects on phytoremediation of petroleum-contaminated saline-alkali soil. Chemosphere 117:303–308. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2014.07.026
Machuca A, Milagres AMF (2003) Use of cas-agar plate modified to study the effect of different variables on the siderophore production by aspergillus. Lett Appl Microbiol 36:177–181. https://doi.org/10.1046/j.1472-765x.2003.01290
Mahanta D, Rai RK, Dhar S, Varghese E, Raja A, Purakayastha TJ (2018) Modification of root properties with phosphate solubilizing bacteria and arbuscular mycorrhiza to reduce rock phosphate application in soybean-wheat crop** system. Ecol Eng 111:31–43. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecoleng.2017.11.008
Nautiyal CS (1999) An efficient microbiological growth medium for screening phosphate solubilizing microorganisms. FEMS Microbiol Lett 170:265–270. https://doi.org/10.1016/s0378-1097(98)00555-2
Naz I, Bano A (2010) Biochemical, molecular characterization and growth promoting effects of phosphate solubilizing Pseudomonas sp. isolated from weeds grown in salt range of Pakistan. Plant Soil 334:199–207. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11104-010-0372-8
Nishma KS, Adrisyanti B, Anusha SH, Rupali P, Sneha K, Jayamohan NS, Kumudini BS (2014) Induced growth promotion under in vitro salt stress tolerance on Solanum lycopersicum by fluorescent pseudomonads associated with rhizosphere [online]. Int J Appl Sci Eng Res 3:422–430. https://doi.org/10.6088/ijaser.030200012
O´Sullivan DJ, O´Gara F (1992) Traits of fluorescent Pseudomonas spp. involved in suppression of plant root pathogens. Microbiol Rev 56:662–676
Patel AK, Michaud P, Singhania RR, Soccol CR, Pandey A (2010) Polysaccharides from probiotics: new developments as food additives. Food Technol Biotechnol 48:451–463
Pérez E, Sulbarán M, Ball MM, Yarzábal LA (2007) Isolation and characterization of mineral phosphate-solubilizing bacteria naturally colonizing a limonitic crust in the south-eastern venezuelan region. Soil Biol Biochem 39:2905–2914. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.soilbio.2007.06.017
Pirhadi M, Enayatizamir N, Motamedi H, Sorkheh K (2018) Impact of soil salinity on diversity and community of sugarcane endophytic plant growth promoting bacteria (Saccharum officinarum var. cp48). Appl Ecol Environ Res 16:725–739. https://doi.org/10.15666/aeer/1601_725739
Puente ME, Bashan Y, Li CY, Lebsky VK (2004) Microbial populations and activities in the rhizoplane of rock-weathering desert plants. I. Root colonization and weathering of igneous rocks. Plant Biol 6:629–642. https://doi.org/10.1055/s-2004-821100
Qurashi AW, Sabri AN (2012) Bacterial exopolysaccharide and biofilm formation stimulate chickpea growth and soil aggregation under salt stress. Br J Microbiol 43:1183–1191. https://doi.org/10.1590/s1517-83822012000300046
Rodríguez H, Fraga R (1999) Phosphate solubilizing bacteria and their role in plant growth promotion [online]. Biotechnol Adv 17:319–339. https://doi.org/10.1016/s0734-9750(99)00014-2
Sadgir MD, Totawar MV, Shinde SB (2016) Assessment of phosphate solubilizing activity of different fungal and bacterial isolates. Int J Plant Sci 11:40–46. https://doi.org/10.15740/has/ijps/11.1/40-46
Sarkar A, Islam T, Biswas GC, Alam S, Hossain M, Talukder NM (2012) Screening for phosphate solubilizing bacteria inhabiting the rhizoplane of rice grown in acidic soil in bangladesh. Acta Microbiol Immunol Hung 59:199–213. https://doi.org/10.1556/AMicr.59.2012.2.5
Sashidhar B, Podile AR (2010) Mineral phosphate solubilization by rhizosphere bacteria and scope for manipulation of the direct oxidation pathway involving glucose dehydrogenase. J Appl Microbiol 109:1–12. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1365-2672.2009.04654.X
Shao J, Xu Z, Zhang N, Shen Q, Zhang R (2015) Erratum to: contribution of indole-3-acetic acid in the plant growth promotion by the rhizospheric strain Bacillus amyloliquefaciens, SQR9. Biol Fertil Soils 51:331–331. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00374-014-0978-8
Singh JS, Pandey VC, Singh DP (2011) Efficient soil microorganisms: a new dimension for sustainable agriculture and environmental development. Agric Ecosyst Environ 140:339–353. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.agee.2011.01.017
Tao GC, Tian SJ, Cai MY, **e GH (2008) Phosphate–solubilizing and–mineralizing abilities of bacteria isolated from soils. Pedosphere 18:515–523. https://doi.org/10.1016/S1002-0160(08)60042-9
Vyas P, Gulati A (2009) Organic acid production in vitro and plant growth promotion in maize under controlled environment by phosphate-solubilizing fluorescent pseudomonas. BMC Microbiol 9:174. https://doi.org/10.1186/1471-2180-9-174
Wahyudi AT, Rina PA, Asri W, Anja M, Abdjad AN (2011) Characterization of Bacillus spp. strains isolated from rhizosphere of soybean plants for their use as potential plant growth for promoting rhizobacteria. J Microbiol Antimicrob 3:34–40
Wei Y, Zhao Y, Shi M, Cao Z, Lu Q, Yang T, Fan Y, Wei Z (2018) Effect of organic acids production and bacterial community on the possible mechanism of phosphorus solubilization during composting with enriched phosphate-solubilizing bacteria inoculation. Bioresour Technol 247:190–199. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2017.09.092
Acknowledgements
This study was supported with grants from the State Key Laboratory of Urban Water Resource and Environment (2017DX15), the National Ten Thousand Youth Talents Plan of 2014, China Agriculture Research System (CARS14), the National Natural Science Foundation of China (31000728 and 31200211), and the Natural Science Fund of Shandong Province (ZR2014YL011 and ZR2014YL012).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
All authors have seen and approved the manuscript and its contents, and declare they are aware of the responsibilities connected to authorship. Pei-shi Qi and **ao-yuan Chi designed the study and performed critical revision of the manuscript; Huan-huan Jiang and Ming-na Chen performed the experiment and data analysis; Huan-huan Jiang composed the manuscript; Tong Wang and Na Chen collected the samples; and Mian Wang and Li-juan Pan guided the research.
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
On behalf of all authors, the corresponding author states that there is no conflict of interest.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Jiang, H., Qi, P., Wang, T. et al. Isolation and characterization of halotolerant phosphate-solubilizing microorganisms from saline soils. 3 Biotech 8, 461 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13205-018-1485-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13205-018-1485-7