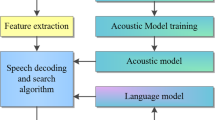
Abstract
With the popularization of computers, artificial intelligence technology has become more and more mature, among which speech recognition technology in artificial intelligence is favored by people. In the past few years, the acoustic model combined with the Gaussian mixture model and the hidden Markov model has always been in the leading position. In the field of speech recognition technology, because the development of speech data has gradually expanded, and the complexity of the data has also increased. The larger the data, the traditional data network model is slowly showing inadequacy. However, the deep neural network model is easy to deal with large and complex data modeling. This article combines the advantages of basic learning theory and speech recognition technology, and launches in-depth research on embedding learning theoretical knowledge into the field of speech recognition. Nowadays, large-scale text information databases relying on computers are becoming more and more important in linguistic research, and a large-scale corpus that fully reflects language facts and contains rich language information has been constructed. The establishment of the text information database system is long, from word segmentation, part-of-speech tagging to syntactic tagging to semantic tagging. Therefore, the characteristic of information system processing is that the systematic description depends on the application environment of understanding vocabulary and reasoning. According to different scenarios, the realization methods of semantic description roles are also different, and the description of semantic roles in correct scenarios is clearer, more detailed and systematic. Therefore, this article is of great significance for solving the semantic problem of using Chinese frame network for Chinese information processing in the context of speech recognition.








Similar content being viewed by others
References
Chen HHJ (2011) Develo** and evaluating an oral skills training website supported by automatic speech recognition technology. ReCALL 23(1):59–78
Dragsted B, Mees IM, Hansen IG (2011) Speaking your translation: students’ first encounter with speech recognition technology. Transl Interpreting 3(1):10–43
Greenwood CR, Thiemann-Bourque K, Walker D et al (2011) Assessing children’s home language environments using automatic speech recognition technology. Commun Disord Q 32(2):83–92
Khalighinejad B, da Silva GC, Mesgarani N (2017) Dynamic encoding of acoustic features in neural responses to continuous speech. J Neurosci 37(8):2176–2185
Leaver AM, Rauschecker JP (2010) Cortical representation of natural complex sounds: effects of acoustic features and auditory object category. J Neurosci 30(22):7604–7612
Lee D, Cha H, Kim K, Shin D (2015) Development of BIM-based construction document information database structure through the link to the BIM model and construction document information. Korean J Constr Eng Manag 16(5):42–53
Liu K, Hogan WR, Crowley RS (2011) Natural language processing methods and systems for biomedical ontology learning. J Biomed Inform 44(1):163–179
Liu X, Xu M, Li M et al (2019) Improving English pronunciation via automatic speech recognition technology. Int J Innov Learn 25(2):126–140
Sakhavi S, Guan C, Yan S (2018) Learning temporal information for brain-computer interface using convolutional neural networks. IEEE Trans Neural Netw Learn Syst 29(11):5619–5629
Schmidt SE, Holst-Hansen C, Hansen J et al (2015) Acoustic features for the identification of coronary artery disease. IEEE Trans Biomed Eng 62(11):2611–2619
Svalberg AML (2012) Language awareness in language learning and teaching: a research agenda. Lang Teach 45(3):376–388
Vani K, Gupta D (2018) Unmasking text plagiarism using syntactic-semantic based natural language processing techniques: comparisons, analysis and challenges. Inf Process Manage 54(3):408–432
Wang H, Zhang W, Zeng Q et al (2014) Extracting important information from Chinese Operation Notes with natural language processing methods. J Biomed Inform 48:130–136
**e J, Hou Y, Wang Y et al (2020) Chinese text classification based on attention mechanism and feature-enhanced fusion neural network. Computing 102(3):683–700
**ong Y, Wang Z, Jiang D et al (2019) A fine-grained Chinese word segmentation and part-of-speech tagging corpus for clinical text. BMC Med Inform Decis Mak 19(2):179–184
Funding
The study and all authors have received no funding.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors report no conflicts of interest.
Ethical approval
This article does not contain any studies with human participants performed by any of the authors.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Mengzhan, Z. Simulation of Chinese language and text information system processing mode based on hidden Markov model. Int J Syst Assur Eng Manag (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13198-023-02053-5
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13198-023-02053-5